Using Fiscal Efficiency to Avoid Financial Crisis in Nakhon Si Thammarat Public Hospitals
Keywords:
Public Hospital Financial Efficiency, Financial management, Financial CrisisAbstract
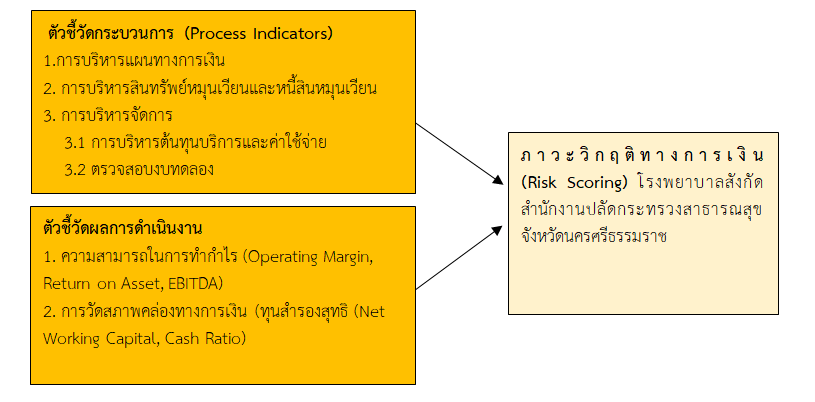
This retrospective research aimed to study the fiscal efficiency against financial crisis in hospitals under the Ministry of Public Health in Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, and the relationships between financial performance and financial crisis. Study focused on data from the fiscal years of 2019 – 2021, inclusively. A total of 19 hospitals were included. The financial data were collected from the reports of the Division of Economics and Health Security, as well as from the Ministry of Public Health. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and Chi-square.
Using a 3-year average score between the fiscal year 2019 - 2021, the results showed that 14 hospitals had a financial crisis score in the range of 0.00 - 3.99 points, representing 73.68%. There were five hospitals with a financial crisis score in the range of 4.00 – 6.00 points, which was expected to encounter problems, representing 26.32%. The financial efficiency in terms of profit making ability was statistically and significantly correlated with financial crisis (p-value = < 0.05).
These findings must be seen keeping in mind there was a global Covid-19 pandemic. They also can be used to weight individual indicators of different aspects of financial performance for assessing overall financial performance that may result in a financial crisis and monitoring and adjusting financial performance in the short and long term as well as able to provide quality service.
References
Boonyamalik, P. & Maneewat, T. (2021). Trends in financial management of the hospital under the office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Public Health: a qualitative study. Journal of Health Systems Research, 15(4), 477-89.
Division of Health Economics and Health Security. (2019). Financial status. Retrieved January 15, 2023 from https://www.healthkpi.moph.go.th/kpi2/kpi/index2/?kpi_year=2561. (in Thai)
Jungpanich, V. (2018). Factors affecting finance administration efficiency of the hospital. Hua Hin Sook Jai Klai Kangwon Journal, 3(1), 97-111.
Krejcie, R. V. & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607-610.
National Health Security. (2019). Annual report 2019. Retrieved January 15, 2023 from https://www.nhso.go.th. (in Thai)
Paek, S. C., Meemon, N., & Wan, T. T. W. (2016). Thailand’s universal coverage scheme and its impact on health-seeking behavior. Springer Plus (2016), 5:1952. https://doi:10.1186/s40064-016-3665-4.
Phettun, P. (2019). Analysis of financial management efficiency of Tha Rong Chang hospital, Surat Thani province, fiscal year 2014 - 2018. Journal of Health Research and Innovation, 2(4), 77-90.
Pramualratana, P. & Wibulpolprasert, S. (2002). Health insurance systems in Thailand. Health Systems Research Institute (HSRI). Nonthaburi. (in Thai)
Salangsingha, S. & Manasathitpong, N. (2021). The efficiency financial management of community hospital in Mukdahan province. Research and development health system Journal, 14(2), 151-161.
Tunkam, P. & Chandee, J. (2020). Assessment and recommendations for financial and fiscal management in hospitals who have experienced a severe financial crisis level 7 in Health Region 1. Retrieved January 15, 2023 from https://wwwnno.moph.go.th/nanhealth/index.php/news/int-news/item/4320-research- jintana2021.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




