ทาฟามิดิส: ยาชนิดใหม่ในกลุ่มที่ทำให้ transthyretin คงตัว สำหรับผู้ป่วยคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิสชนิดเอทีทีอาร์
คำสำคัญ:
โรคคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิส, โรคคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิสชนิดเอทีทีอาร์, โปรตีน transthyretin, ทาฟามิดิสบทคัดย่อ
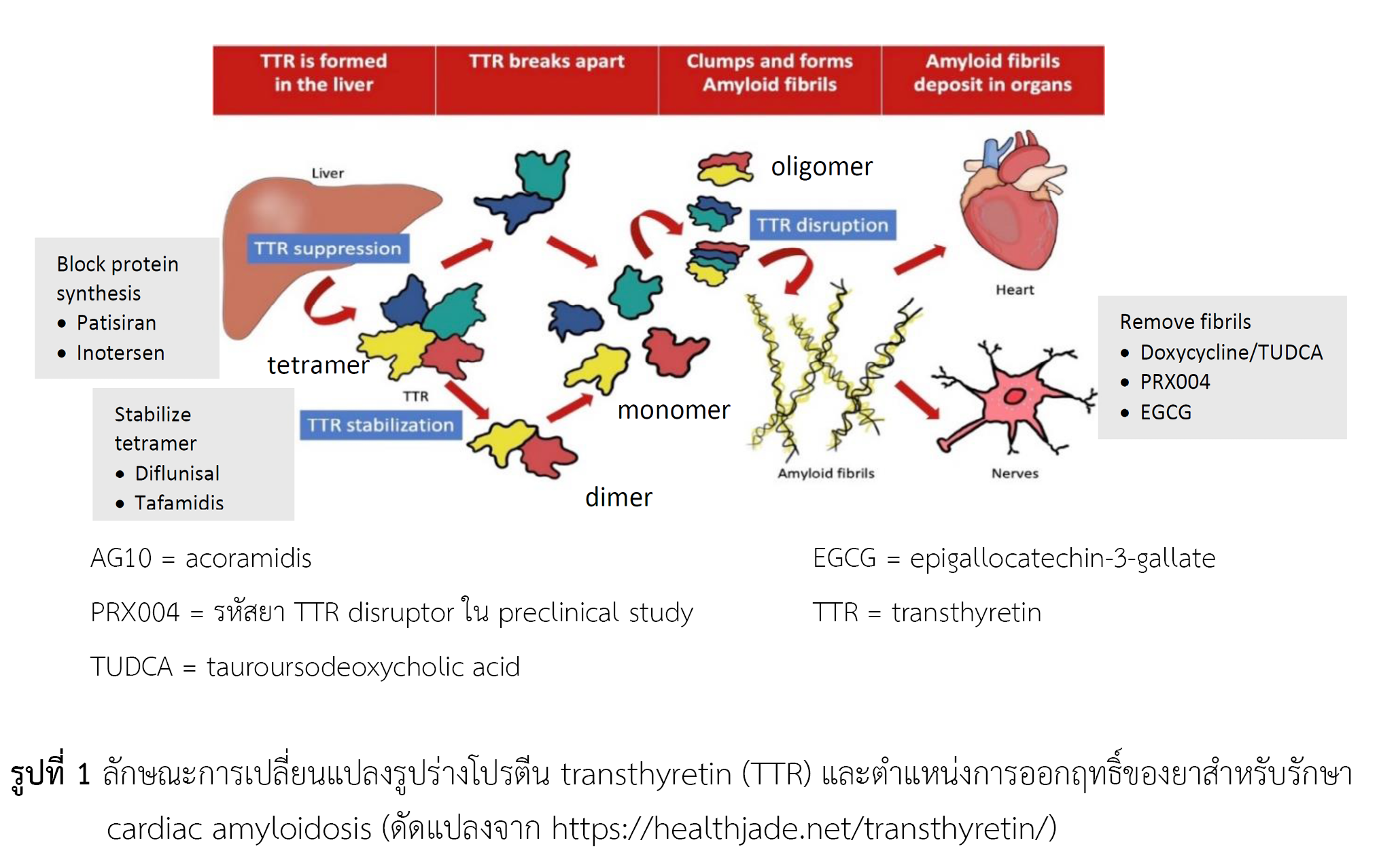
ในปัจจุบันแนวทางการรักษาโรคคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิส อาศัยการออกฤทธิ์ของยาตามลักษณะของการเกิดโรค โดยโรคคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิสชนิดเอทีทีอาร์ จะใช้ยาที่มีเป้าหมายต่อ transthyretin (TTR) เพื่อลดการสะสมของโปรตีนอะมัยลอยด์ โดยสามารถแบ่งกลุ่มของยาตามกลไกการออกฤทธิ์ได้เป็น 3 กลุ่ม ดังนี้ (1) TTR silencing (2) TTR stabilization และ (3) TTR disruption ทั้งนี้ ทาฟามิดิส คือยาใหม่ในกลุ่ม TTR stabilization เป็นยาที่ทำหน้าที่ป้องกันการเปลี่ยนแปลงรูปร่างของโปรตีนทำให้ไม่เกิดการสะสมของ amyloid fibril สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา อนุมัติการใช้ ทาฟามิดิส ในเดือนพฤษภาคม พ.ศ. 2565 ในข้อบ่งใช้เพื่อลดอัตราการเสียชีวิตและอัตราการเข้าโรงพยาบาลด้วยโรคคาดิแอคอะมัยลอยโดซิสชนิดเอทีทีอาร์ รวมถึงเพิ่มคุณภาพชีวิตให้แก่ผู้ป่วย ยานี้ถูกดูดซึมได้ดี จับกับโปรตีนในเลือดได้สูง และกำจัดออกทางอุจจาระในรูปที่ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลงเป็นหลัก อย่างไรก็ตาม ควรระมัดระวังการใช้ร่วมกับยาอื่นที่มีการเปลี่ยนสภาพยาผ่าน cytochromes P450 เนื่องจากทาฟามิดิสสามารถเหนี่ยวนำการทำหน้าที่ของ CYP2B6 และ CYP3A4 ได้ นอกจากนี้ ทาฟามิดิสยังสามารถยับยั้ง efflux transporter ที่มีชื่อว่า breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) ได้ จึงมีโอกาสเกิดปฏิกิริยากับยาอื่นที่เป็น substrate ของ BCRP
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Garcia-Pavia P, Rapezzi C, Adler Y, Arad M, Basso C, Brucato A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis: a position statement of the ESC working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(16):1554–68. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab072.
