Health Literacy and Fall Prevention Behavior Among Elderly People in the Community Mueang District, Surat Thani Province
Keywords:
Health Literacy, Fall Prevention Behaviors, ElderlyAbstract
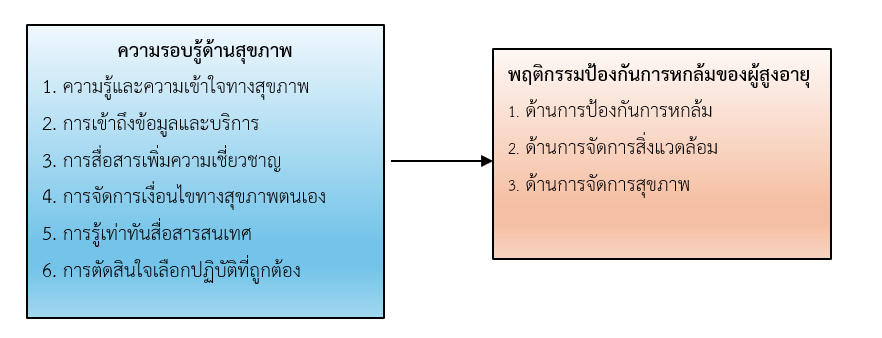
This descriptive research aimed to examine: 1) health literacy regarding fall prevention, 2) fall prevention behaviors, and 3) the relationship between health literacy and fall prevention behaviors among elderly individuals in the community of Mueang District, Surat Thani Province. The sample consisted of 365 elderly participants. The research instruments included: 1) a health literacy questionnaire and 2) a fall prevention behavior questionnaire, with content validity indices of 0.80 and 0.82, and reliability coefficients of 0.86 and 0.80, respectively. Data analysis employed descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation analysis.
The findings revealed that elderly participants demonstrated high levels across all dimensions: knowledge and understanding of fall prevention (M=4.27, SD=0.70), access to fall prevention information and services (M=4.07, SD=0.77), communication regarding fall prevention (M=4.17, SD=0.77), self-management of health conditions (M=4.20, SD=0.73), media literacy for fall prevention (M=4.20, SD=0.70), decision-making for fall prevention (M=4.15, SD=0.69), and fall prevention behaviors (M=4.35, SD=0.68). Health literacy in fall prevention demonstrated significant positive correlations with fall prevention behaviors at the 0.01 level across all dimensions. Communication for enhancing expertise showed a moderate correlation (r=0.494), while self-management of health conditions (r=0.445), media literacy (r=0.426), knowledge and understanding of health (r=0.389), and decision-making for appropriate practices (r=0.386) all exhibited moderate correlations. Access to information and services demonstrated a low correlation (r=0.285).
Healthcare organizations should develop comprehensive health literacy enhancement programs for elderly individuals, focusing on improving understanding, health information seeking skills, and providing specific guidance tailored to each individual’s life context to facilitate behavioral changes in fall prevention. Additionally, programs should be established to develop health-related decision-making skills that are appropriate for elderly individuals and can be effectively implemented in their daily lives.
References
Chatchaisucha, S., & Ananpatiwet, S. (2023). Health literacy in elderly: Guidelines for health promotion in the 21st century. Journal of the Police Nurses, 15(1), 135–142.
Department of Older Persons. (2023). Situation of the Thai older persons 2023. Department of Older Persons. Retrieved 2025, January 9 from https://www.dop.go.th/th/know/side/1/1/2449. (in Thai)
Department of Older Persons. (2023). General information for the elderly. Retrieved 2025, January 9 from https://www.dop.go.th/th/statistics_page?cat=1&id=1. (in Thai)
Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health. (2024). [FP] Fall data (W00–W19). Retrieved 2025, January 9 from https://ddc.moph.go.th/dip/news.php?news=23567&deptcode. (in Thai)
Davis, J. A. (1971). Elementary survey analysis. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Foundation of Thai Gerontology Research and Development Institute (TGRI). (2023). Situation of the Thai older persons 2022. Bangkok: Amarin Corporations Public Company Limited. (in Thai)
Hongchuvech, Y. (2024). Reducing the risk factors of falls in the elderly. EAU Heritage Journal of Science and Technology, 18(1), 32–43.
Intarakamhaeng, U. (2017). Creating and developing of Thailand Health Literacy Scales. (Research report). Bangkok: The Behavioral Science Research Institute, Srinakharinwirot University. (in Thai)
Kittipimpanon, K., & Kraithaworn, P. (2021). Association between personal factors, health status, and health literacy about falling, with fall prevention behaviors among older adults living in the community. Ramathibodi Nursing Journal, 27(3), 331–342.
