ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับภาวะซึมเศร้าของนักศึกษาพยาบาลในภูมิภาคหนึ่งของประเทศไทย
คำสำคัญ:
ภาวะซึมเศร้า, สื่อสังคมออนไลน์, การเปรียบเทียบทางสังคม, นักศึกษาพยาบาลบทคัดย่อ
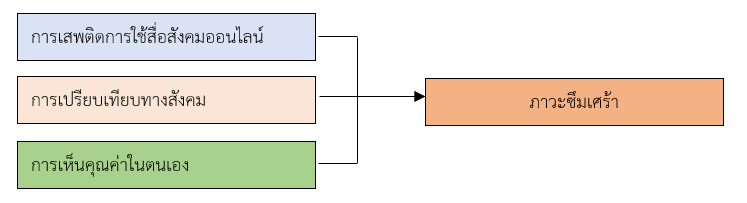
การวิจัยเชิงวิเคราะห์นี้เพื่อศึกษาปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับภาวะซึมเศร้าของนักศึกษาพยาบาลในภูมิภาคหนึ่งของประเทศไทย ประชากรที่ใช้ในการศึกษา คือ นักศึกษาหลักสูตรพยาบาลศาสตรบัณฑิต ชั้นปีที่ 1 - 4 ของสถาบันการศึกษาพยาบาลสังกัดสถาบันพระบรมราชชนก ในภูมิภาคหนึ่งของประเทศไทย ปีการศึกษา 2567 กลุ่มตัวอย่าง จำนวน 300 คน คัดเลือกกลุ่มตัวอย่างโดยใช้วิธีการสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบแบ่งชั้นภูมิ ตามสถาบันการศึกษา เพศ และระดับชั้นปีที่ 1 - 4 ในแต่ละสถาบันการศึกษา และรับสมัครนักศึกษาที่สนใจเป็นอาสาสมัครในการให้ข้อมูลโดยประชาสัมพันธ์ผ่านทางผู้ประสานงานการวิจัยของแต่ละสถาบัน จนกระทั่งครบตามจำนวน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการรวบรวมข้อมูล คือ แบบสอบถาม 5 ส่วน ประกอบด้วย 1) ข้อมูลทั่วไป 2) การเสพติดการใช้เครือข่ายสังคมออนไลน์ 3) การเปรียบเทียบทางสังคม 4) การเห็นคุณค่าในตนเอง 5) ภาวะซึมเศร้า (9Q) เก็บรวบรวมผ่านระบบออนไลน์ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติเชิงพรรณนา และ Multiple logistic regression
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า มากกว่าครึ่งหนึ่งของกลุ่มตัวอย่าง มีการเสพติดการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์ การเปรียบเทียบทางสังคม การเห็นคุณค่าในตนเอง อยู่ระดับในน้อย (ร้อยละ 52.67, 53.67 และ 56.00 ตามลำดับ) กลุ่มตัวอย่าง
มีภาวะซึมเศร้า ร้อยละ 13.33 และปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับภาวะซึมเศร้า การเสพติดการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์สูง
มีโอกาสเกิดภาวะซึมเศร้า เท่ากับ 2.40 เท่า เมื่อเทียบกับผู้ที่มีพฤติกรรมการเสพติดการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์ต่ำ (adjOR = 2.40, 95%CI = 1.02 - 5.67) และการเปรียบเทียบทางสังคมสูงมีโอกาสเกิดภาวะซึมเศร้า เท่ากับ 3.71 เท่า เมื่อเทียบกับผู้ที่มีการเปรียบเทียบทางสังคมต่ำ (adjOR = 3.71, 95%CI = 1.53 - 9.00)
ดังนั้นอาจารย์และบุคลากรทางสุขภาพควรมีการคัดกรองพฤติกรรมการเสพติดการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์
การเปรียบเทียบทางสังคม และภาวะซึมเศร้าของนักศึกษา เพื่อให้ได้รับการช่วยเหลืออย่างทันท่วงที และพัฒนารูปแบบการป้องกันพฤติกรรมการ เสพติดการใช้สื่อสังคมออนไลน์ในนักศึกษาพยาบาล
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Beck, J. S. (1997). Personality disorders: Cognitive approaches. In L. J. Dickstein, M. B. Riba, & J. M. Oldham (Eds.), American Psychiatric Press review of psychiatry, 16, 23-45.
