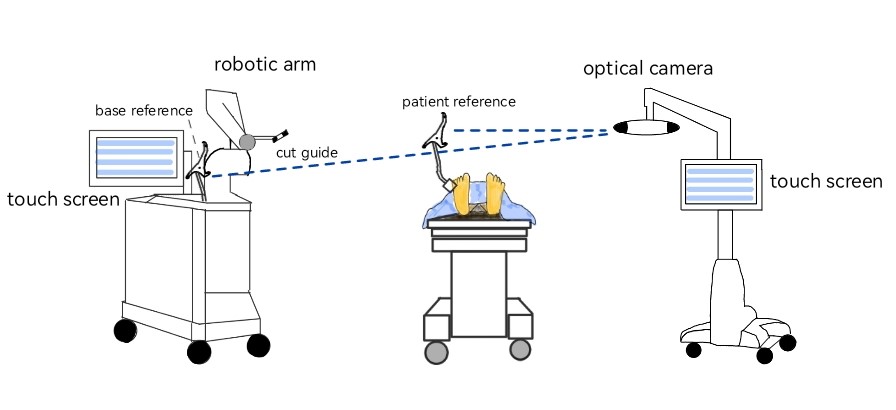
Robotic Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty
Main Article Content
Abstract
Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is considered the gold standard of treatment for patients with severe knee arthrosis who failed conservative treatment. Conventional TKA is generally accepted as the standard technique which shows excellent long-term result. Whereas, robotic assisted TKA, has become an interesting technique recently. Main goal of robotic assisted TKA is to minimize human errors in surgical technique. Theoretically advantages are ability to plan the size and position of implants based on preoperative imaging and by assisting surgeons to more precisely and more accurately prepare the bone, minimized soft tissue injury, the physiological kinematics of the joint and the overall alignment of lower limb are also better restored. In this article, we demonstrate basic principles, basic instruments and summarize basic steps of robotic assisted TKA into four main steps; preoperative imaging process, bone registration process, preoperative planning process and bone cutting process. We review various robotic systems and categorize into different groups base on requirements of preoperative imaging usage and level of interaction of the surgeon in operations. The different robotic systems were subdivided into image-based/imageless and active/passive/ semi-active. We also report outcomes of this technology from literatures reviews.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Goldsmith MF. For better hip replacement results, surgeon's best friend may be a robot. JAMA. 1992;267(5):613-4.
Banerjee S, Cherian JJ, Elmallah RK, Pierce TP, Jauregui JJ, Mont MA. Robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13(1):47-56.
Banerjee S, Cherian JJ, Elmallah RK, Jauregui JJ, Pierce TP, Mont MA. Robotic-assisted knee arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015;12(6):727-35.
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA. The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1588-96.
Bargar WL, Bauer A, Borner M. Primary and revision total hip replacement using the Robodoc system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998(354):82-91.
Chun YS, Kim KI, Cho YJ, Kim YH, Yoo MC, Rhyu KH. Causes and patterns of aborting a robot-assisted arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(4):621-5.
Parratte S, Price AJ, Jeys LM, Jackson WF, Clarke HD. Accuracy of a New Robotically Assisted Technique for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Cadaveric Study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(11):2799-803.
Lang JE, Mannava S, Floyd AJ, Goddard MS, Smith BP, Mofidi A, et al. Robotic systems in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(10):1296-9.
Hassebrock JD, Makovicka JL, Wong M, Patel KA, Scott KL, Deckey DG, et al. Minimally Invasive Robotic-Assisted Patellofemoral Arthroplasty. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(4):e425-e33.
Batailler C, White N, Ranaldi FM, Neyret P, Servien E, Lustig S. Improved implant position and lower revision rate with robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1232-40.
Herry Y, Batailler C, Lording T, Servien E, Neyret P, Lustig S. Improved joint-line restitution in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty using a robotic-assisted surgical technique. Int Orthop. 2017;41(11):2265-71.
Agarwal N, To K, McDonnell S, Khan W. Clinical and Radiological Outcomes in Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3393-409 e2.
Saradej K, Sirapat P, Danai H, Ong-art P, Thanainit C. COMPARISON BETWEEN IMAGE-FREE ROBOTIC ASSISTED AND CONVENTIONAL TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY: POSTOPERATIVE CT ASSESSMENT OF ALIGNMENT. Journal of Southeast Asian Medical Research. 2020;4(1).
Thiengwittayaporn S, Uthaitas P, Senwiruch C, Hongku N, Tunyasuwanakul R. Imageless robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty accurately restores the radiological alignment with a short learning curve: a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2021;45(11):2851-8.