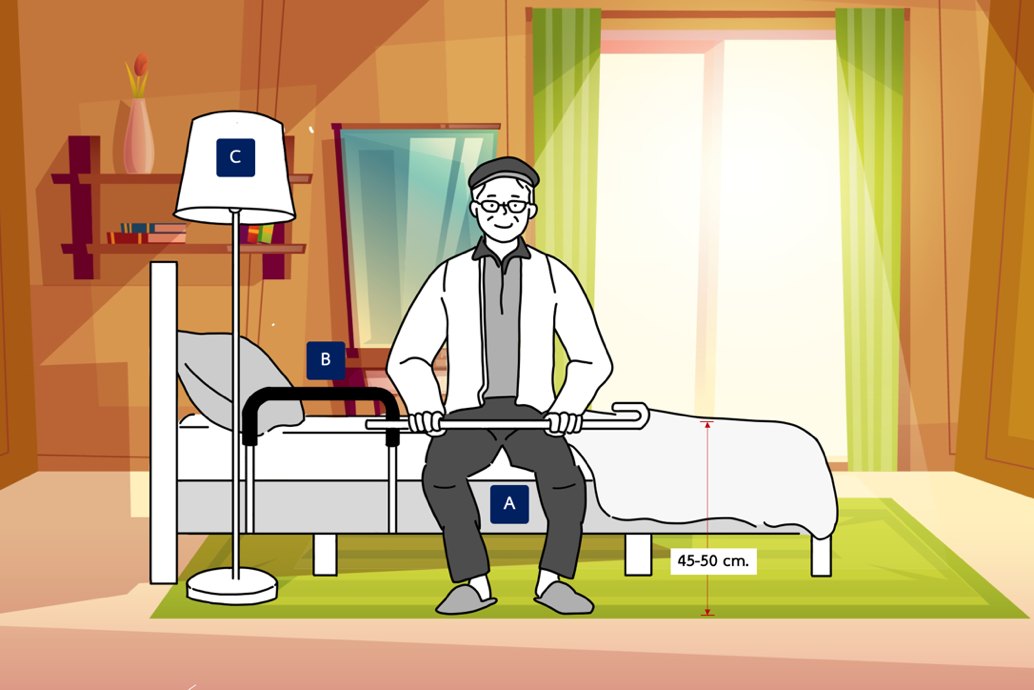
Online House Modification to Prevent Falls for Elderly Patients in the Community
Main Article Content
Abstract
Home with several hazards could considerably lead to indoor falls in elderly patients with dementia, cerebrovascular disease, and undergone hip or knee replacements resulting in disability and death from falls more than other age groups. Appropriate and safe house modification represents an important role for indoor fall prevention in elderly patients by decreasing the rate of falls compared to hazardous houses without any modification. During the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the home visit program for house modification was canceled for several years. Then, online house modification was developed by the cooperation of assistive technologists for disabilities and physical therapists to access three dangerous sites for falls at home including bathroom, bedroom, and stairs. Checklists and recommendations for house modification are advised through the online communication system to relatives or caregivers with the goals of promoting elders’ independence, fall prevention, well physical and mental health, and improved quality of life of elderly patients and their families.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Organization WH, Ageing WHO, Unit LC. WHO global report on falls prevention in older age: World Health Organization; 2008.
Elo S, Saarnio R, Isola A. The physical, social and symbolic environment supporting the well-being of home-dwelling elderly people. International Journal of Circumpolar Health. 2011;70(1):90-100.
Chang N-T, Chi L-Y, Yang N-P, Chou P. The impact of falls and fear of falling on health-related quality of life in Taiwanese elderly. Journal of community health nursing. 2010;27(2):84-95.
Li F, Fisher KJ, Harmer P, McAuley E, Wilson NL. Fear of falling in elderly persons: association with falls, functional ability, and quality of life. J. Gerontol. Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences. 2003;58(5):P283-P90.
Nipha Srichang, Kawee L. Fall forecast report for elderly (aged 60 years and over) in Thailand 2017−2021. Division of Non-Communicable Diseases DoDC, Ministry of Public Health; 2017.
วิชัย เอกพลากร. รายงานการสำรวจสุขภาพประชาชนไทยโดยการตรวจร่างกาย ครั้งที่ 5 พ.ศ. 2557. นนทบุรี: สำนักพิมพ์อักษรกราฟฟิคแอนด์ดีไซน์; 2557.
กองป้องกันการบาดเจ็บ กรมควบคุมโรค กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. จำนวนและอัตราการเสียชีวิตจากการพลัดตกหกล้มในผู้ที่มีอายุ 60 ปีขึ้นไป ต่อประชากรแสนคน จำแนกรายจังหวัด ปี พ.ศ. 2559-2563 [รายงานอิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. 2564 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 13 มกราคม 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://ddc.moph.go.th/dip/news.php?news=21859&deptcode=dip
Sophonratanapokin B, Sawangdee Y, Soonthorndhada K. Effect of the living environment on falls among the elderly in Thailand. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicineand Public Health. 2012;43(6):1537.
Zhang L, Ding Z, Qiu L, Li A. Falls and risk factors of falls for urban and rural community-dwelling older adults in China. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):1-17.
Kamei T, Kajii F, Yamamoto Y, Irie Y, Kozakai R, Sugimoto T, et al. Effectiveness of a home hazard modification program for reducing falls in urban community‐dwelling older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Japan journal of nursing science. 2015;12(3):184-97.
Pighills A, Ballinger C, Pickering R, Chari S. A critical review of the effectiveness of environmental assessment and modification in the prevention of falls amongst community dwelling older people. British Journal of Occupational Therapy. 2016;79(3):133-43.
Stark S, Keglovits M, Somerville E, Hu Y-L, Barker A, Sykora D, et al. Home Hazard Removal to Reduce Falls Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Network Open. 2021;4(8):e2122044-e.
Nikolaus T, Bach M. Preventing falls in community‐dwelling frail older people using a home intervention team (HIT): results from the randomized Falls‐HIT trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003;51(3):300-5.
De Clercq H, Naudé A, Bornman J. Older Adults’ Perspectives on Fall Risk: Linking Results to the ICF. Journal of Applied Gerontology. 2021;40(3):328-38.
Yen T-H, Lin L-F, Wei T-S, Chang K-H, Wang Y-H, Liou T-H. Delphi-Based Assessment of Fall-Related Risk Factors in Acute Rehabilitation Settings According to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014;95(1):50-7.
Ambrose AF, Paul G, Hausdorff JM. Risk factors for falls among older adults: a review of the literature. Maturitas. 2013;75(1):51-61.
Scheffer AC, Schuurmans MJ, van Dijk N, van der Hooft T, de Rooij SE. Fear of falling: measurement strategy, prevalence, risk factors and consequences among older persons. Age and Ageing. 2008;37(1):19-24.
Van Doorn C, Gruber‐Baldini AL, Zimmerman S, Richard Hebel J, Port CL, Baumgarten M, et al. Dementia as a risk factor for falls and fall injuries among nursing home residents. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003;51(9):1213-8.
พรรณวลัย ผดุงวณิชย์กุล. โรคหลอดเลือดสมอง (Stroke) [บทความอิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://www.med.nu.ac.th/dpMed/fileKnowledge/106_2017-08-19.pdf
Jørgensen L, Engstad T, Jacobsen BK. Higher incidence of falls in long-term stroke survivors than in population controls: depressive symptoms predict falls after stroke. Stroke. 2002;33(2):542-7.
Suzuki T, Sonoda S, Misawa K, Saitoh E, Shimizu Y, Kotake T. Incidence and consequence of falls in inpatient rehabilitation of stroke patients. Exp. Aging Res. 2005;31(4):457-69.
Mackintosh SF, Hill K, Dodd KJ, Goldie P, Culham E. Falls and injury prevention should be part of every stroke rehabilitation plan. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2005;19(4):441-51.
Tutuarima J, Van der Meulen J, De Haan R, Van Straten A, Limburg M. Risk factors for falls of hospitalized stroke patients. Stroke. 1997;28(2):297-301.
Said CM, Goldie PA, Patla AE, Sparrow WA. Effect of stroke on step characteristics of obstacle crossing. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001;82(12):1712-9.
Lamontagne A, Paquette C, Fung J. Stroke affects the coordination of gaze and posture during preplanned turns while walking. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 2007;21(1):62-7.
Ramnemark A, Nyberg L, Lorentzon R, Olsson T, Gustafson Y. Hemiosteoporosis after severe stroke, independent of changes in body composition and weight. Stroke. 1999;30(4):755-60.
Ackerman DB, Trousdale RT, Bieber P, Henely J, Pagnano MW, Berry DJ. Postoperative patient falls on an orthopedic inpatient unit. The Journal of arthroplasty. 2010;25(1):10-4.
Matsumoto H, Okuno M, Nakamura T, Yamamoto K, Osaki M, Hagino H. Incidence and risk factors for falling in patients after total knee arthroplasty compared to healthy elderly individuals. Yonago Acta Med. 2014;57(4):137.
Lo CW, Tsang W, Yan C, Lord SR, Hill KD, Wong AY. Risk factors for falls in patients with total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis and cartilage. 2019;27(7):979-93.
Ikutomo H, Nagai K, Nakagawa N, Masuhara K. Falls in patients after total hip arthroplasty in Japan. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015;20(4):663-8.
Swinkels A, Newman JH, Allain TJ. A prospective observational study of falling before and after knee replacement surgery. Age and ageing. 2009;38(2):175-81.
Moutzouri M, Gleeson N, Billis E, Tsepis E, Panoutsopoulou I, Gliatis J. The effect of total knee arthroplasty on patients’ balance and incidence of falls: a systematic review. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 2017;25(11):3439-51.
Teixeira DKdS, Andrade LM, Santos JLP, Caires ES. Falls among the elderly: environmental limitations and functional losses. Revista Brasileira de Geriatria e Gerontologia. 2019;22.
Neslihan L, Belgin A. Domestic environmental risk factors associated with falling in elderly. Iran. J. Public Health. 2013;42(2):120.
ยอดเยี่ยม เทพธรานนท์. การเตรียมสภาพแวดล้อมเพื่อผู้สูงอายุ ผู้พิการและเด็ก[หนังสืออิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. 2558[เข้าถึงเมื่อ 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://tast.or.th/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/เรื่อง-“การเตรียมสภาพแวดล้อมเพื่อผู้สูงอายุ-ผู้พิการและเด็ก”-ดร.-ยอดเยี่ยม-เทพธรานนท์.pdf
ไตรรัตน์ จารุทัศน์. สภาพแวดล้อมและที่อยู่อาศัยที่เหมาะสมสำหรับผู้ป่วยสมองเสื่อม. ครั้งที่ 2. กรุงเทพฯ: จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย; 2561.
ไตรรัตน์ จารุทัศน์. คู่มือการออกแบบเพื่อทุกคน Universal Design Guidebook. ครั้งที่ 2. กรุงเทพฯ: โรงพิมพ์เทพเพ็ญวานิสย์; 2558.
หน่วยปฏิบัติการวิจัย สภาพแวดล้อมที่เหมาะสมกับผู้สูงอายุ คณะสถาปัตยกรรมศาสตร์ จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย. ข้อแนะนำการออกแบบสภาพแวดล้อมและที่พักอาศัยของผู้สูงอายุ[หนังสืออิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. 2559 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://www.dop.go.th/download/knowledge/knowledge_th_20160906103629_1.pdf
สำนักส่งเสริมศักยภาพและสิทธิ สำนักงานส่งเสริมและพัฒนาคุณภาพชีวิตคนพิการแห่งชาติ กระทรวงการพัฒนาสังคมและความมั่นคงของมนุษย์. ตัวอย่างที่ดีในการจัดสิ่งอำนวยความสะดวกสำหรับคนพิการและคนทุกวัย[หนังสืออิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. ครั้งที่ 2. [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก http://web1.dep.go.th/?q=th/publishdocument/ตัวอย่างที่ดีในการจัดสิ่งอำนวยความสะดวก-สำหรับคนพิการและคนทุกวัย
จีระนันท์ คุณาชีวะ. การฟื้นฟูผู้สูงอายุและภาวะถดถอยของร่างกาย Rehabilitation in elderly and Deconditioning[บทความอิเล็กทรอนิกส์]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 6 กุมภาพันธ์ 2565]. เข้าถึงได้จาก https://w1.med.cmu.ac.th/rehab/images/Study_guide/05_1%20Deconditioning%20and%20Rehabilitation%20in%20elderly_2018.pdf