Braghieri, L., Levy, R., & Makarin, A. (2022). Social media and mental health. American Economic Review, 112(11), 3660–3693. https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20211218
Campbell, J. D., Chew, B., & Scratchley, L. S. (1991). Cognitive and emotional reactions to daily events: The effects of self‐esteem and self‐complexity. Journal of Personality, 59(3), 473- 505.
Cheng, C., Lau, Y. C., Chan, L., & Luk, J. W. (2021). Prevalence of social media addiction across 32 nations: Meta-analysis with subgroup analysis of classification schemes and cultural values. Addictive Behaviors, 117, 106845. www.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106845.
Dailey, S. L., Howard, K., Roming, S. M. P., Ceballos, N., & Grimes, T. (2020). A biopsychosocial approach to understanding social media addiction. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, 2, 158.167. www.https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.182.
Dullaphan, K. (2018). Social network usage behavior and psychological factors predicting Depression. Master’s thesis, communnication arts and innovation.. National Institute of Development Administration. (in Thai)
Gibbons, F. X., & Buunk, B. P. (1999). Individual differences in social comparison: Development of a scale of social comparison orientation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(1), 129–142.
Hamidi, F., Tahıllıoglu, A., Bilaç, O., & Onder, A. (2021). Evaluation of quality of life and psychiatric comorbidity in adolescents with social media addiction. Neuropsychiatric Investigation, 59(2), 31. www.https://doi.org/10.5152/NeuropsychiatrInvest.2021.01-02.
Hanmontri, C., Kanniam, N., Thoomthiang, A., Phonloet, A., Kumchan, N., Sukbantheang, O., et al. (2021). Factors influencing depression among families of 4th-year nursing students at Huachiew Chalermprakiet University during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Nursing and Health, 3(3), 1-16.
Jantapad, W., Kittipichai, W., Thongworn, S., & Yodmai, K. (2022). Internet usage behaviors in the new normal era among high school students in Nakhon Sawan Province, Thailand. Thai Journal of Public Health, 52(3), 221-233.
Jiang, S., & Ngien, A. (2020). The effects of Instagram use, social comparison, and self-esteem on social anxiety: a survey study in Singapore. Social Media + Society. www.https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305120912488.
Kanjanasuwan, K., Jirapornkul, C., & Maneenin, N. (2020). Depression in health science students in one field in Thailand. Journal of the Psychiatric Association of Thailand, 65(4), 343-354.
Korte, M. (2022). The impact of the digital revolution on human brain and behavior: Where do we stand? DCNS, 101-111. www.https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.2/mkorte.
Kulsawat, T. & Narkwatchara, P. (2021). Factors affecting social media addiction of undergraduate students in the eastern region university. Journal of MCU Nakhondhat, 8(10), 1-15.
Lamarre, T. (2020). Your brain on screens: Neuronal risk and media addiction. In The Routledge Companion to Media and Risk. www.https://doi.org/10.4324/ 9781315637501.
Malaeb, D., Salameh, P., Barbar, S., Awad, E., Haddad, C., Hallit, R., et al. (2020). Problematic social media use and mental health (depression, anxiety, and insomnia among lebanese adults: any mediating effect of stress?. Perspectives in Psychiatric Care. www.https://doi.org/10.1111/ppc.12576
Maslow, A. H. (1954). Motivation and Personality. New York: Harper & Row.
Nomraks, R., Jantham, W., & Buajaroen, H. (2024). The relationship between mental health literacy, resilience, and depression among students at Nakhon Pathom Rajabhat University. Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research, 4(2), 1-16.
Panova, T., & Carbone, X. (2022). Social media addiction. In Behavioral addictions. Studies in Neuroscience, Psychology, and Behavioral Economics.
Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Sidani, J. E., Escobar-Viera, C. G., & Fine, M. J. (2021). Temporal associations between social media use and depression. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 60(2), 179–188. www.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2020.07.009.
Rosenberg, M. (1989). Society and the adolescent self-image. Revised edition. Middletown, CT: Wesleyan University Press.
