Perceived Health and Behavioral Health of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus in the Internal Medicine Ward at Chumphon Khet Udomsak Hospital, Thailand
Keywords:
Health Awareness, Health Behaviors, DiabeticsAbstract
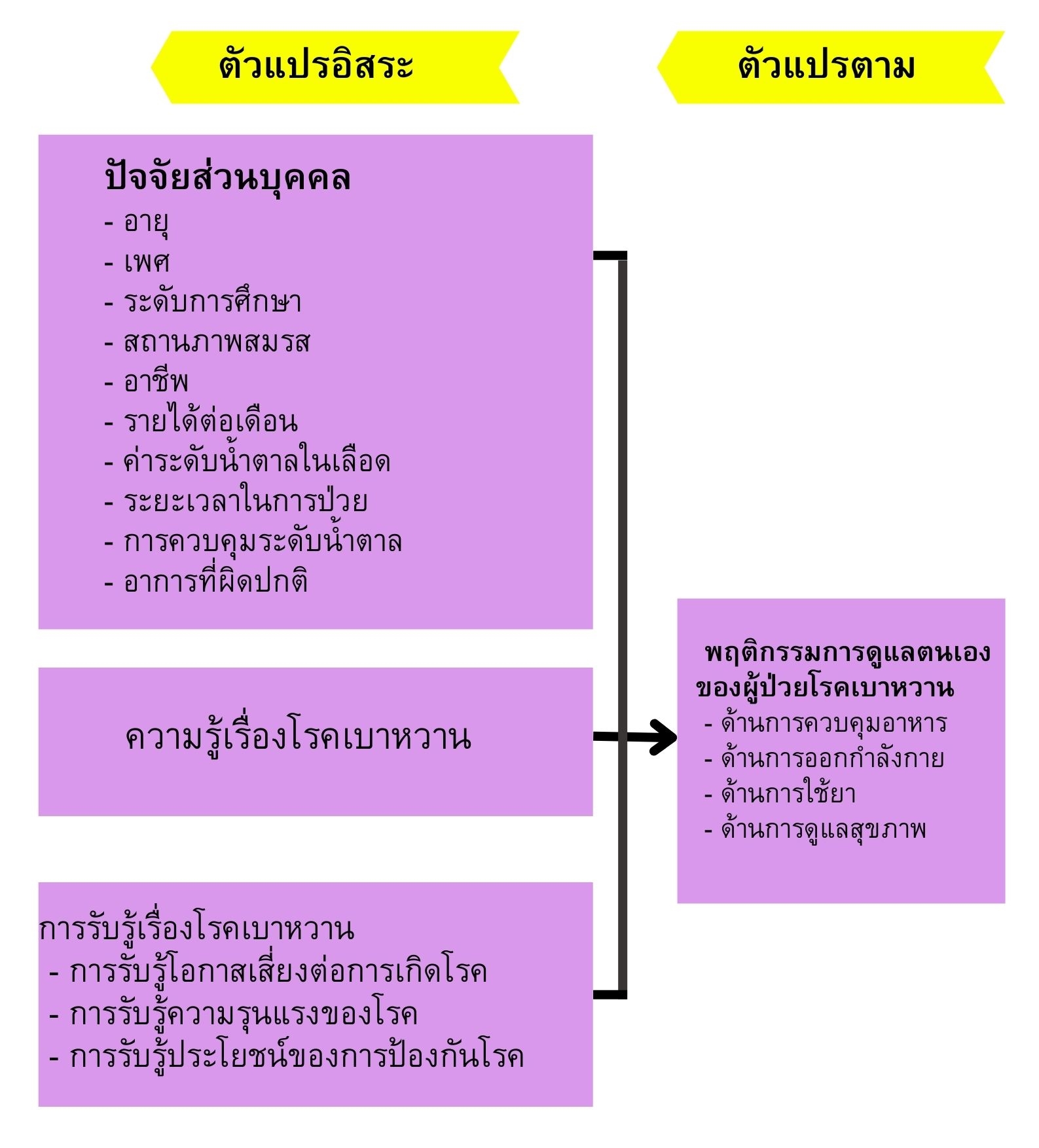
We conducted a descriptive research study. Our objective was to study the level of knowledge and awareness level regarding health and self-care behavior among diabetic patients in the medical ward at Chumphon Khet Udomsak Hospital, Chumphon province, Thailand. Our study participants were 180 diabetic patients admitted between April and June 2020. We calculated the appropriate sample size using a sample size estimation table (Krejcie & Morgan 1970). We collected patient information with the following tools: general diabetes questionnaire, diabetes knowledge questionnaire, health belief stereotypes questionnaire, and self-care behavioral questionnaire about prevention of diabetes. We used descriptive statistics to analyze data including frequency distribution, percentage, average, and standard deviation. Our results indicated that:
- Most diabetic patients had knowledge at a high level (average = 2.37, S.D.= 0.52). The three items with the highest averages were: 1) abstaining from water for at least 8 hours before blood glucose testing (average = 2.87, S.D.= 0.31), 2) patients’ own healthcare habits are one cause of diabetes (average = 2.76, S.D.= 0.62), 3)diabetics should clearly schedule their medications and take them on time every day (average = 2.71, S.D.= 0.64).
