The Effectiveness of a Health Behavior Modification Program on Risk Factor Reduction in Patients with Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases Attending at Tambon Health Promotion Hospital in the Southern Thailand
Keywords:
Health Behavior Modification Program, Risk factors, Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)Abstract
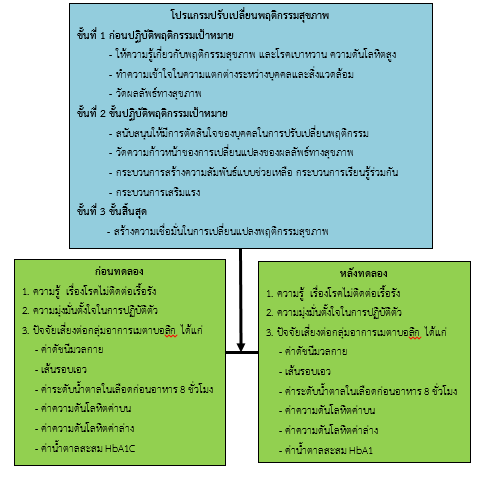
This quasi-experimental research (one-group pretest-posttest design) aimed to study the effects of a health behavior modification program on risk factors reduction in patients with chronic NCDs who attended at a Tambon Health Promoting Hospital in Southern Thailand. The program was created based on Transtheoretical Model (TTM). Sample was 46 patients with diabetes or hypertension or both diseases who attended at Khao-Huachang Health Promotion Hospital of Khanom district in Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, and voluntarily participated in the program. The experiment was carried out by organizing 3 activities in 3 months. The program’s follow-up was performed by village health volunteers (VHS) for 6 months. Research tools were an interview form, and a questionnaire. Content validity of those tools were validated by experts, obtaining values of 0.797, and 0.72, respectively. Data were collected between March and September, 2019, and then analyzed using descriptive statistics, paired t-test, and Wilcoxon Signs test.
Results showed that, after participating into the program: 1) the patients’ determination to change their behaviors were significantly higher than before participating (p < 0.001), 2) the disease control practice slightly increased, but not significantly, 3) risk factors including BMI, systolic BP, blood sugar, waist circumference, and HbA1C were significantly reduced (p<0.01), 3) the values for reduction of BMI, systolic BP, blood sugar, and HbA1C, were 60.87 %, 84.79%, 80.44%, and 80.44%, respectively, while waist circumference reduction was 72.73% in male, and 68.57% in female.
References
Banklang, A. Duangpunmat, U. & Rodseeda, P. (2016). Factors affecting to health behavior among type 2 diabetes patients, in area of Sila health promoting hospital, Muang District, Khon Kaen province. Journal of the Office of DPC 7 Khon Kaen, 23(1), 85-94.
Boonyasopun, U., Perngmark, P. & Thongtamlung, J. (2011). Perceived susceptibility to hypertension and preventive behaviors among transitional aged women in Thachang district, Suratthani province. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 3(1), 47-60.
Bureau of Non Communicable Disease. (2018). Report of the office of NCDs, year 2018. Nonthaburi: Aksorn Grphic and Design Publishing Limited Partnership. (in Thai)
Dheengarm, B., Tiautchasuwan, Y., & Boromtanarat, C. (2012). Factors affecting the practice in prevention of diabetes and hypertension of population at risk group in the responsible area of Ban Phon Muang health center, Chumphonburi district, Surin province. Research and Development Health System Journal, 5(3), 127-134.
Jangwang, S. (2014). Factors related to self-care behavior in the prevention of diabetes and hypertension among at risk group In Sadao district, Songkhla province. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master of public health program in community health of graduate school, Songkhla Rajabhat University, (in Thai)
Jugsingto, C., (2017). Effectiveness of health behavior modification program In high risk group for diabetes hypertention and obesity. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master of public health program in health management, Rajabhat Rajanagarindra University. (in Thai)
Klinwichit, W., Piriyapun, P. & Inchai, P. (2003). Health status, health perception, health promotion behavior and social support of pre-diabetic and metabolic syndrome in students: Burapha University. Journal of Nursing and Education, 3(2), 86-89.
Mattayakorn, K. (2016). The development of the transtheoretical model on exercise behavior of working people. A dissertation is an integral part of the study of the doctor of philosophy program, exercise and sport science; Burapha University. (in Thai)
Panidchakul, K. & Samranbua, A. (2013). An application of transtheoretical model to promote exercise. The Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhonratchasima, 19(1), 66-75.
Srisaluk, J. (2014). Trends for non-communicable diseases research NCD. Retrieved November 10, 2019 from https://www.hsri.or.th/ researcher/research/trend/detail/4999. (in Thai)
Thianthawon, W. (2019). Diabetes: silent disaster every 8 seconds, 1 person dies. Retrieved November 10, 2019 from https://www.matichon.co.th/columnists/news_1747055. (in Thai)
Vijitsoonthornkul, K. & Chasombut, S. (2015). A study of the situation of premature death in Thailand. Retrieved January 12, 2020 from https://www.thaincd.com/2016/mission3. (in Thai)
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




