บทบาทของวิตามินอีในโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือดและโรคไขมันพอกตับ
คำสำคัญ:
วิตามินอี, α-tocopherol, โรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือด, โรคไขมันพอกตับบทคัดย่อ
วิตามินอีมีคุณสมบัติต้านอนุมูลอิสระที่เกิดจากกระบวนการเมแทบอลิซึมต่าง ๆ ด้วยการป้องกันการเกิดออกซิเดชันของไขมัน (lipid peroxidation) เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้สารอนุมูลอิสระไปทำลายเซลล์และเนื้อเยื่อภายในร่างกาย รูปแบบของวิตามินอีที่ออกฤทธิ์ได้ดีและมีฤทธิ์ต้านอนุมูลอิสระสูงสุดคือ α-tocopherol การใช้วิตามินอีในโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือด (cardiovascular disease) ที่มีพยาธิสภาพจากการเกิดออกซิเดชันของไลโพโปรตีนชนิดความหนาแน่นต่ำ (low-density lipoprotein; LDL) จากการศึกษาในปัจจุบันพบว่ายังไม่มีหลักฐานสนับสนุนเพียงพอให้ใช้วิตามินอีเพื่อป้องกันโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือด ส่วนในโรคไขมันพอกตับ (fatty liver disease) ที่ไม่ได้เกิดจากแอลกอฮอล์ (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NAFLD) ซึ่งมีภาวะเครียดออกซิเดชัน (oxidative stress) ทำให้เกิดการดำเนินของโรค จากการศึกษาในปัจจุบันพบว่าวิตามินอีไม่มีผลต่อความแตกต่างของระดับเอนไซม์ในตับ (alanine aminotransferase; ALT และ aspartate aminotransferase; AST) และพยาธิสภาพของตับในเด็กอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ แต่ในผู้ใหญ่พบว่าวิตามินอีสามารถลดระดับเอนไซม์ในตับและทำให้พยาธิสภาพของตับดีขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ อย่างไรก็ตาม คำแนะนำในการใช้วิตามินอีในผู้ป่วยกลุ่มดังกล่าวยังไม่สอดคล้องกัน ดังนั้นการพิจารณาใช้วิตามินอีในผู้ป่วยโรคไขมันพอกตับที่ไม่ได้เกิดจากแอลกอฮอล์ จึงควรพิจารณาถึงประโยชน์และความเสี่ยงต่อผู้ป่วยร่วมด้วย
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Subasree S. Role of vitamin C and vitamin E in health and disease. J Pharm Sci Res. 2014;6(1):52-5.
Rizvi S, Raza ST, Ahmed F, Ahmad A, Abbas S, Mahdi F. The role of vitamin E in human health and some diseases. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2014;14(2):157-65.
ศรมน สุทิน. วิตามินกับอนุมูลอิสระ. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี หัวเฉียวเฉลิมพระเกียรติ. 2559;2(1):80-92.
อธิป สกุลเผือก. อนุมูลอิสระและสารต้านอนุมูลอิสระ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. ศูนย์การศึกษาต่อเนื่องทางเภสัชศาสตร์. ปรับปรุงเมื่อ 27 ธันวาคม 2559 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 20 มีนาคม 2563]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ccpe.pharmacycouncil.org/index.php?option=article_detail&subpage=article_detail&id=204.
ชรินญา พิมพ์สอน, กนกวรรณ จารุกำจร. การเหนี่ยวนำภาวะไขมันพอกตับในหนูทดลอง. วารสารเภสัชศาสตร์อีสาน. 2557;10(1):16-31.
Hadzi-Petrushev N, Dimovska K, Jankulovski N, Mitrov D, Mladenov M. Supplementation with alpha-tocopherol and ascorbic acid to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease’s statin therapy in men. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2018;2018:1-7. doi:10.1155/2018/4673061.
Sato K, Gosho M, Yamamoto T, Kobayoshi Y, Ishii N, Ohashi T, et al. Vitamin E has a beneficial effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition. 2015;31(7-8):923–30.