- The scores for overall health belief patterns were at a moderate level (average = 2.29, S.D.= 0.58). The highest average score was for the perception of the benefits of prophylaxis (average =2.48, S.D.= 0.60). The second highest average score was for the perception of the likelihood of disease (average = 2.45, S.D.= 0.70). The third highest average score was for the perception of the severity of disease (average = 2.21, S.D.= 0.48). The fourth highest average score was for awareness of barriers to preventing diabetes (average = 2.00, S.D.= 0.53).
- The diabetic patients in our study had very good scores for self-care behaviors to prevent diabetes (average = 2.51, S.D.= 0.66). The items with the highest scores, in descending order of average score, were: physical activity (average = 3.00, S.D.= 0.65), healthcare (average = 2.62, S.D.= 0.72), drug use (average = 2.33, S.D.= 0.66), and diet (average = 2.10, S.D.= 0.59).
References
Apinya Sanchai. (2012). Medication behavior of non-insulin dependent diabetes patients
Nong Khu Subdistrict, Maha Sarakham Province. Bachelor of Public Health, University
Maha Sarakham. (In Thai)
Atchara Jindawatthanawong . (2013) Relationship between perception and
perception. Beliefs in health With defensive behaviors Type2 diabetes in high school students Prachuap Khiri Khan ProvinceRamathibodi Sarn, 18 (1):58 - 69. (In Thai)
Bupphachat Teengam et al., (2012). Factors affecting the practice in prevention of diabetes
and hypertension of population at risk group in the responsible area of Ban Phom
Muang health center, Chumphonburi district, Surin province. Research and
development health system journal, 5(3): 127-134. (In Thai)
Bureau of Non-communicable Diseases , Department of Disease Control. (2014). Non-
communicable disease information. [Online]. Retrieved 10 November 2020 from http://thaincd.com/index. php. (In Thai)
Chaiyaporn Phonmanee. (2015). Chronic complications in large blood vessels of diabetes
mellitus. [ Online ]. Retrieved 10 November 2020 from http : //www.Si.Mahidol.
Ac.Th/th division/diabetes/. (In Thai)
Diabetes Association of Thailand In the royal patronage of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha
Chakri Sirindhorn. (2011) Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes 2011, 1st edition,
Bangkok: Association. (In Thai).
Issara Japhichom. (2012). Self-Care Behavior of Diabetic Patients in the area of responsibility
Ning Tat Health Promoting Hospital, Talat Sai Subdistrict, Chum Phuang District,
Province Nakhon Ratchasima. Bachelor of Public Health Mahasarakham University.
(In Thai).
Jesakorn Noin et al. (2015). Report sequel Conference Symposium (Proceedings).
Bringing Research at national level. Graduate Network Northern Rajapat University
No. 17. (In Thai)
Jessada Paweenkiatkhun (2014). The recognized efficacy and self-care behaviors of patients
with Type I diabetes.2 Health Promotion Hospital of the Securities Division of the
guest District Mae Jam , Chiang Mai. Maha Chakri Sirindhorn Public Health
Graduate Chiang Mai University. (In Thai).
Krejcie, R. V. & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining Sample Size for Research Activities.
Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3): 607-610.
Kurt Lewin. (1951). Field. Theory and Leaning. Ind. Cartwright Field theory in Social Science :
Selected Theoretical. New York : Harper and Row.
Petcharat Kerddonfaek , Boonchan Wongsunopparat , Umaporn Udamtharaphayakul and
Chalerm Sri Nanthawan . (2010). The risk of developing diabetes according to the criteria and lifestyle that promotes health in the direct relatives. First of all people with diabetes. Searched on 10 May November Sky in 2563 from. http ://www. tcithaijo.org/index. a php / RNJ / Article / download On / 9040 / 7702. (In Thai)
Sumet Sansingchai. (2006). Health belief and preventive behavior of risk group diabetes
mellitus in Pa Sak subdistrict, Mueng district, Lamphun province. Master of Public
Health, Graduate school Chiang Mai University. (In Thai).
Petchnoi Singchuangchai. (1993). Techniques for creating and developing nursing research
tools. Songkhla:Faculty of Nursing Prince of Songkla University. (In Thai).
Petcharat Jiewkaew. (2017). Health awareness. And health behavior of diabetic patients who
come to the hospital Health subdistricts , lotus pond, the water district W. Barr has
Phichit. In a the meeting of Norwich of the value of the channel , the Latinos No. 4.
Innovation and Technology of the hard drives in 4.0: 1082-1087. Kamphaeng
Institute. Rajapat Kamphaeng Phet University. (In Thai).
Rosenstock, I. M., Strecher, V. J. & Becker, M. H. (1988). Social Learning Theory and the
Health Belief Model. Health Education Quarterly, 15(2): 175-183.
Sultan N, Pope JE, Clements PJ. (2004) The health assessment questionnaire
(HAQ) is strongly predictive of good outcome in early diffuse scleroderma: results from an analysis of two randomized controlled trials in early diffuse scleroderma. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004; (43): 472-8.
Watkins, M. J. (2000). Competency for nursing practice. Journal of Clinical Nursing, (9): 338-346.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Thai Journal of Public Health and Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความทุกบทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วารสารสาธารณสุข















