Methylphenidate SODAS: ยารักษาโรคสมาธิสั้นรูปแบบออกฤทธิ์นาน
คำสำคัญ:
โรคสมาธิสั้น, รูปแบบยาออกฤทธิ์นาน, SODAS, methylphenidateบทคัดย่อ
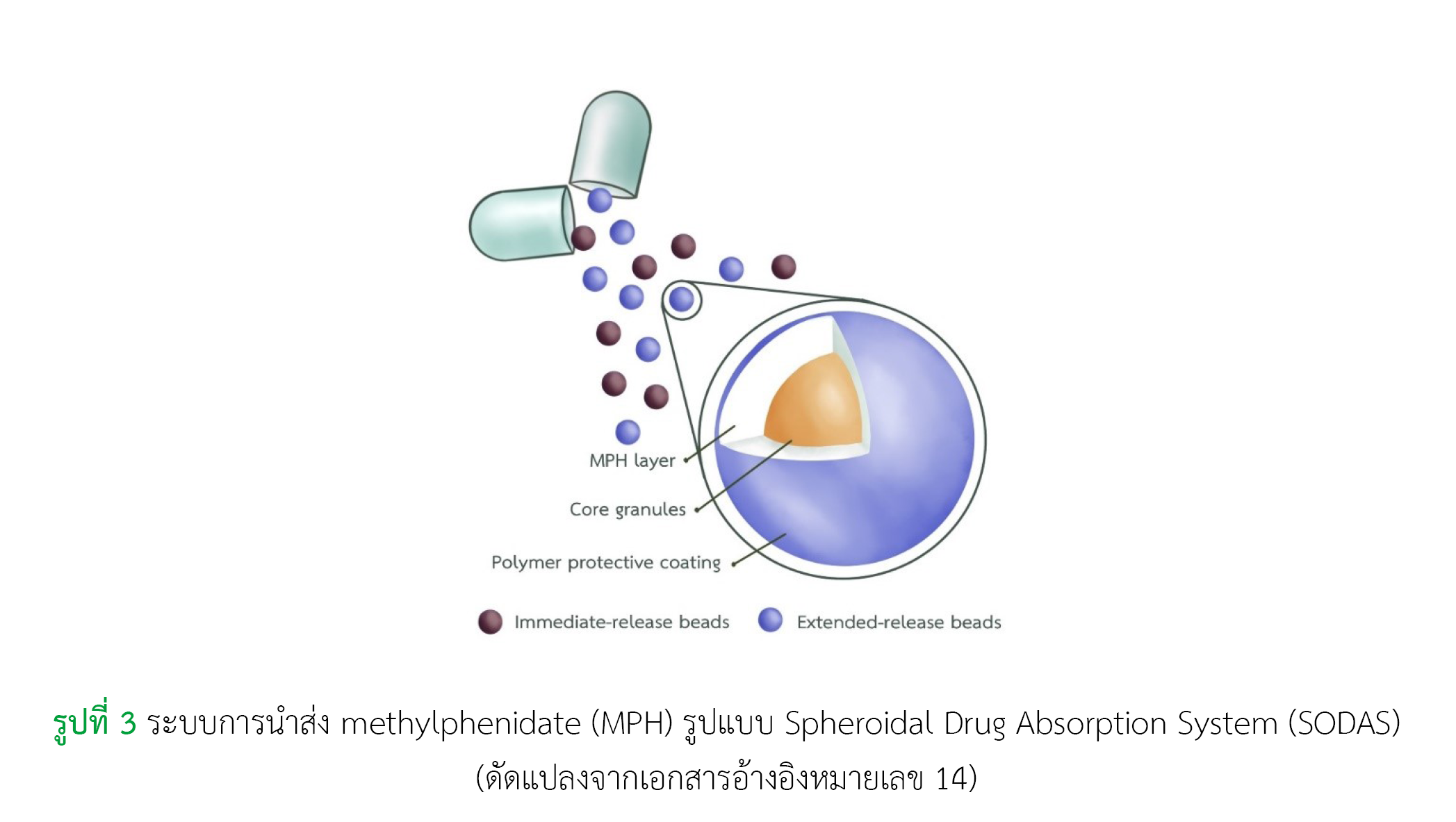
Methylphenidate เป็นยาที่มีฤทธิ์ต่อระบบประสาทส่วนกลางในกลุ่ม stimulant ที่ใช้สำหรับการรักษาโรคสมาธิสั้นกันอย่างแพร่หลาย จากข้อจำกัดในการใช้ methylphenidate รูปแบบปลดปล่อยทันที คือการมีค่าครึ่งชีวิตที่สั้น ทำให้ต้องบริหารยาหลายครั้งในแต่ละวัน และทำให้เกิดปัญหาต่าง ๆ อาทิ ความไม่สะดวกในการใช้ยา ความไม่ร่วมมือในการรับประทานยา ปัจจุบันจึงมีการพัฒนา methylphenidate ในรูปแบบออกฤทธิ์นาน นั่นคือ methylphenidate Spheroidal Oral Drug Absorption System (SODAS) เป็นยาในรูปแบบออกฤทธิ์นาน ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี SODAS โดยภายในแคปซูลแข็งประกอบด้วยเม็ดบีดส์ (beads) ที่มีตัวยาสำคัญในรูปแบบปลดปล่อยทันทีร้อยละ 50 และรูปแบบปลดปล่อยแบบทยอยร้อยละ 50 ทำให้ยาออกฤทธิ์ได้เร็วภายใน 1 ชั่วโมง และมีระยะเวลาการออกฤทธิ์นานถึง 8 ชั่วโมง จึงสามารถบริหารยาเพียงวันละ 1 ครั้ง จากผลการศึกษาทางคลินิก พบว่า methylphenidate SODAS มีประสิทธิภาพในการรักษาอาการหลักของโรคสมาธิสั้นได้ ไม่แตกต่างจากยารูปแบบออกฤทธิ์ทันทีและรูปแบบออกฤทธิ์นานอื่น ๆ นอกจากนี้ methylphenidate SODAS ยังมีข้อดีสำหรับผู้ป่วยที่มีปัญหาการกลืนหรือมีภาวะทางเดินอาหารอุดตัน เนื่องจากสามารถแกะเปลือกแคปซูลนำเม็ดบีดส์ที่อยู่ด้านในออกมาได้ อีกทั้งเม็ดบีดส์ยังสามารถละลายได้ดีไม่ทำให้เกิดการอุดตันของทางเดินอาหาร ขนาดยาแนะนำสำหรับการใช้ methylphenidate SODAS ในการรักษาโรคสมาธิสั้น เริ่มต้นด้วย 20 มิลลิกรัม/วัน และปรับขนาดยาเพิ่มขึ้น 10 มิลลิกรัม/สัปดาห์ โดยขนาดยาสูงสุด คือ 60 มิลลิกรัม/วัน (เด็ก) และ 80 มิลลิกรัม/วัน (ผู้ใหญ่) ทั้งนี้การปรับขนาดยาจะพิจารณาตามอาการทางคลินิกและผลข้างเคียงที่เกิดขึ้น
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Data and statistics about ADHD [Internet]. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 5]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
Dopheide JA, Pliszka SR. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In: DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM, editors. Pharmacotherapy: a pathophysiological approach. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2014. p.957-71.
Boon-yasidhi V. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: diagnosis and management. J Psychiatr Assoc Thailand [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2023 Jan 5];57(4):373-86. Available from: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JPAT/article/view/5792
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed (DSM-5). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. p.59-66.
Thapar A, Cooper M, Jefferies R, Stergiakouli E. What causes attention deficit hyperactivity disorder?. Arch Dis Child. 2012;97(3):260–5. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2011-300482.
Brown KA, Samuel S, Patel DR. Pharmacologic management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a review for practitioners. Transl Pediatr. 2018;7(1):36–47. doi: 10.21037/tp.2017.08.02.
Coghill D, Banaschewski T, Zuddas A, Pelaz A, Gagliano A, Doepfner M. Long-acting methylphenidate formulations in the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review of head-to-head studies. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13(1):237. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-237.
Liu F, Muniz R, Minami H, Silva RR. Review and comparison of the long acting methylphenidate preparations. Psychiatr Q. 2005;76(3):259–69. doi: 10.1007/s11126-005-2979-0.
Maldonado R. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of new extended-release formulations of methylphenidate. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013;9(8):1001–14. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2013.786041.
Patrick KS, González MA, Straughn AB, Markowitz JS. New methylphenidate formulations for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2005;2(1):121–43. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2.1.121.
Majeed MH, Zafar MK. ADHD symptoms are stable, then a sudden relapse. Curr Psychiatr [Internet]. 2016 [cited . 2023 Apr 2];15(10):26-30. Available from: https://www.mdedge.com/psychiatry/article/114026/adhd/adhd-symptoms-are-stable-then-sudden-relapse
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา. ตรวจสอบการอนุญาต [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: สํานักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา กระทรวงสาธารณสุข; 2566 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 2 เม.ย. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก: https://porta.fda.moph.go.th/fda_search_all/main/search_center_main.aspx
National Library of Medicine. PubChem, compound summary methylphenidate [Internet]. Bethesda, Maryland: National Library of Medicine; 2023 [cited 2023 Apr 6]. Available from: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Methylphenidate
Siddiqui MA. SODAS® (Spheroidal oral drug absorption system) [Internet]. n.p.: Pharmaceutical Research; 2012 [cited 2023 Apr 6]. Available from: https://pharmaceuticalresearch.wordpress.com/2012/07/05/sodas-spheroidal-oral-drug-absorption-system/
Stahl SM. Stahl’s essential psychopharmacology: neuroscientific basis and practical applications. 5th ed. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press; 2022. p.449-85.
Volkow ND, Swanson JM. Variables that affect the clinical use and abuse of methylphenidate in the treatment of ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(11):1909–18. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.11.1909.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Ritalin LA® (methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release capsules) prescribing information [Internet]. New Jersey: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2021 [cited 2023 Apr 5]. Available from: https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/ritalin_la.pdf
Novartis (Thailand) Ltd. Ritalin LA® [package insert]. Bangkok (Thailand): Novartis (Thailand) Ltd; 2021.
Markowitz JS, Straughn AB, Patrick KS, DeVane CL, Pestreich L, Lee J, et al. Pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate after oral administration of two modified-release formulations in healthy adults. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(4):393–401. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200342040-00007.
Biederman J, Quinn D, Weiss M, Markabi S, Weidenman M, Edson K, et al. Efficacy and safety of Ritalin LA®, a new, once daily, extended-release dosage form of methylphenidate, in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Paediatr Drugs. 2003;5(12):833–41. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200305120-00006.
Lopez F, Silva R, Pestreich L, Muniz R. Comparative efficacy of two once daily methylphenidate formulations (Ritalin LA® and Concerta®) and placebo in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder across the school day. Paediatr Drugs. 2003;5(8):545–55. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200305080-00005.
Haertling F, Mueller B, Bilke-Hentsch O. Effectiveness and safety of a long-acting, once-daily, two-phase release formulation of methylphenidate (Ritalin LA®) in school children under daily practice conditions. Atten Defic Hyperact Disord. 2015;7(2):157–64. doi: 10.1007/s12402-014-0154-x.
Medicines Adverse Reactions Committee. Methylphenidate and risk of birth defects [Internet]. Wellington: Medsafe; 2022 [cited 2023 Apr 5]. Available from: https://www.medsafe.govt.nz/committees/marc/reports/190-Methylphenidate-and-risk-of-%20birth-defects.pdf
Kelsey JJ. Drug principles in lactation. In: Pharmacotherapy Self-Assessment Programs (PSAP) [Internet]. Lenexa, Kansas: The American College of Clinical Pharmacy; 2016 [cited 2023 Apr 5]. Available from: https://www.accp.com/docs/bookstore/psap/p2016b3_sample.pdf
Zhang L, Yao H, Li L, Du Rietz E, Andell P, Garcia-Argibay M, et al. Risk of cardiovascular diseases associated with medications used in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(11):e2243597. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43597
Man KKC, Lau WCY, Coghill D, Besag FMC, Cross JH, Ip P, et al. Association between methylphenidate treatment and risk of seizure: a population-based, self-controlled case-series study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4(6):435–43. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30100-0.
Bingöl-Kızıltunç P, Yürümez E, Atilla H. Does methylphenidate treatment affect functional and structural ocular parameters in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder? - a prospective, one year follow-up study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022;70(5):1664-8. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2966_21.
Wolraich ML, Hagan JF Jr, Allan C, Chan E, Davison D, Earls M, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2019;144(4):e20192528. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2528.
Bolea-Alamañac B, Nutt DJ, Adamou M, Asherson P, Bazire S, Coghill D, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: update on recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28(3):179–203. doi: 10.1177/0269881113519509.
Almagor D, Duncan Don, Gignac M, editors. Canadian ADHD practice guidelines. 4.1th ed. [Internet]. Toronto: Canadian ADHD Resource Alliance (CADDRA); 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 3]. Available from: https://adhdlearn.caddra.ca/purchase-guidelines/
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล(ประเทศไทย)

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

