ผลการพัฒนาการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรังระยะ 1 - 4 โรงพยาบาลพรหมคีรี
บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยกึ่งทดลอง แบบหนึ่งกลุ่มวัดผลก่อนและหลังการทดลองนี้ มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อศึกษา 1) ความรู้เรื่องยา เรื่องโรคไตเรื้อรัง และความร่วมมือในการใช้ยา ก่อนและหลังการให้การบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรม 2) ผลการพัฒนาการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรม ในการค้นหาปัญหาจากการใช้ยาและการแก้ไขปัญหาจากการใช้ยาในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 1 - 4 ที่มารับการรักษาที่โรงพยาบาลพรหมคีรี ประชากรที่ศึกษา คือ ผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวาน และ/หรือโรคความดันโลหิตสูงที่มารับบริการในโรงพยาบาล และมีภาวะเป็นโรคไตเรื้อรังระยะที่ 1 - 4 ในรอบปี พ.ศ. 2565 จำนวน 162 คน เลือกกลุ่มตัวอย่างโดยการสุ่มอย่างง่าย จำนวน 60 คน เครื่องมือในการทดลอง คือ การบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรม วัดผลก่อนการทดลองและติดตามผลหลังการทดลอง 1 - 2 เดือน เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล โดยใช้แบบสอบถามระหว่างเดือนพฤศจิกายน - ธันวาคม พ.ศ. 2565 วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทั่วไปโดยใช้สถิติ
ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย และส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และเปรียบเทียบผลก่อนและหลังการทดลองโดยใช้การทดสอบ
ค่าทีแบบจับคู่ (Paired t-Test)
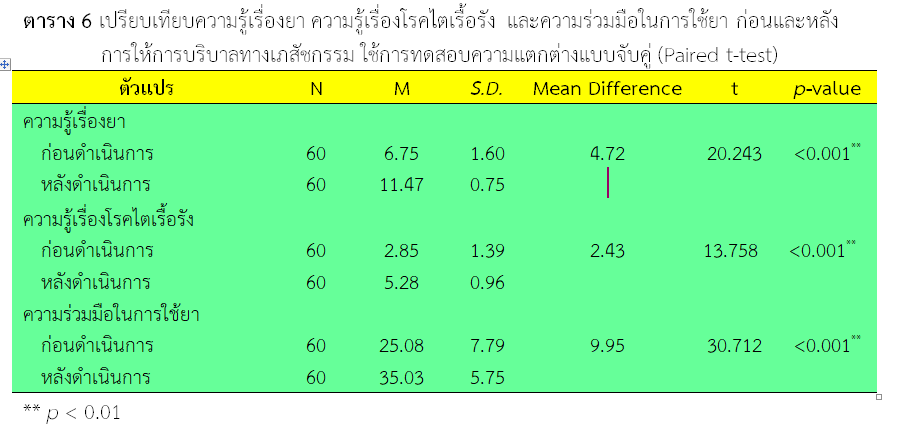
ผลการวิจัย พบว่า ก่อนการทดลองความรู้เรื่องการใช้ยาอยู่ในระดับต่ำ (ร้อยละ 76.66) หลังการทดลอง อยู่ในระดับสูง (ร้อยละ 98.33) ความรู้เรื่องโรคไตเรื้อรังก่อนการทดลองอยู่ในระดับต่ำ (ร้อยละ 68.33) หลังการทดลองอยู่ในระดับสูง (ร้อยละ 78.33) และความร่วมมือในการใช้ยาก่อนการทดลองอยู่ในระดับไม่ดี (ร้อยละ 83.33) หลังการทดลองอยู่ในระดับดี (ร้อยละ 71.67) เมื่อเปรียบเทียบระหว่างก่อนและหลังการทดลอง ความรู้เรื่องการใช้ยา ความรู้เรื่องโรคไตเรื้อรัง และความร่วมมือในการใช้ยาเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ ส่วนผลลัพธ์การบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรม พบว่า การสั่งใช้ยา ACEIs/ARBs หลังการดำเนินการมีสัดส่วนเพิ่มขึ้นอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p < 0.05)
ดังนั้น จึงควรพัฒนาการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมในผู้ป่วยไตเรื้อรังระยะ 1- 4 ให้มีความเหมาะสมกับบริบทของโรงพยาบาลมากขึ้น โดยการนำระบบสารสนเทศทางคอมพิวเตอร์ช่วยในการบันทึกและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลของผู้ป่วย
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Bhumirajanakarindra Kidney Institute Hospital. (2014). Knowledge of kidney disease for the people. (2nd ed). Bangkok; Health Works Company Lomited.