Kaeodumkoeng, K. (2018). Health literacy: access, understanding, and application. 2nded. Bangkok: Amarin Printing and Publishing Public. (in Thai).
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607–610.
Krearprasert, R., Kengganpanich, M., & Pekale, A. (2023). The predictive factors associated with fall prevention behavior of elderly people in Bang Khen Subdistrict Health Promoting Hospital Area, Nonthaburi province. Thai Journal of Health Education, 46(1), 94–106.
Liu, F., Yu, H., Xu, Q., Gong, J., Huo, M., & Huang, F. (2024). Risk Assessment of Falls Among Older Adults Based on Probe Reaction Time During Water-Carrying Walking. Clinical interventions in aging, 19, 21–29.
Luehan, S., Narin, R., & Sripetwandee, N. (2024). Effect of a health literacy for fall prevention enhancing program on practices of recurrent fall prevention among the elderly in communities. Nursing Journal CMU, 51(2), 150–164.
Mark, J. A., Henry, A., Moreland, B., Dobash, D., & Bergen, G. (2025). Assessing older adults’ readiness for adopting fall prevention recommendations using the Transtheoretical Stages of Change. Journal of Applied Gerontology, 44(5), 726–736.
Nutbeam, D. (2000). Health literacy as a public health goal: A challenge for contemporary health education and communication strategies into the 21st century. Health Promotion International, 15(3), 259–267.
Nutbeam, D. (2008). The evolving concept of health literacy. Social Science & Medicine, 67(12), 2072-8.
Pensuk, P., Valaisathien, J., & Thangtham, N. (2025). The effects of enhancing health literacy program on falls prevention behaviors among village health volunteer in a community, Nakhon Ratchasima province. Journal of the Office of Disease Prevention and Control 9 Nakhon Ratchasima, 31(2), 5–17.
Poomriew, R. (2022). Fall prevention in Thai older adults. Thai Journal of Health Education, 45(2), 1–10.
Sawangbumrung, M., Chaiarporn, N., & Vongverapant, M. (2024). Literature synthesis on falls of the elderly in the year 2013–2022. Regional Health Promotion Center 9 Journal, 18(3), 918–934.
Saengkeaw, S., & Chansong, S. (2024). Scale development of digital health literacy for the elderly. Journal of Business, Innovation and Sustainability (JBIS), 19(3), 136–150.
Sarapun, A., Sirisopon, N., Kainaka, P., Onsiri, S., Outayanik, B., Threrawachjareanchai, S., & Sukomol, N. (2017). Factors Ralated to a Fall Prevention Behaviors of Elderly. Journal of The Royal Thai Army Nurses, 18(Suppl. 1), 215–222.
Saenwa, S., Wattanaburanon, A., & Maharachpong, N. (2022). Effect of fall prevention program based on health belief model and social support on fall prevention behaviors among the elderly in Kochan district Chonburi. Province Research and Development Health System Journal, 15(2), 214–227.
Srisa-ard, B. (2017). Preliminary research. (10th ed.). Bangkok: Suweeriya Sarn. Stormacq, C., Wosinski, J., Boillat, E., & Van den Broucke, S. (2020). Effects of health literacy interventions on health-related outcomes in socioeconomically disadvantaged adults living in the community: A systematic review. JBI Evidence Synthesis, 18(7), 1389–1469.
Tasuwanin, T. (2016). Falls in the elderly. UBRU Journal for Public Health Research, 5(2), 119–131.
Tiparat, W., Rodniam, J., & Suwanweala, P. (2022). The effects of an enhancing health literacy program with family participation on health literacy of caregivers, fall prevention behaviours, and balance of older adults at risk for fall. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 14(3), 72–91.
Wungrath, J., & Mongkol, P. (2020). Effectiveness of a health literacy enhancement program for caregivers of dependent older persons in a community of the Northern Part, Thailand. Journal of Public Health and Development, 18(2), 24–36.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). Thailand’s leadership and innovations towards healthy ageing. Retrieved 2025, January 9 from https://www.who.int/southeastasia/news/feature-stories/detail/thailands-leadership-and-innovation-towards-healthy-ageing
Wisetkaew, S., & Suwan, P. (2024). The causal relationship model of factors influencing fall prevention behaviors of the elderly in Lopburi Province. Journal of Medical and Public Health Region 4, 14(2), 1–12.
Zolbin, M. G., Huvila, I., & Nikou, S. (2022). Health literacy, health literacy interventions and decision-making: A systematic literature review. Journal of Documentation, 78(7), 405–428.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Nakhon Si Thammarat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของ วิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความแต่ละเรื่องในวารสารวิชาการเล่มนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี นครศรีธรรมราช และบุคคลากรท่านอื่น ๆ ในวิทยาลัยฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใดๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเองแต่ผู้เดียว




