Effects of Collagen Extract On Skin Aging
Main Article Content
Abstract
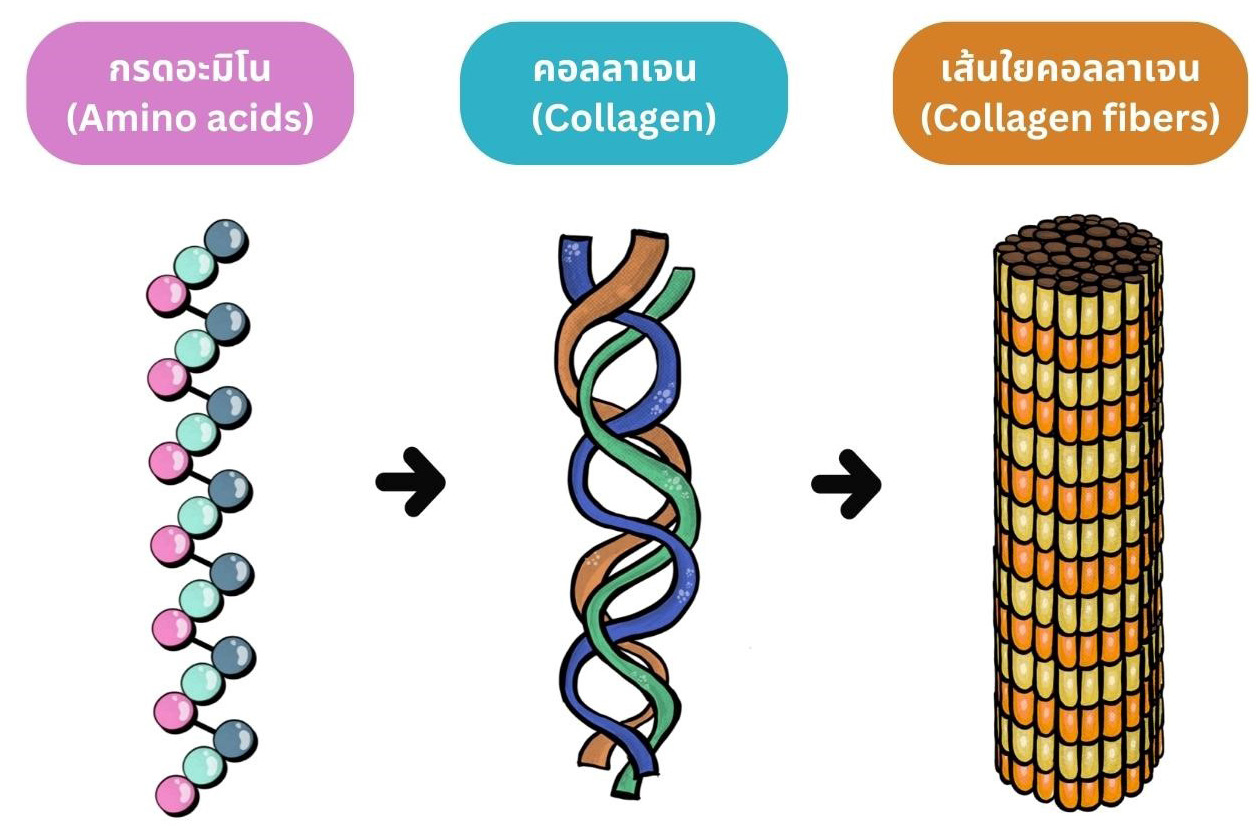
Skin aging is a condition influenced by internal and external factors, manifesting as wrinkles, loss of skin elasticity, and functional changes. The main mechanism involves a reduction in fibroblast growth factor levels, responsible for producing essential components of the extracellular matrix, including collagen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, and chondroitin. These substances play an important role in maintaining moisture, elasticity, and shape, with collagen being a key component. Currently, collagen can be extracted from various sources and many studies have reported on the effects of collagen extract consumption. The findings indicate that collagen extract improves skin quality through diverse mechanisms, such as stimulating fibroblast cells, cell remodeling and reducing inflammation. Therefore, recognizing the effects of collagen extract consumption could be beneficial in the mitigation of skin aging.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Schumacher B, Krieg TM. The Aging Skin: From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141(4S):949-50.
Agarwal S, Krishnamurthy K. Histology, Skin. StatPearls [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30726010.
Bolke L, Schlippe G, Gerss J, Voss W. A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density: Results of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Blind Study. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2494.
Asserin J, Lati E, Shioya T, Prawitt J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14(4):291-301.
Proksch E, Segger D, Degwert J, Schunck M, Zague V, Oesser S. Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;27(1):47-55.
Khavkin J, Ellis DA. Aging skin: histology, physiology, and pathology. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2011;19(2):229-34.
de Araujo R, Lobo M, Trindade K, Silva DF, Pereira N. Fibroblast Growth Factors: A Controlling Mechanism of Skin Aging. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;32(5):275-82.
Lee H, Hong Y, Kim M. Structural and Functional Changes and Possible Molecular Mechanisms in Aged Skin. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12489.
Wang Z, Man MQ, Li T, Elias PM, Mauro TM. Aging-associated alterations in epidermal function and their clinical significance. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(6):5551-65.
Wang H. A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical Studies. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(22):3868.
Amirrah IN, Lokanathan Y, Zulkiflee I, Wee M, Motta A, Fauzi MB. A Comprehensive Review on Collagen Type I Development of Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering: From Biosynthesis to Bioscaffold. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2307.
Naomi R, Ridzuan PM, Bahari H. Current Insights into Collagen Type I. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(16):2642.
Wu JJ, Weis MA, Kim LS, Eyre DR. Type III collagen, a fibril network modifier in articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(24):18537-44.
Jimenez SA, Ala-Kokko L, Prockop DJ, Merryman CF, Shepard N, Dodge GR. Characterization of human type II procollagen and collagen-specific antibodies and their application to the study of human type II collagen processing and ultrastructure. Matrix Biol. 1997;16(1):29-39.
Mak KM, Png CY, Lee DJ. Type V Collagen in Health, Disease, and Fibrosis. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016;299(5):613-29.
Avila Rodriguez MI, Rodriguez Barroso LG, Sanchez ML. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018;17(1):20-6.
Hong H, Chaplot S, Chalamaiah M, Roy BC, Bruce HL, Wu J. Removing Cross-Linked Telopeptides Enhances the Production of Low-Molecular-Weight Collagen Peptides from Spent Hens. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(34):7491-9.
Ramadass SK, Perumal S, Gopinath A, Nisal A, Subramanian S, Madhan B. Sol-gel assisted fabrication of collagen hydrolysate composite scaffold: a novel therapeutic alternative to the traditional collagen scaffold. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(17):15015-25.
Zhang G, Sun A, Li W, Liu T, Su Z. Mass spectrometric analysis of enzymatic digestion of denatured collagen for identification of collagen type. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1114(2):274-7.
Hong GP, Min SG, Jo YJ. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Aging Activities of Porcine By-Product Collagen Hydrolysates Produced by Commercial Proteases: Effect of Hydrolysis and Ultrafiltration. Molecules. 2019;24(6):1104.
Yazaki M, Ito Y, Yamada M, Goulas S, Teramoto S, Nakaya MA, et al. Oral Ingestion of Collagen Hydrolysate Leads to the Transportation of Highly Concentrated Gly-Pro-Hyp and Its Hydrolyzed Form of Pro-Hyp into the Bloodstream and Skin. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(11):2315-22.
Salamanca E, Hsu CC, Yao WL, Choy CS, Pan YH, Teng NC, et al. Porcine Collagen-Bone Composite Induced Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Regeneration In Vitro and In Vivo. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(1):93.
Charriere G, Bejot M, Schnitzler L, Ville G, Hartmann DJ. Reactions to a bovine collagen implant. Clinical and immunologic study in 705 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;21(6):1203-8.
Aluko RE. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2015;6:235-62.
Felician FF, Xia C, Qi W, Xu H. Collagen from Marine Biological Sources and Medical Applications. Chem Biodivers. 2018;15(5):e1700557.
Salvatore L, Gallo N, Natali ML, Campa L, Lunetti P, Madaghiele M, et al. Marine collagen and its derivatives: Versatile and sustainable bio-resources for healthcare. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;113:110963.
Saiga A, Iwai K, Hayakawa T, Takahata Y, Kitamura S, Nishimura T, et al. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides obtained from chicken collagen hydrolysate. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56(20):9586-91.
Zhao Y, Wang Z, Zhang J, Su T. Extraction and characterization of collagen hydrolysates from the skin of Rana chensinensis. 3 Biotech. 2018;8(3):181.
Benson HAE, Caccetta R, Chen Y, Kearns P, Toth I. Transdermal Delivery of a Tetrapeptide: Evaluation of Passive Diffusion. Letters in Peptide Science. 2003;10(5):615-20.
Benson HA, Namjoshi S. Proteins and peptides: strategies for delivery to and across the skin. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(9):3591-610.
Osawa Y, Mizushige T, Jinno S, Sugihara F, Inoue N, Tanaka H, et al. Absorption and metabolism of orally administered collagen hydrolysates evaluated by the vascularly perfused rat intestine and liver in situ. Biomed Res. 2018;39(1):1-11.
Watanabe-Kamiyama M, Shimizu M, Kamiyama S, Taguchi Y, Sone H, Morimatsu F, et al. Absorption and effectiveness of orally administered low molecular weight collagen hydrolysate in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58(2):835-41.
Ohara H, Iida H, Ito K, Takeuchi Y, Nomura Y. Effects of Pro-Hyp, a collagen hydrolysate-derived peptide, on hyaluronic acid synthesis using in vitro cultured synovium cells and oral ingestion of collagen hydrolysates in a guinea pig model of osteoarthritis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(10):2096-9.
Ohara H, Ichikawa S, Matsumoto H, Akiyama M, Fujimoto N, Kobayashi T, et al. Collagen-derived dipeptide, proline-hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol. 2010;37(4):330-8.
O'Rourke SA, Dunne A, Monaghan MG. The Role of Macrophages in the Infarcted Myocardium: Orchestrators of ECM Remodeling. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019;6:101.
Tiemessen MM, Jagger AL, Evans HG, van Herwijnen MJ, John S, Taams LS. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells induce alternative activation of human monocytes/macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(49):19446-51.
Liu G, Ma H, Qiu L, Li L, Cao Y, Ma J, et al. Phenotypic and functional switch of macrophages induced by regulatory CD4+CD25+T cells in mice. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011;89(1):130-42.
Fisher GJ, Datta SC, Talwar HS, Wang ZQ, Varani J, Kang S, et al. Molecular basis of sun-induced premature skin ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature. 1996;379(6563):335-9.
Silva S, Ferreira M, Oliveira AS, Magalhaes C, Sousa ME, Pinto M, et al. Evolution of the use of antioxidants in anti-ageing cosmetics. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019;41(4):378-86.
Leon-Lopez A, Fuentes-Jimenez L, Hernandez-Fuentes AD, Campos-Montiel RG, Aguirre-Alvarez G. Hydrolysed Collagen from Sheepskins as a Source of Functional Peptides with Antioxidant Activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16):3931.
Pyun HB, Kim M, Park J, Sakai Y, Numata N, Shin JY, et al. Effects of Collagen Tripeptide Supplement on Photoaging and Epidermal Skin Barrier in UVB-exposed Hairless Mice. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2012;17(4):245-53.
Edgar S, Hopley B, Genovese L, Sibilla S, Laight D, Shute J. Effects of collagen-derived bioactive peptides and natural antioxidant compounds on proliferation and matrix protein synthesis by cultured normal human dermal fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10474.
Ito N, Seki S, Ueda F. Effects of Composite Supplement Containing Collagen Peptide and Ornithine on Skin Conditions and Plasma IGF-1 Levels—A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Marine Drugs. 2018;16(12):482.
Kim DU, Chung HC, Choi J, Sakai Y, Lee BY. Oral Intake of Low-Molecular-Weight Collagen Peptide Improves Hydration, Elasticity, and Wrinkling in Human Skin: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients. 2018;10(7):826.
Czajka A, Kania EM, Genovese L, Corbo A, Merone G, Luci C, et al. Daily oral supplementation with collagen peptides combined with vitamins and other bioactive compounds improves skin elasticity and has a beneficial effect on joint and general wellbeing. Nutr Res. 2018;57:97-108.
Schwartz SR, Hammon KA, Gafner A, Dahl A, Guttman N, Fong M, et al. Novel Hydrolyzed Chicken Sternal Cartilage Extract Improves Facial Epidermis and Connective Tissue in Healthy Adult Females: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Altern Ther Health Med. 2019;25(5):12-29.
Sangsuwan W, Asawanonda P. Four-weeks daily intake of oral collagen hydrolysate results in improved skin elasticity, especially in sun-exposed areas: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32(8):991-6.
de Miranda RB, Weimer P, Rossi RC. Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2021;60(12):1449-61.
DePhillipo NN, Aman ZS, Kennedy MI, Begley JP, Moatshe G, LaPrade RF. Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(10):2325967118804544.