Cazarim MDS, F.O.(2016). Impact assessment of pharmaceutical care in the management of hypertension and coronary risk factors after discharge. PLoSONE, 10(1371), 1-14.
Cipolle, R. J., Strand, L. M., & Morley, P. C. (1998). Pharmaceutical care practice. St. Louis (MO): McGrawHill. Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power-analysis for the behavioral sciences. New York: Department of Psychology New York University.
Jongwilaikasem, K. & Lerkiatbundit, S. (2021). Development of the medication adherence scale for Thais (MAST). Thai Journal of Pharmacy Practice, 13(1), 17-30.
Kaewchana, S. & Anusornsangiam, W. (2020). Development of care model for patients with chronic kidney disease by multidisciplinary providers at Nang Rong hospital. Thai Journal of Pharmacy Practice, 12(4), 195-206.
Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcome. (2022). Clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Retrieved September 1, 2021 from https://www.kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/KDIGO-2022-Diabetes-Management- GL_Public-Review-draft_1Mar2022.pdf
Kitpaiboontawee, S. (2017). Pharmaceutical care in general medical ward at middle-level Hospital. Region 11 Medical Journal, 31(3), 369-383.
Khanadnid, W. (2020). Monitoring of adverse drug reactions in patients receiving 2 types of RAS Blockage (ACEI/ARB) in the treatment of hypertension. Buddhachinaraj Medical Journal, 37(3), 319-326.
Khumsiri, N. & Tantivichitvej, R. (2021). Factors associated with prescriptions for angiotensin- converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers and the effect on slowing kidney function decline in chronic kidney disease patients in Photharam hospital. Region 4-5 Medical Journal, 40(4), 473-485.
Monane, M., Bohn, R. L., Gurwitz, J. H., Glynn, R. J., Levin, L., & Avorn, J. (1997). The effects of initial drug choice and comorbidity on antihypertensive therapy compliance. Results from a population-based study in the elderly. American Journal of Hypertension, 15(10), 697-704.
Mongkolchaipak, T., Pichayapaiboon, S., & Sangviroon, A. (2015). Factors affecting medication adherence of diabetic patients at Police General hospital. Thai Journal of Pharmacy Practice, 7(1), 48-59.
Nuanchuay, P. (2012). Effect of pharmaceutical care on the control of risk factors for progression of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease at Thasala hospital. A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of master of pharmaceutical science in clinical pharmacy, Prince of Songkla University. (in Thai)
Pattanamongkol, O., Chantaracha, D., Chalongsuk, R., Pongchaidecha, M., Rungprai, D., & Muongmee, S. (2018). The cost-effectiveness of pharmaceutical care to slow Progression of the kidney in chronic kidney disease with diabetes patients at Leam Chabang Hostipal, Chonburi province. Thai Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 13(1), 53-67.
Penlap, N. & Rungnirundorn, T. (2016). Stress and associated factors among caregivers of chronic kidney disease patients at Department of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial hospital. Chulalongkorn Medical Journal, 60(4), 425-438
Phromkamdang, K. & Sirilak, T. (2023). Effects of pharmaceutical care on clinical outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease in Wiang Haeng hospital, Chiang Mai province. Journal of Nursing and Public Health Research, 3(1), 1-19.
Phulmueangrat, A., Rungrueangkri, N., Yongwanit, K., & Poiphan, N. (2017). The cost of providing patients with chronic kidney disease using Time Driven Activity-based Costing (TDABC) for hemodial unit Buddhasothorn hospital Chachoengsao province. Ph.D. in Social Science Journal, 7(1), 164-176.
Praying, C., Putha, K., & Klomkaew, W. (2020). Development of a model for prevention and resolution of chronic kidney disease in Banthi district, Lamphun province, Thailand. Journal of Health Science, 29(6), 1035-1043.
Tungsawang, W. (2021). The antimicrobial dosage adjustment for inpatient with renal impairment in Maharaj Nakhon Si Thammarat hospital. Maharaj Nakhon Si Thammarat Hospital Medical Journal, 4(2), 1-8.
Unaphak, P. & Rattanamanee, K. (2015). The correlation factors of self-care behaviors to prevent complications among patients with chronic kidney disease at Somdetphraphutthalertla hospital in Samutsongkhram province. The Public Health Journal of Burapha University, 10(2), 44–54.
Yodklaew, N. & Suggaravetsiri, P. (2019). Prevalence and factors associated with chronic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes millitus in the community medical unit Khon Kaen province. Journal of the Office of DLC 7 Khon Kaen, 26(2), 24–35.22-
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว





