Physical Therapy with Cawthorne-Cooksey Exercise for Reducing the Risk of Falling in Older People with Dizziness from Vestibular Hypofunction
Main Article Content
Abstract
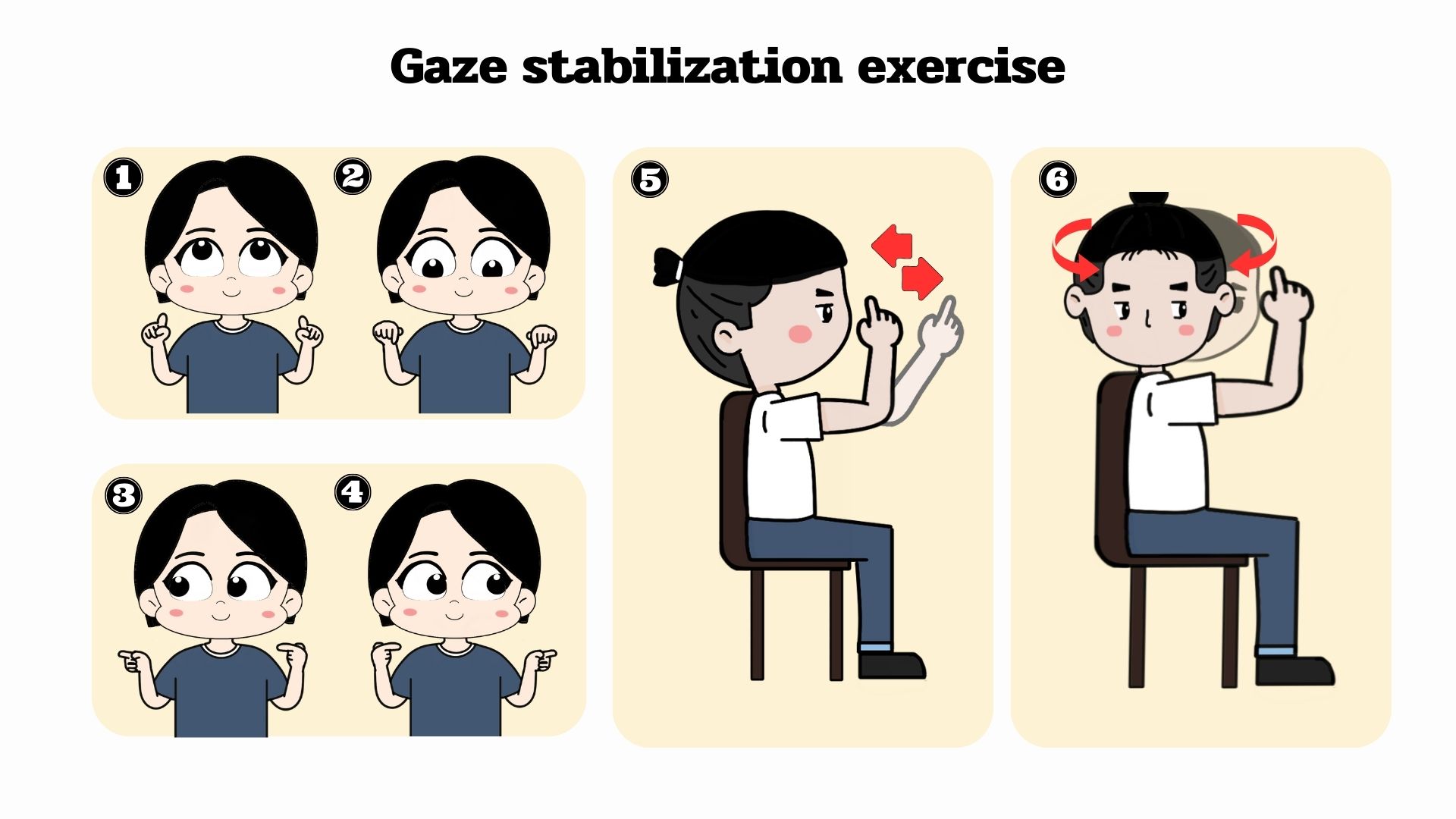
Falling is the main problem for the older people which brings about disability and admission to the hospital. A critical factor of falls is vestibular hypofunction disorder (VH) leads to dizziness, nystagmus, and instability. The disease results in impairment of balance, limitation of daily activities, and participation in the VH patient. The impairments require appropriate treatment and rehabilitation. Physical therapy uses the Cawthorne-Cooksey exercise for recovering because it reduces dizziness and improves balancing in the vestibular hypofunction patient. The Cawthorne-Cooksey exercise components are gaze stabilization exercise, habituation exercise, balance and gait training, and endurance. The exercise induces sensory substitution and physiologic habituation to encourage the mechanism of adaptation compensation in VH. At this moment, VH rehabilitation is unclear due to confusion in the physiology of the vestibular system, the pathology of VH, and the mechanics of the Cawthorne-Cooksey exercise. Accordingly, if the physical therapist and multidisciplinary have good information and understanding of the physiology, pathology, and mechanical of the Cawthorne-Cooksey exercise, it will be valuable for the elderly patient with VH disorder in increasing balancing ability and confidence in movement, decreasing the risk of falls, and improving the fine quality of life.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Hülse R, Biesdorf A, Hörmann K, Stuck B, Erhart M, Hülse M, et al. Peripheral vestibular disorders: An epidemiologic survey in 70 million individuals: An epidemiologic survey in 70 million individuals. Otol Neurotol. 2019;40(1):88–95.