Sperry BW, Saeed IM, Raza S, Kennedy KF, Hanna M, Spertus JA. Increasing rate of hospital admissions in patients with amyloidosis (from the National Inpatient Sample). Am J Cardiol. 2019;124(11):1765-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.08.045.
Tan SY, Pepys MB, Hawkins PN. Treatment of amyloidosis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;26(2):267-85. doi: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90647-9.
Park GY, Jamerlan A, Shim KH, An SSA. Diagnostic and treatment approaches involving transthyretin in amyloidogenic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):2982. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122982.
Kittleson MM, Ruberg FL, Ambardekar AV, Brannagan TH, Cheng RK, Clarke JO, et al. 2023 ACC expert consensus decision pathway on comprehensive multidisciplinary care for the patient with cardiac amyloidosis: a report of the American college of cardiology solution set oversight committee. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(11):1076–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2022.11.022.
ศิริภา อันนานนท์, พรทิพย์ ประพันธ์พจน์. ความเป็นพิษของ transthyretin กลายพันธุ์ชนิด V30M และ L55P ที่มีต่อเซลล์มนุษย์. วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์บูรพา. 2564;26(1):1-18
Siddiqi OK, Ruberg FL. Cardiac amyloidosis: an update on pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2018;28(1):10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.07.004.
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145(18):e895–1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063.
Berk JL, Suhr OB, Obici L, Sekijima Y, Zeldenrust SR, Yamashita T, et al. Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;310(24):2658–67. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.283815.
Vedantham S, Goldhaber SZ, Julian JA, Kahn SR, Jaff MR, Cohen DJ, et al. Pharmacochemical catheter-directed thrombolysis for deep-vein thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(23):2240–52. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1615066.
Judge DP, Heitner SB, Falk RH, Maurer MS, Shah SJ, Witteles RM, et al. Transthyretin stabilization by AG10 in symptomatic transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74(3):285–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.012.
สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา. แสดงรายละเอียดผลิตภัณฑ์ยา VYNDAMAX ใน: ตรวจสอบผลิตภัณฑ์ [อินเทอร์เนต]. กรุงเทพฯ: สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา; 27 กรกฎาคม 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 20 ตุลาคม 2565]. สืบค้นจาก: http://pertento.fda.moph.go.th/FDA_SEARCH_DRUG/SEARCH_DRUG/pop-up_drug_ex.aspx?Newcode=U1DR1C1012651507211C
Pfizer Inc. Compassionate use programs: expanded access to investigational drugs [Internet]. n.p.: Pfizer Inc.; 2023 [cited 2023 May 22]. Available from: https://www.pfizer.com/science/clinical-trials/expanded-access
Coelho T, Merlini G, Bulawa CE, Fleming JA, Judge DP, Kelly JW, et al. Mechanism of action and clinical application of tafamidis in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Neurol Ther. 2016;5(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/s40120-016-0040-x.
Verma B, Patel P. Tafamidis. [Updated 2023 May 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2022 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574508/
Waddington Cruz M, Benson MD. A review of tafamidis for the treatment of transthyretin-related amyloidosis. Neurol Ther. 2015;4(2):61-79. doi: 10.1007/s40120-015-0031-3.
Maurer MS, Schwartz JH, Gundapaneni B, Elliott PM, Merlini G, Waddington-Cruz M, et al. Tafamidis treatment for patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379(11):1007-16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805689.
Klamerus KJ, Watsky E, Moller R, Wang R, Riley S. The effect of tafamidis on the QTc interval in heathy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79(6):918–25. Doi:10.1111/bcp.12561.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new treatments for heart disease caused by a serious rare disease, transthyretin mediated amyloidosis [Internet]. n.p.: U.S. Food and Drug Administration; 2019 [cited 2022 Oct 17]. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-treatments-heart-disease-caused-serious-rare-disease-transthyretin-mediated
VYNDAQEL® and VYNDAMAX® [Package insert]. Pfizer Labs; 2019.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล(ประเทศไทย)

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