Szymanska R, Nowicka B, Trela A, Kruk J. Vitamin E: structure and forms [Internet]. ScienceDirect; updated 2020 [cited 2020 Apr 13]. Available from: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978012811907500021X.
Mingpakanee R. The role of small dense LDL in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease. J Med Tech Assoc Thailand. 2018;46(3):6657-70.
รุ่งรัตน์ นิลธเสน. ไนตริกออกไซด์กับโรคหลอดเลือดตีบแข็ง. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี หัวเฉียวเฉลิมพระเกียรติ. 2559;2(1):71-9.
Mathur P, Ding Z, Saldeen T, Mehta JL. Tocopherols in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular disease. Clin Cardiol. 2015;38(9):570–6.
Vardi M, Levy NS, Levy AP. Vitamin E in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: the importance of proper patient selection. J Lipid Res. 2013;54(9):2307–14.
Virtamo J, Rapola JM, Ripatti S, Heinonon OP, Taylor PR, Albanes D, et al. Effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of primary nonfatal myocardial infarction and fatal coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158(6):668–75.
Lee IM, Cook NR, Gaziano JM, Gordon D, Ridker PM, Manson JE, et al. Vitamin E in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: the women’s health study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;294(1):56–65.
Sesso HD, Buring JE, Christen WG, Kurth T, Belanger C, Macfadyen J, et al. Vitamins E and C in the prevention of cardiovascular disease in men: the physicians’ health study II randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2008;300(18):2123–33.
Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza nell’Infarto miocardico. Dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E after myocardial infarction: results of the GISSI-Prevenzione trial. Lancet. 1999;354(9177):447–55.
Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators, Yusuf S, Dagenais G, Pogue J, Bosch J, Sleight P. Vitamin E supplementation and cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(3):154–60.
Boaz M, Smetana S, Weinstein T, Matas Z, Gafter U, Iaina A, et al. Secondary prevention with antioxidants of cardiovascular disease in endstage renal disease (SPACE): randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2000;356(9237):1213-8.
Heat Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of antioxidant vitamin supplementation in 20,536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;360(9326):23-33.
American Heart Association. Vitamin supplements: hype or help for healthy eating [Internet]. USA: American Heart Association; updated 2014 [cited 2020 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/vitamin-supplements-hype-or-help-for-healthy-eating.
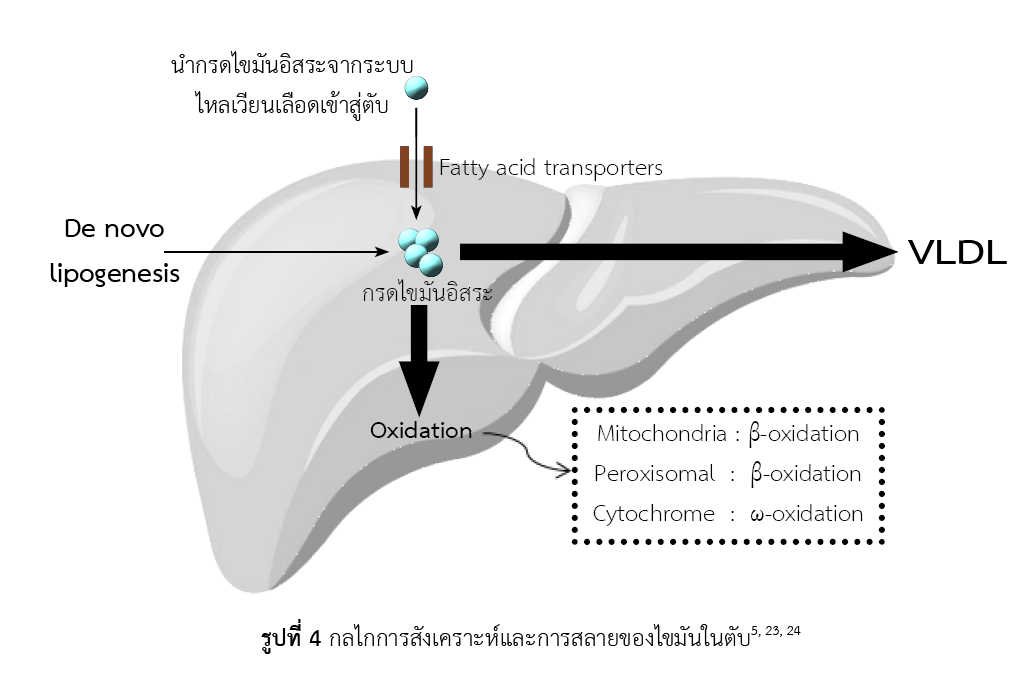
นัดดา สุขเกษม, วรัญญา จตุพรประเสริฐ, กนกวรรณ จารุกำจร. พยาธิกำเนิดของโรคไขมันเกาะตับและโมเดลสัตว์ทดลองขนาดเล็ก. วารสารเภสัชศาสตร์อีสาน. 2561;14(2):1-15.
กนกวรรณ จารุกำจร, วิลัดดา สินทร, ชรินญา พิมพ์สอน. ความสัมพันธ์ของภาวะเครียดออกซิเดชั่นและภาวะไขมันในเลือดสูง. วารสารพิษวิทยาไทย. 2557;29(1-2):57-69.
Ipsen DH, Lykkesfeldt J, Tveden-Nyborg P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(18):3313-27.
Ameer F, Scandiuzzi L, Hasnain S, Kalbacher H, Zaidi N. De novo lipogenesis in health and disease. Metabolism. 2014;63(7):895-902.
Amanullah I, Khan YH, Anwar I, Gulzar A, Mallhi TH, Raja AA. Effect of vitamin E in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Postgrad Med J. 2019;95(1129):601-11.
Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, Van Natta ML, Molleston JP, Murray KF, Rosenthal P, et al. Effect of vitamin E or metformin for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: the TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2011;305(16):1659–68.
Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328-57.
Vajro P, Mandato C, Franzese A, Ciccimarra E, Lucariello S, Savoia M, et al. Vitamin E treatment in pediatric obesity-related liver disease: a randomized study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;38(1):48-55.
Nobili V, Manco M, Devito R, Di Ciommo V, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, et al. Lifestyle intervention and antioxidant therapy in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 2008;48(1):119-28.
Larion S, Khurana S. Clinical studies investigating the effect of vitamin E therapy in patients with NASH. Clin Liver Dis. 2018;11(1):16-21.
Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, McCullough A, Diehl AM, Bass NM, et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(18):1675-85.
Leoni S, Tovoli F, Napoli L, Serio I, Ferri S, Bolondi L. Current guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review with comparative analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(30):3361-73.
Harrison SA, Torgerson S, Hayashi P, Ward J, Schenker S. Vitamin E and vitamin C treatment improves fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(11):2485-90.
Foster T, Budoff MJ, Saab S, Ahmadi N, Gordon C, Guerci AD. Atorvastatin and antioxidants for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the St Francis heart study randomized clinical trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(1):71-7.
Hoofnagle JH, Van Natta ML, Kleiner DE, Clark JM, Kowdley KV, Loomba R, et al. Vitamin E and changes in serum alanine aminotransferase levels in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38(2):134-43.
Abner EL, Schmitt FA, Mendiondo MS, Marcum JL, Kryscio RJ. Vitamin E and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis. Curr Aging Sci. 2011;4(2):158-70.
Miller ER 3rd, Pastor-Barriuso R, Dalal D, Riemersma RA, Appel LJ, Guallar E. Meta-analysis: high-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142(1):37-46.
Klein EA, Thompson IMJR, Tangen CM, Crowley JJ, Lucia MS, Goodman PJ, et al. Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial (SELECT). JAMA. 2011;306(14):1549-56.
MICROMEDEX® (2021). IBM Watson Health, Greenwood Village, Colorado, USA. [cited: 2021 Mar 16]. Available from: https://www.micromedexsolutions.com/.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

