ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการดื่มเครื่องดื่มแอลกอฮอล์ ของผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูงในอำเภอบ้านไผ่ จังหวัดขอนแก่น
คำสำคัญ:
ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ , การดื่มแอลกอฮอล์ , โรคความดันโลหิตสูงบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยเชิงวิเคราะห์แบบภาคตัดขวางนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการดื่มแอลกอฮอล์ ของผู้ป่วยโรคความความดันโลหิตสูงในอำเภอบ้านไผ่ จังหวัดขอนแก่น กลุ่มตัวอย่าง คือผู้ป่วยโรคความดันโลหิตสูง จำนวน 225 คน โดยเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลจจากการสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบเป็นระบบ ในผู้ป่วยโรคความความดันโลหิตสูง อำเภอบ้านไผ่ กลุ่มวิเคราะห์ด้วยโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์สำเร็จรูป นำเสนอข้อมูลด้วยค่าสถิติ ความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ยและส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน ค่าต่ำสุด ค่าสูงสุด และสมการการถดถอยพหุโลจิสติก พร้อมช่วงเชื่อมั่น (95%CI)
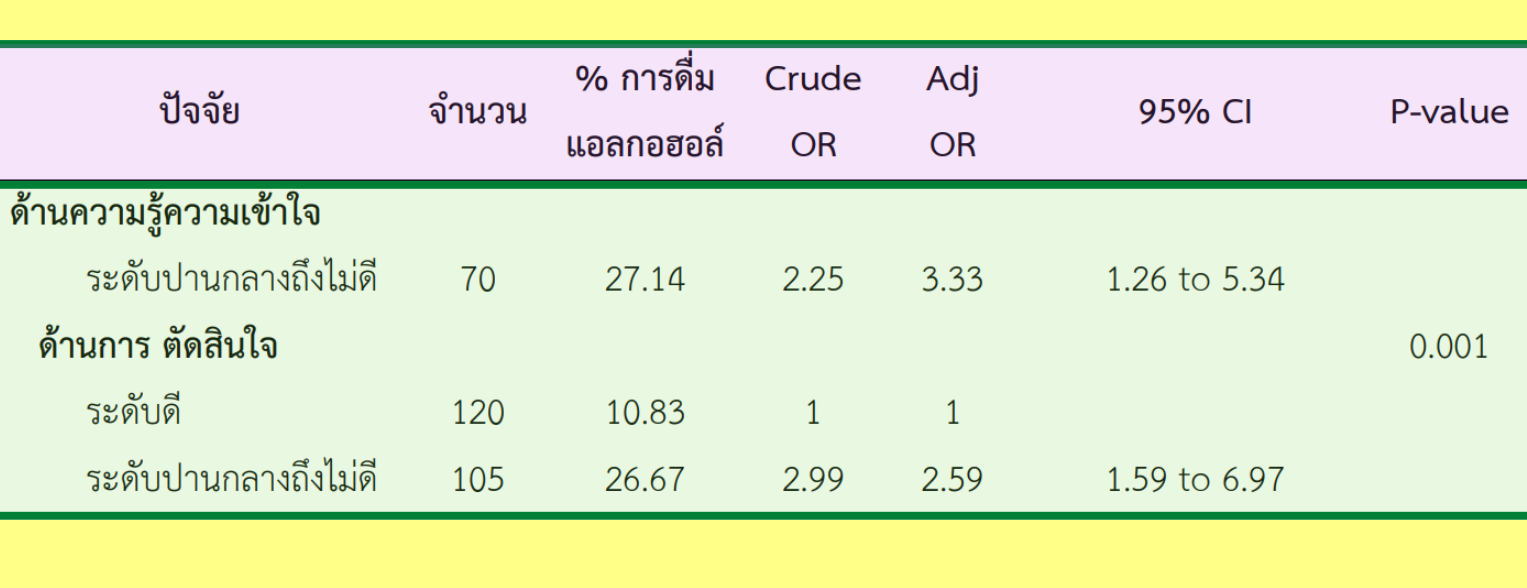
ผลการศึกษาพบว่า ความชุกของการดื่มแอลกอฮอล์เท่ากับร้อยละ 18.22 (95% CI: 12.88 to 23.12) ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ด้านความรู้ความเข้าใจ ส่วนมากอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง (44.44%) ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ด้านการเข้าถึงข้อมูลและการบริการ ส่วนมากอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ร้อยละ 66.22 ความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ด้านทักษะการสื่อสารส่วนมากอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ร้อยละ 82.22 ด้านการจัดการตนเองส่วนมากอยู่ระดับปานกลาง ร้อยละ 49.78 ด้านการรู้เท่าทันสื่ออยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ร้อยละ 62.67 และด้านการตัดสินใจส่วนมากอยู่ในระดับดี ร้อยละ 53.33 ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการดื่มแอลกอฮอล์ของผู้ป่วยโรคความความดันโลหิตสูง ได้แก่ ปัจจัยความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพ ด้านความรู้ความเข้าใจ (Adj. OR=3.33; 95%CI: 1.26 to 5.34; p-value = 0.010) และ ปัจจัยความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพด้านการตัดสินใจ (Adj. OR=2.59; 95%CI: 1.59 to 6.97; p-value = 0.001)
ข้อเสนอแนะ หน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้องควรส่งเสริมกิจกรรมเชิงรุกหรือรณรงค์สร้างความรู้ความเข้าใจและการตัดสินใจเพื่อปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมการดื่มแอลกอฮอล์รวมถึงเพิ่มระดับความรอบรู้ด้านสุขภาพให้สูงขึ้น
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Auttama, N., Seangpraw, K. (2018). Factors Predictor Health Literacy among Older Adults with Risk Hypertension Disease, Phayao Province. Journal of Health Education, 42(2), 75- 85. (In Thai).
BanPhai District Health Office. (2018). Morbidity rate of hypertension per hundred thousand population in Health Region 7KhonKaen Province CUP BanPhai Hospital. Retrieved November 20,2019, from https://hdcservice.moph.go.th/hdc
Best, John W. (1977) . Research in Education. 3rd ed. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey : Prentice Hall, Inc.
Bloom, B.S.. (1956). Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, the classification of educational goals – Handbook I: Cognitive Domain. New York: McKay.
Cho, YI., Lee, SY., Arozullah, AM., Crittenden, KS. (2008) Effects of health literacy on health status and health service utilization amongst the elderly, Social Science & Medicine, 66(8). 1809-16.
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika. 16, 297-334.
Darun, P. (2018). Health literacy factors influencing on Health behavior of population in Buengkan Provice. Journal of Department of Health Service Support, 15(3), 71-82. (In Thai).
Eftekhar Ardebili, H., Fathi, S., Moradi, H., Mahmoodi, M. & Maheri, A. (2014) Effect of Educational Intervention based on the Health Belief Model in Blood Pressure Control in Hypertensive Women. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci , 24(119). 62–71
Ginggeaw, S., Prasertsri, N. (2014). The Relationship between Health Literacy and Health Behaviors among Older Adults who have Multi-morbidity, Nursing Journal of The Ministry of Public Health, 43-54 (In Thai).
Health education division Department of health service support Ministry of public health. (2015). Situations and trends of health problems and Desirable behavior and criteria for alcohol drinking behavior. In Health education division, Changing behavior of drinking alcohol behavior or alcoholic beverages for working (pp. 7 – 13). Nonthaburi: Online.
Health education division Department of health service support Ministry of public health. (2018). Strengthening and assessing health literacy and health behavior Children and youth aged 7-14 years and people aged 15 and older
Hsieh, Y.F., Bloch, A.D., & Larsen, D.M. (1998). A Simple Method of Sample Size Calculation for Linear and Logistic Regression. Statistics in Medicine, 17,1623-1634.
KhonKaen Provincial Health Office. (2019). The prevalence of hypertension. Retrieved November 20,2019, from https://kkhdc.moph.go.th/hdc/main/index_pk.php
Ministry of Public Health. (2019). Morbidity rate of hypertension per hundred thousand population. Retrieved November 20,2019, from https://hdcservice.moph.go.th/hdc/reports/
National Revolution Committee for Health and Environment. (2016). Health Literacy Revolution and Health Communication. Available at: https://library2.parliament.go.th/giventake/content_nrsa2558/d111459-03.pdf
Niyakit, S. (2016). Factors Related to Alcohol Drinking Behavioral of the People in Rainoi sub-district, Meuang District, Ubon Ratchathani Province. Journal of ODPC 10th Ubon Ratchathani, 14(2), 16-32. (In Thai).
Nutbeam, D. (2000). Health literacy as a public health goal: a challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International.15(3), 259–267.
Office of Public Health System Develop Division of Non Communicable Diseases Department of diseases control. (2018). Campaign issues on World Hypertension Day 2018. In World Hypertension day 2018 (pp. 1 ). Nonthaburi: Bureau of non Communicable disease.
Prompim, A., Laohasiriwong, W., Udompanich, S., Phajan, T., Suwannaphant, K. (2016). Alcohol Use Disorder Situations and It’s Associated Factors among Working Age Males in The Industrial Areas, Khon Kaen Province. The Journal of Baromarajonani College of Nusing, Nakhonratchasima, 23(2), 18-31. (In Thai).
Raretong, A. (2018). Health Literacy and Health Behaviour, 3Aor 2Sor, for the Village Health Volunteers (VHVs) : Case study of Hintok Sub-district, Ronphibun District, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, Journal of Department of Health Service Support, 15(3), 71-82. (In Thai).
Rattanamanee, N., Phasunon, P., Chantuk, T. (2018). Factors affecting alcohol drinking of the rotal thai navy officials in Sattahip Chonburi Provice, Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Thonburi University, 12(28) , 197-211. (In Thai).
Strategy and Planning Division Ministry of Public Health. Public Health Statistics A.D. (2015). Bangkok : Samcharoen Printing House.
Waivongkitjakarn, S., Sangpaibool, S., Kimavaha, S., Panichsombat, C., Chutrakoolwong, J., Theerathitiwong, P., Pinitsuntorn, S., Paileklee, S. (2018). Health Literacy of Hypertension in Hypertensive Patients in Sam Liam Community, Khon Kaen Province, Srinagarind Med J 2018;33. (In Thai).
Wongkongdech, R., Wongkongdech, A., Hansawong, J. (2018). Health literacy in social media using for alcohol prevention among junior urban high school students. Journal of the Office of DPC 7, 26(1), 46-57. (In Thai).
World Health Organization (WHO). (2013). A global brief on hypertension Silent killer, global public health crisis. Retrieved November 20,2019, from http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/publications/global_brief_hypertension/en/
World Health Organization [WHO]. (2009) World health report. Available at: https://www.who.int/whr/media_centre/factsheet3/en/.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 วารสารสาธารณสุขและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความทุกบทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสาธารณสุข















