ผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ ต่อการลดปัจจัยเสี่ยงของผู้ป่วยโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรังที่มารับบริการ ณ โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลแห่งหนึ่งในภาคใต้ของประเทศไทย
คำสำคัญ:
โปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพ, ปัจจัยเสี่ยงกลุ่มเมตาบอลิก, ผู้ป่วยโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรังบทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยกึ่งทดลองแบบกลุ่มเดียววัดซ้ำก่อนและหลังการทดลอง มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษาผลของโปรแกรมการปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมสุขภาพต่อปัจจัยเสี่ยงกลุ่มเมตาบอลิกในผู้ป่วยโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง ซึ่งมารับบริการที่โรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบลแห่งหนึ่งในภาคใต้ ประชากร คือ ผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวาน โรคความดันโลหิตสูง หรือทั้ง 2 โรค ที่มารับบริการในคลินิกโรคเรื้อรัง จำนวน 46 คน กลุ่มตัวอย่างจากทั้งหมดที่สมัครใจเข้าร่วมโครงการ ดำเนินการทดลองโดยจัดกิจกรรมจำนวน 3 ครั้ง ห่างกันครั้งละ 1 เดือน ดำเนินการวัดซ้ำ โดยอาสาสมัครสาธารณสุขประจำหมู่บ้าน (อสม.) เป็นเวลา 6 เดือน เครื่องมือใช้ในการเก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล คือ แบบสัมภาษณ์ ที่ผ่านการทดสอบความตรงเชิงเนื้อหา ค่าความเที่ยงของแบบสอบถามความรู้ เท่ากับ 0.72 และค่าความเชื่อมั่นแบบสัมภาษณ์ เท่ากับ 0.797 เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูลระหว่างเดือน มีนาคม พ.ศ. 2562 ถึงเดือนกันยายน พ.ศ. 2562 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติเชิงพรรณนา ค่าความถี่ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย และส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน สถิติวิเคราะห์ ใช้ Paired t-test และ Wilcoxon Signs test
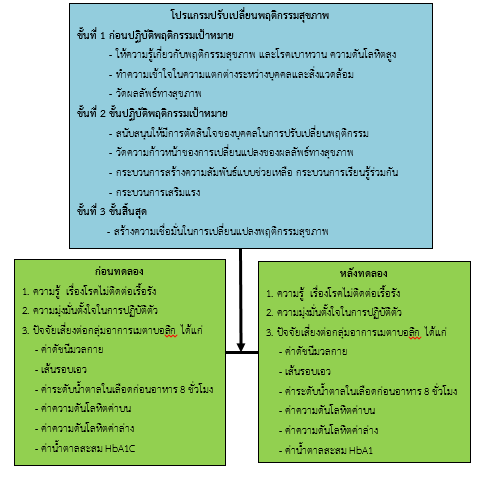
ผลการวิจัยพบว่า ความรู้เรื่องโรคไม่ติดต่อเรื้อรัง และความมุ่งมั่นตั้งใจในการปฏิบัติตัวหลังโมเดลทดลอง เพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.001 ส่วนการปฏิบัติตัวในการควบคุมป้องกันโรคหลังทดลองมีค่าเฉลี่ยเพิ่มขึ้นเล็กน้อยแต่ไม่มีนัยสำคัญ ปัจจัยเสี่ยงต่อกลุ่มอาการเมตาบอลิกก่อนและหลังการทดลอง พบว่า ค่าดัชนีมวลกาย ระดับความดันโลหิตค่าบน ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด รอบเอว และระดับน้ำตาลสะสมในเลือด ลดลงอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ ที่ระดับ 0.01 (p < 0.01) และพบว่า ค่าดัชนีมวลกายลดลง ร้อยละ 60.87 ระดับความดันโลหิตค่าบนลดลง ร้อยละ 84.79 ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดลดลง ร้อยละ 80.44 รอบเอวลดลง ร้อยละ 72.73 ในเพศชาย ร้อยละ 68.57 ในเพศหญิง และระดับน้ำตาลสะสมในเลือดลดลง ร้อยละ 80.44
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Banklang, A. Duangpunmat, U. & Rodseeda, P. (2016). Factors affecting to health behavior among type 2 diabetes patients, in area of Sila health promoting hospital, Muang District, Khon Kaen province. Journal of the Office of DPC 7 Khon Kaen, 23(1), 85-94.
Boonyasopun, U., Perngmark, P. & Thongtamlung, J. (2011). Perceived susceptibility to hypertension and preventive behaviors among transitional aged women in Thachang district, Suratthani province. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 3(1), 47-60.
Bureau of Non Communicable Disease. (2018). Report of the office of NCDs, year 2018. Nonthaburi: Aksorn Grphic and Design Publishing Limited Partnership. (in Thai)
Dheengarm, B., Tiautchasuwan, Y., & Boromtanarat, C. (2012). Factors affecting the practice in prevention of diabetes and hypertension of population at risk group in the responsible area of Ban Phon Muang health center, Chumphonburi district, Surin province. Research and Development Health System Journal, 5(3), 127-134.
Jangwang, S. (2014). Factors related to self-care behavior in the prevention of diabetes and hypertension among at risk group In Sadao district, Songkhla province. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master of public health program in community health of graduate school, Songkhla Rajabhat University, (in Thai)
Jugsingto, C., (2017). Effectiveness of health behavior modification program In high risk group for diabetes hypertention and obesity. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master of public health program in health management, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University. (in Thai)
Klinwichit, W., Piriyapun, P. & Inchai, P. (2003). Health status, health perception, health promotion behavior and social support of pre-diabetic and metabolic syndrome in students: Burapha University. Journal of Nursing and Education, 3(2), 86-89.
Mattayakorn, K. (2016). The development of the transtheoretical model on exercise behavior of working people. A dissertation is an integral part of the study of the doctor of philosophy program, exercise and sport science; Burapha University. (in Thai)
Panidchakul, K. & Samranbua, A. (2013). An application of transtheoretical model to promote exercise. The Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhonratchasima, 19(1), 66-75.
Srisaluk, J. (2014). Trends for non-communicable diseases research NCD. Retrieved November 10, 2019 from https://www.hsri.or.th/ researcher/research/trend/detail/4999. (in Thai)
Thianthawon, W. (2019). Diabetes: silent disaster every 8 seconds, 1 person dies. Retrieved November 10, 2019 from https://www.matichon.co.th/columnists/news_1747055. (in Thai)
Vijitsoonthornkul, K. & Chasombut, S. (2015). A study of the situation of premature death in Thailand. Retrieved January 12, 2020 from https://www.thaincd.com/2016/mission3. (in Thai)
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2021 วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว





