Del Nido Cardioplegia
Keywords:
del Nido cardioplegia, modified del Nido cardioplegia, lactated ringer’s solution, cardiac surgeryAbstract
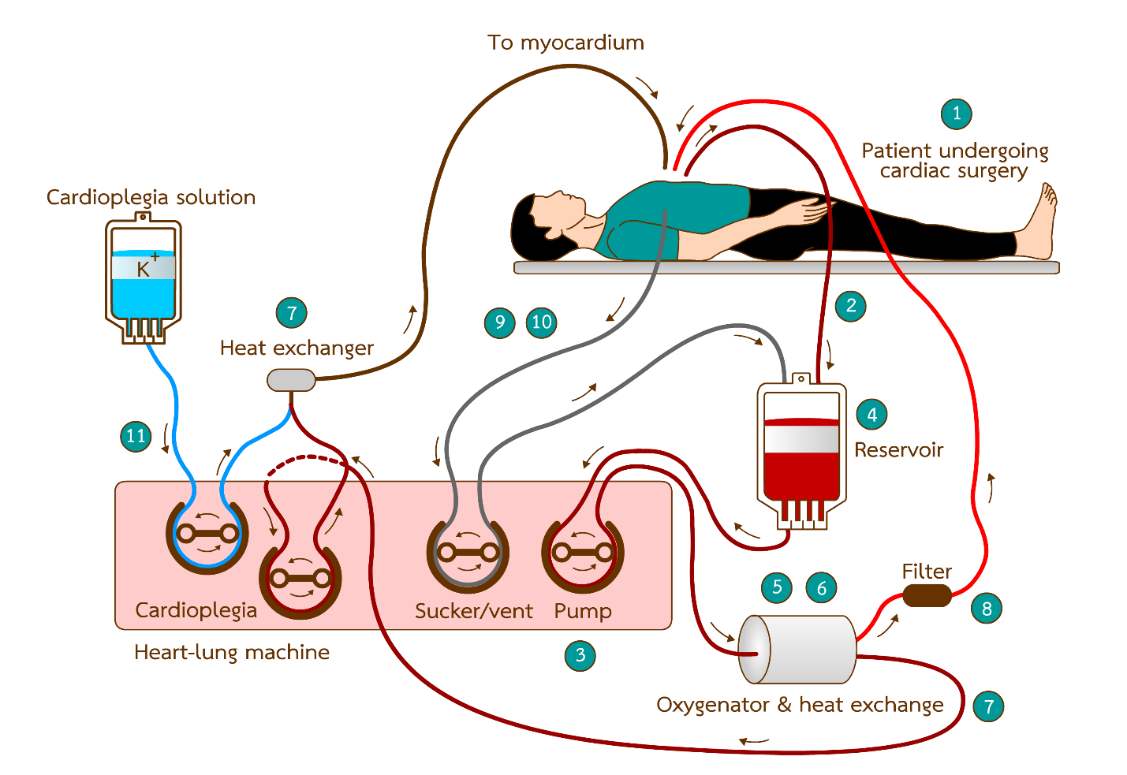
Cardiac surgery, one of the treatments for cardiovascular disease, is used to correct heart pathology. The surgery is divided into closed heart surgery and open heart surgery. The open heart surgery can be more coverage on correcting pathology and treating heart diseases, compared to the closed heart surgery. However, the open heart surgery involves the extracorporeal circuit through a heart-lung machine as a replacement of body heart and lung. In addition, a pharmaceutical solution known as cardioplegia is needed. This pharmaceutical solution mainly contains high concentration of potassium, aims to stop the heartbeat so that the surgeon can perform the surgery easier. Other components in cardioplegia are used to protect cardiac muscle during surgery, limit myocardial damage during cardiac arrest and lack of blood supply, return heart to normal function after the cardiac surgery, and reduce surgical complications. From past to present, the cardioplegia has been developed in many formulations with different components. The del Nido cardioplegia is one of them that has the advantage of stopping the heartbeat and protecting cardiac muscle throughout the duration of surgery and providing a good surgical outcome. Hospital pharmacists have role in compounding sterile solution such as del Nido cardioplegia that meets standard of practice. In Thailand, although some components in the original formulation are not available, but other substance can be substituted so that patients have opportunity to access medicines.
References
World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; updated 2017 May 17 [cited 2020 Sep 30]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
กองยุทธศาสตร์และแผนงาน สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข. สถิติสาธารณสุข พ.ศ. 2562 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. นนทบุรี: กระทรวงสาธารณสุข; กันยายน 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 มิถุนายน 2564]. สืบค้นจาก: https://bps.moph.go.th/ new_bps/sites/default/files/statistic62.pdf
Myles PS. Meaningful outcome measures in cardiac surgery. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2014;46(1):23-7.
แพรวพรรณ สุวรรณกิจ. เครื่องหัวใจและปอดเทียม: หลักการและการปฏิบัติ Heart-Lung Machine: Principle and Practice. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. พิษณุโลก: สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร; 2561.
จรัญ สายะสถิตย์. ศัลยศาสตร์โรคหัวใจที่พบบ่อย = Common Cardiac Surgery. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. พิษณุโลก: คณะแพทยศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร; 2555.
ชวลิต อ่องจริต. ประวัติวิวัฒนาการศัลยกรรมหัวใจที่คณะแพทยศาสตร์โรงพยาบาลจุฬาลงกรณ์ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. กรุงเทพมหานคร: The Society of Thoracic Surgeons of Thailand; [สืบค้นเมื่อ 30 กันยายน 2563]. สืบค้นจาก: http://thaists.org/history_detail.php?news_id=35
สมาคมศัลยแพทย์ทรวงอกแห่งประเทศไทย. สถิติผ่าตัดหัวใจในปี พ.ศ. 2544-2562 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. กรุงเทพมหานคร: The Society of Thoracic Surgeons of Thailand; [สืบค้นเมื่อ 9 มิถุนายน 2564]. สืบค้นจาก: https://ststhai.org/en/stats/
พงศ์เสน่ห์ ดวงภักดี. เครื่องปอดและหัวใจเทียมสำหรับนักศึกษาแพทย์ (introduction to cardiopulmonary bypass for medical students) [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. สงขลา: แพทยศาสตรศึกษา มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์; 2564 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 11 มิถุนายน 2564]. สืบค้นจาก: https://meded.psu.ac.th/binla/class05/388_531/Cardiopulmonary_bypass/index2.html
Shiroishi MS. Myocardial protection: The rebirth of potassium-based cardioplegia. Tex Heart Inst J. 1999;26(1):71-86.
Dobson GP, Faggian G, Onorati F, Vinten-Johansen J. Hyperkalemic cardioplegia for adult and pediatric surgery: End of an era? Front Physiol. 2013;4:228.
Carvajal C, Goyal A, Tadi P. Cardioplegia [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; updated 2020 Jul 31 [cited 2020 Sep 30]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554463/
กรองกาญจน์ ชูทิพย์. สรีรวิทยาระบบหัวใจร่วมหลอดเลือดกับการประยุกต์ใช้ทางเภสัชวิทยา. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. พิษณุโลก: สำนักพิมพ์มหาวิทยาลัยนเรศวร; 2560.
Sanetra K, Pawlak I, Cisowski M. Del Nido cardioplegia - what is the current evidence?. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2018;15(2):114-8.
Oliveira MA, Brandi AC, Santos CA, Botelho PH, Cortez JL, Braile DM. Modes of induced cardiac arrest: Hyperkalemia and hypocalcemia--literature review. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2014;29(3):432-6.
Kim K, Ball C, Grady P, Mick S. Use of del Nido cardioplegia for adult cardiac surgery at the Cleveland Clinic: Perfusion implications. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2014;46(4):317-23.
Matte GS, del Nido PJ. History and use of del Nido cardioplegia solution at Boston Children's Hospital. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2012;44(3):98-103.
Kantathut N, Shaishana C, Thongcherd W, Sornprasit W, Jiraratkul S, Vilaikan S, et al. Experience in the use of del Nido cardioplegia in Ramathibodi Hospital. J Med Assoc Thai [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2020 Sep 30]; 100(11): 115. Available from: http://www.thaiscience.info/Journals/Article/JMAT/10988983.pdf
Kantathut N, Cherntanomwong P, Khajarern S, Leelayana P. Lactated Ringer's as a base solution for del Nido cardioplegia. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2019;51(3):153-9.
The United States Pharmacopeia Convention. USP general chapter <797> pharmaceutical compounding—sterile preparations [Internet]. Rockville, MD: USP42-NF37; 2019 May 1 [cited 2020 Sep 30]. Available from: https://www.usp.org/compounding/general-chapter-797
ลีณา สุนทรสุข, ชุติมา เพชรกระจ่าง, ปิยนุช โรจน์สง่า, สวรรยา บูรณะผลิน, เยาวสิเนห์ เพ็งผลา, จิตรลดา เหมินทราภรณ์. รายงานการตรวจวิเคราะห์ความคงสภาพของน้ำยาหยุดการเต้นของหัวใจชนิด del Nido (in use stability of del Nido cardioplegia). กรุงเทพมหานคร: ภาควิชาเภสัชเคมี คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล; 2564.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