Sagar, M. E. (2021). Predictive role of cognitive flexibility and self-control on social media addiction in university students. International Education Studies, 14(4), 1-10.
Salovey, P. (2024). Social comparison processes in envy and jealousy. In J. Suls & T. A. Wills (Eds.), Social comparison: Contemporary theory and research. New York: Oxford University Press.
Shannon, H., Bush, K., Villeneuve, P. J., Hellemans, K. G. C., & Guimond, S. (2022). Problematic social media use in adolescents and young adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance, 9(4), e33450. www.https://doi.org/10.2196/33450.
Srioat, P., Thointh, P., & Koyun, S. (2023). Depression among nursing students and related factors during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sakonnakhon Hospital Journal, 26(2), 91-102.
Suchadaphong, K. (2016). The influence of social media usage on conspicuous consumption: the role of envy, narcissism, desire for self-promotion and face-saving. An independent study submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the deegress of master of science marketing management faculty of commerce and accountancy, Thammasat University. (in Thai)
Sun, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2021). A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addictive Behaviors, 114, 106699. www.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106699.
Thongbang, P. (2021). The relationship of social media addiction on adhd among college students Sirindhorn Public Health Suphanburi. Journal of Yanasangvorn Research Institute, 12(2), 1-15.
Thongpradub, J., Thaveekoon, T., & Nindachan, C. (2019). The relationship between Facebook addiction, self-esteem, and depression among high school students. Thai Red Cross Nursing Journal, 12(2), 117-133.
Tiggemann, M., & Anderberg, I. (2020). Social media is not real: The effect of ‘Instagram vs reality’ images on women’s social comparison and body image. New Media & Society, 22(12), 2183–2199. www.https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444819888720.
Tosangwan, S. (2021). Self-esteem, resilience, and depression among nursing students in a nursing college in northeastern Thailand. Journal of Health and Nursing Education, 27(1), 58-74. (in Thai)
Trikanan, S. (1999). Research methodology in social sciences: a practical approach. Bangkok. Chulalongkorn University Press. (in Thai)
Tungchitphakdeesakul, T. (2002). Factors related to self-esteem and hopelessness among juvenile offenders at the Central Juvenile and Family Court Detention Center [Unpublished Master’s thesis]. Mahidol University. (in Thai)
Uraiwan, P., Leeyuthanon, M., & Kaewsakultong, J. (2019). The relationship between personal factors, internet usage behavior, and depression among nursing students at Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Suratthani. Journal of Health Research and Innovation, 2(1), 13-24.
Verduyn, P., Gugushvili, N., Massar, K., Täht, K., & Kross, E. (2020). Social comparison on social networking sites. Current Opinion in Psychology, 36, 32-37. www.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.04.002.
Wanchaitanawong, W. & Choopan, K. (2014). A survey of internet utilization and impacts of internet utilization on students of Boromarajonnani College of Nursing, Chiangmai. Journal of Nursing and Education, 7(3), 124-132.
Wartberg, L., Kriston, L., & Thomasius, R. (2020). Internet gaming disorder and problematic social media use in a representative sample of German adolescents: Prevalence estimates, comorbid depressive symptoms, and related psychosocial aspects. Computers in Human Behavior, 103, 31–36. www.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.09.014.
Weiß, M., Baumeister, H., Cohrdes, C., Deckert, J., Grundahl, M., Pryss, et al. (2022). Extraversion moderates the relationship between social media use and depression. Journal of Affective Disorders Reports, 8, 100343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadr.2022.100343.
Weinstein, A. M. (2023). Problematic social networking site use—effects on mental health and the brain. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. www.https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1106004.
Young, K. S. (1996). Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 1(3), 237-244. www.https://doi.org/10.1089/cpb.1998.1.237.
Young, K. S. (1998). Internet addiction: symptoms, evaluation, and treatment. In L. VandeCreek & T. L. Jackson (Eds.), Innovations in clinical practice: a source book, 17, 19-31.
Wongpakaran T, Wongpakaran N. (2012). A comparison of reliability and construct validity between the original and the revised version of the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale. Psychiatry Investig, 9(1), 548.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว





