Factors Related to Self-Care Behaviors of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending the Diabetes Clinic at Khlong Thom Hospital, Krabi Province
Keywords:
Attitudes, Self-Care Behaviors, Type 2 Diabetes MellitusAbstract
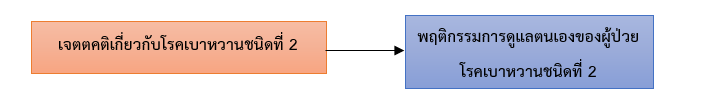
This cross-sectional study aimed to 1) examine the levels of attitudes and self-care behaviors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and 2) identify the factors associated with self-care behaviors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending the diabetes clinic at Khlong Thom Hospital, Krabi Province. The sample consisted of 275 participants. Data were collected using a questionnaire, which was validated by three experts, yielding a content validity index ranging from 0.67 to 1.00. The reliability coefficients were 0.77 and 0.78, respectively. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and Pearson’s correlation coefficient, with the level of statistical significance set at 0.05.
The study found that overall attitudes toward type 2 diabetes mellitus were at a good level (M = 4.29, SD = 0.54). Similarly, overall self-care behaviors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were at a good level (M = 4.68, SD = 0.59). Attitudes toward type 2 diabetes mellitus were positively correlated with self-care behaviors (r = 0.519) among patients attending the diabetes clinic at Khlong Thom Hospital, Krabi Province, with statistical significance at the 0.01 level.
Therefore, it is essential to promote positive attitudes and awareness of self-care among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus through activities that enhance self-confidence, such as education on nutrition, exercise, medication adherence, foot care, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Emphasis should be placed on continuity and the active participation of both patients and their families in order to foster sustainable self-care behaviors, reduce complications, and improve quality of life.
References
Best, J. W. (1977). Research in education (3rd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Bloom, B. S. (1976). Human characteristics and school learning. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Chaengsaeng, P. (2022). Factors associated with blood glucose control behaviors among diabetes patients in the Nong Khayang district network, Uthai Thani province. Singburi Hospital Journal, 31(2), 68–80.
Davies, I. K. (1971). The management of learning. London: McGraw-Hill.
Duangpratoom, N., & Rattanakanahutanon, F. (2019). Factors associated with self-care behaviors of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Huai Khamin Health Promoting Hospital, Dan Chang, Suphan Buri Province. Valaya Alongkorn Review Journal, 9(2), 53–67.
Health Data Center. (2024). Annual health data report 2024. Retrieved January 5, 2025 from https://hdc.moph.go.th/center/public/main/
Magliano, D. J. & Boyko, E. J. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas (10th ed.). Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation. Retrieved January 5, 2025 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK581934/
Ministry of Public Health. (2024). Annual report 2024. Nonthaburi, Thailand: Ministry of Public Health. (in Thai)
National Health Security Office. (2023). Universal health coverage in Thailand. Retrieved January 10, 2025 from https://www.nhso.go.th/.
Orem, D. E. (2001). Nursing: Concepts of practice (6th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby.
Khlong Thom Hospital. (2024). Medical records [Unpublished internal document]. Khlong Thom, Krabi Province. (in Thai)
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607–610.
Watthanachot, S. (2010). Knowledge, attitude, and practices in disease control among diabetes patients at Ban Rai Hospital, Uthai Thani Province. Mahasarakham Hospital Journal, 7(2), 69–77.
Sasiwimonluk, K., Surat, S., Khruachak, K., & Mongkolthep, W. (2016). The relative factors of self- care behaviors of diabetes mellitus patients in Mae Chan District, Chiang Rai Province. Journal of Community Development and Quality of Life, 4(2), 297–307.
Sukwatsana, Y., Sikhaw, O., & Kasipol, T. (2021). Relationship between personal factors, health literacy, self-care behaviors, and blood glucose control among type 2 diabetes patients. Rajawadee Journal of Boromarajonani College of Nursing Surin, 11(1), 52–65.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