Tungvachirakul V, Lisnichuk H, O’Leary SJ. Epidemiology of vestibular vertigo in a neuro-otology clinic population in Thailand. J Laryngol Otol. 2014;128 Suppl 2(S2):S31-8.
Yetiser S. Review of the pathology underlying benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Int Med Res.2020;48(4):1-12.
Spiegel R, Kirsch M, Rosin C, Rust H, Baumann T, Sutter R, et al. Dizziness in the emergency department: an update on diagnosis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2017;147:w14565.
จารุภา เลขทิพย์, ธีระ วรธนารัตน์, ศักรินทร์ ภูผานิล, ศราวุธ ลาภมณีย์. ปัจจัยเสี่ยงต่อการหกล้มในผู้สูงอายุ. วารสารการแพทย์และวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ 2562;26:85-103.
Lo AX, Harada CN. Geriatric dizziness: evolving diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for the emergency department. Clin Geriatr Med. 2013;29(1):181-204.
Giommetti G, Lapenna R, Panichi R, Dehgani Mobaraki P, Longari F, Ricci G, et al. Residual dizziness after successful repositioning maneuver for idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a review. Audiology Research. 2017;7(178):31-7.
Lacour M, Barthelemy J, Borel L, Magnan J, Xerri C, Chays A, et al. Sensory strategies in human postural control before and after unilateral vestibular neurotomy. Exp Brain Res. 1997;115 (2):300-10.
Schubert MC, Tusa RJ, Grine LE, Herdman SJ. Optimizing the sensitivity of the head thrust test for identifying vestibular hypofunction. Phys Ther. 2004;84(2):151-8.
Khan S, Chang R. Anatomy of the vestibular system: a review. Neuro Rehabilitation. 2013;32(3):437–43.
Lacour M, Helmchen C, Vidal PP. Vestibular compensation: the neuro-otologist's best friend. J Neurol. 2016;263 (S1):S54-64.
Herdman SJ, Clendaniel R. Vestibular Rehabilitation. 4thed. United States: F.A .Davis Company;2014.
Jones S, Jones T, Mills K, Gaines G. Anatomical and physiological considerations in vestibular dysfunction and compensation. Semin Hear. 2009;30(4):231–41.
Hall CD, Herdman SJ, Whitney SL, Anson ER, Carender WJ, Hoppes CW, et al. Vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction: An updated clinical practice guideline from the Academy of Neurologic Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2022;46(2):118–77.
Grill E, Heuberger M, Strobl R, Saglam M, Holle R, Linkohr B, et al. Prevalence, determinants, and consequences of vestibular hypofunction. Results from the KORA-FF4 survey. Front Neurol. 2018;9:1-8.
Eggers SDZ, Zee DS. Vertigo and imbalance: clinical neurophysiology of the vestibular system. 1sted. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2010.
Cohen HS, Mulavara AP, Peters BT, Sangi-Haghpeykar H, Bloomberg JJ. Standing balance tests for screening people with vestibular impairments. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124(2):545-50.
ภิมุกข์ สิงห์พิทักษ์, มัณฑนา วงศ์ศิรินวรัตน์, อลงกต เอมะสิทธิ์. ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างระยะการดำเนินโรคกับผลการตรวจประเมินทางคลินิกสำหรับผู้ที่มีภาวะเวียนศีรษะจากความผิดปกติของระบบการประสาทการทรงตัวหูชั้นใน.วารสารกายภาพบำบัด. 2565;44:82-96.
Wrisley DM, Marchetti GF, Kuharsky DK, Whitney SL. Reliability, internal consistency, and validity of data obtained with the functional gait assessment. Phys Ther. 2004; 84 (10):906-18.
Cawthorne T. The physiological basis for head exercise. Journal of the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy.1944;30:106.
Shumway-Cook A, Horak FB. Rehabilitation strategies for patients with vestibular deficits. Neurol Clin. 1990;8(2):441–57.
Ribeiro A dos SB, Pereira JS. Balance improvement and reduction of likelihood of falls in older women after Cawthorne and Cooksey exercises. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;71(1):38–46.
Afrasiabifar A, Karami F, Najafi Doulatabad S. Comparing the effect of Cawthorne–Cooksey and Frenkel exercises on balance in patients with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2017;32(1):57–65.
Smółka W, Smółka K, Markowski J, Pilch J, Piotrowska-Seweryn A, Zwierzchowska A. The efficacy of vestibular rehabilitation in patients with chronic unilateral vestibular dysfunction. Int J Occup Med Environ Health. 2020;33(3):273–82.
Fallahzadeh Abarghuei A, Fadavi-Ghaffari M, Tousi S, Amini M, Salehi AR. Effect of cawthorne and cooksey exercises on balance and quality of life of 60 to 80 year- old individuals in Shiraz: A randomized clinical trial. Medical Journal of The Islamic Republic of Iran. 2018;32(1):429–33.
Hall CD, Herdman SJ, Whitney SL, Anson ER, Carender WJ, Hoppes CW, et al. Vestibular Rehabilitation for Peripheral Vestibular Hypofunction: An Updated Clinical Practice Guideline from the Academy of Neurologic Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association. J Neurol Phys. 2022;46(2):118-77.