ประสิทธิภาพของยาพ่นจมูกสูตรผสมระหว่าง azelastine hydrochloride และ fluticasone propionate ในการรักษาโรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้
คำสำคัญ:
โรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้, ยาพ่นจมูก, ยาสูตรผสม azelastine และ fluticasoneบทคัดย่อ
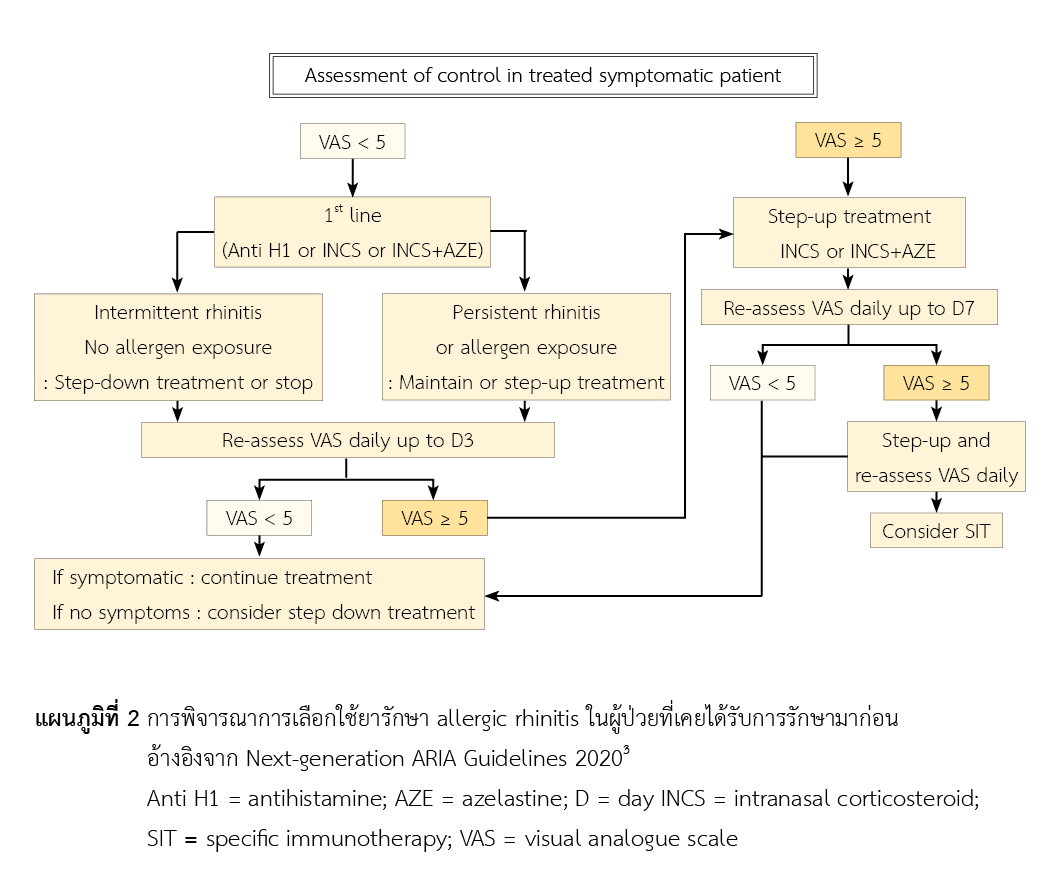
ยาสเตียรอยด์พ่นจมูกเป็นยาที่มีบทบาทในการรักษาโรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้โดยเฉพาะผู้ป่วยที่มีระดับความรุนแรงของอาการปานกลางถึงมาก ซึ่งเป็นแนวทางหลักในการเลือกใช้ยามาตั้งแต่แนวทางการรักษาฉบับก่อนที่ชื่อ Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) Guidelines 2016 แต่ในปี ค.ศ. 2020 ได้มีแนวทางการรักษาใหม่ของโรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้ และใช้ชื่อ Next-generation ARIA Guidelines 2020 โดยนำระยะเวลาเริ่มออกฤทธิ์เข้ามาเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของการพิจารณาการเลือกใช้ยา ทั้งนี้ แนวทางฉบับใหม่ได้มีการศึกษาระยะเวลาเริ่มออกฤทธิ์ของยาพ่นจมูกสูตรผสมระหว่างยาสเตียรอยด์ (intranasal corticosteroids, INCS) และยาต้านฮีสตามีน (intranasal antihistamine, INAH) เปรียบเทียบกับการใช้ยาเดี่ยว โดยในการศึกษา ทุกสูตรจะถูกพ่นจมูกทั้งสองข้าง ข้างละ 1-2 ที วันละ 2 ครั้ง และพบว่าการใช้ INCS ชนิด fluticasone propionate (FLU) ร่วมกับ INAH ชนิด azelastine hydrochloride (AZE) ในผู้ป่วยโรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้ระดับความรุนแรงอาการปานกลางถึงมาก มีระยะเวลาเริ่มออกฤทธิ์เร็วที่สุด (5 นาที) เปรียบเทียบกับ INCS และ INAH เมื่อใช้เป็นยาเดี่ยว หรือ INCS ชนิดอื่นร่วมกับ AZE และมีประสิทธิภาพในการบรรเทาอาการทางจมูกและตาได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติเมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับยาเดี่ยว INCS หรือ INAH นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถเพิ่มคุณภาพชีวิตของผู้ป่วยได้ด้วย อาการไม่พึงประสงค์ที่พบ ได้แก่ รับรู้รสขม ปวดศีรษะ เลือดกำเดาไหล โดยสรุป อาจพิจารณานำยาพ่นจมูกสูตรผสมระหว่าง AZE และ FLU มาใช้รักษาผู้ป่วยโรคจมูกอักเสบจากภูมิแพ้ระดับความรุนแรงอาการปานกลางถึงมากที่อายุมากกว่าหรือเท่ากับ 12 ปี ในกรณีที่ผู้ป่วยไม่สามารถบรรเทาอาการด้วยการใช้ INCS เพียงอย่างเดียว
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Sheikh J, Jean T. What is the global prevalence of allergic rhinitis (hay fever)? [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 Feb 9]. Available from: https://www.medscape.com/answers/134825-4371/what-is-the-global-prevalence-of-allergic-rhinitis-hay-fever.
Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, Enomoto T, Okamoto Y, Kawauchi H, et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020. Allergol Int. 2020;69(3):331-45.
Bousquet J, Schünemann HJ, Togias A, Bachert C, Erhola M, Hellings PW, et al. Next-generation allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines for allergic rhinitis based on grading of recommendations assessment, development and evaluation (GRADE) and real-world evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145(1):70-80.e3.
Klimek L, Bachert C, Pfaar O, Becker S, Bieber T, Brehler R, et al. ARIA guideline 2019: treatment of allergic rhinitis in the German health system. Allergol Select. 2019;3(1):22-50.
สมาคมแพทย์โรคจมูก (ไทย). แนวทางการพัฒนาการตรวจรักษาโรคจมูกอักเสบภูมิแพ้ในคนไทย (ฉบับปรับปรุง พ.ศ.2554). วารสารหู คอ จมูกและใบหน้า. 2554;2:1-80.
ปารยะ อาศนะเสน, ฉวีวรรณ บุนนาค. โรคจมูกอักเสบภูมิแพ้. วารสารการแพทย์แผนไทยและการแพทย์ทางเลือก. 2552;7(1):71-83.
Dykewicz MS, Wallace DV, Amrol DJ, Baroody FM, Bernstein JA, Craig TJ, et al. Rhinitis 2020: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;146(4):721-67.
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Agache L, Agarwa A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines—2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140(4):950-8.
Bousquet J, Reid J, van Weel C, Baena Cagnani C, Canonica GW, Demoly P, et al. Allergic rhinitis management pocket reference 2008. Allergy. 2008;63(8):990-6.
สงวนศักดิ์ ธนาวิรัตนานิจ. Current practice and gui–dance in allergic rhinitis management. Srinagarind Med J. 2011;26(Suppl):20-9.
Bernstein JA. Azelastine hydrochloride: a review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and tolerability. Curr Med Res Opin. 2007;23(10): 2441-52.
Kaulsay R, Nguyen DT, Kuhl HC. Real-life effectiveness of MP-AzeFlu in Irish patients with persistent allergic rhinitis, assessed by visual analogue scale and endoscopy. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2018;6:456-64.
Bousquet J, Meltzer EO, Couroux P, Koltun A, Kopietz F, Munzel U, et al. Onset of action of the fixed combination intranasal azelastine-fluticasone pro–pionate in an allergen exposure chamber. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6(5):1726-32.e6.
Hampel FC, Ratner PH, Bavel VJ, Amar NJ, Daftary P, Wheeler W, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of azelastine and fluticasone in a single nasal spray delivery device. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105(2):168-73.
Lalitha A, Mamatha KR, Puttamadaiah GM. Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray and its combination with fluticasone propionate in the management of allergic rhinitis - a comparative study. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol. 2019;9(5):356-60.
Ilyina NI, Edin AS, Astafieva NG, Lopatin AS, Sidorenko IV, Ukhanova OP, et al. Efficacy of a novel intranasal formulation of azelastine hydrochloride and fluticasone propionate, delivered in a single spray, for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis: results from Russia. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2019;178(3):255-63.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ




.png)

