Imiglucerase in Gaucher's Disease
Keywords:
imiglucerase, Gaucher’s disease, glucocerebrosidaseAbstract
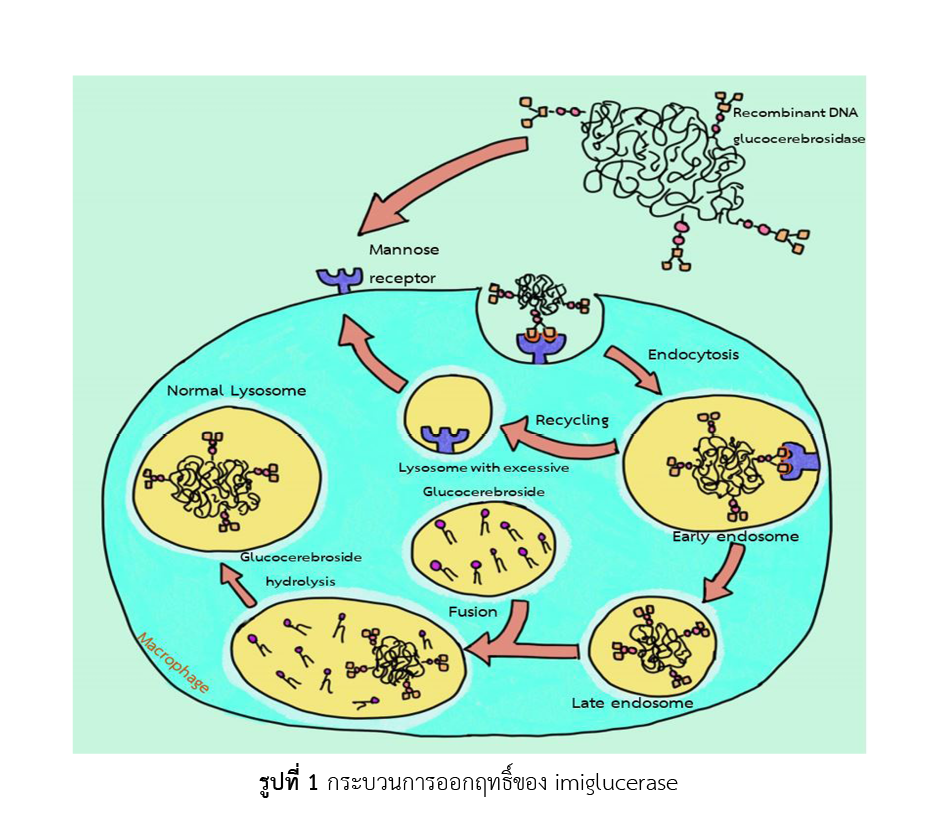
Imiglucerase is an analogue of the human enzyme β-glucocerebrosidase that is produced by recombinant DNA technology. It is used as a replacement enzyme for the treatment of Gaucher’s disease, a rare genetic disorder that causes the functional deficiency of glucocerebrosidase enzyme in lysosomes resulting in the accumulation of lipid substance in lysosomes of macrophage of multiple organs. Mechanism of action of imiglucerase is the hydrolysis of complex lipid accumulated in patients with Gaucher’s disease The drug is indicated to use as enzyme replacement therapy for pediatric and adult patients with Gaucher’s disease type 1. The recommended dosage is 30-60 units per kg of body weight infused within 1-2 hours every two weeks. Imiglucerase is listed in the National List of Essential Medicines B.E.2563 category E(2). This category includes medicines that are labeled for specific patients with specific indications, or prescribed by specialist physicians, or produced by advanced technology, and costly. The drug admixing is very important because it must be compounded by personnels who have knowledge and technique to avoid degradation. One technique is to reconstitute by adding sterile water for injection slowly drop-wise, down inside the wall of each vial, instead of shaking vigorously. It is found that the common adverse reactions (13.8%) are related to imiglucerase administration, frequency or route of administration. Some of adverse reactions are discomfort, pruritus, swelling, burning or abscess at the site of venipuncture.
References
Novo JB, Morganti L, Moro AM, Paes Leme AF, Serrano SMdT, Raw I, et al. Generation of a Chinese hamster ovary cell line producing recombinant human glucocerebrosidase. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:875383.
Tanphaichitr VS, Suvatte V, Mahasandana C, Sachapong P, Veerakul G, Kankirawatana S, et al. Gaucher’s disease; thirty-two years experience at Siriraj Hospital. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1999;30 Suppl 2:143-7.
คณะกรรมการพัฒนาระบบยาแห่งชาติ. บัญชียาหลักแห่งชาติ พ.ศ. 2563 [อินเตอร์เนต]. [สืบค้นเมื่อ 5 กุมภาพันธ์ 2564].
สืบค้นจาก: https://dpf.mod.go.th/pdf/บัญชียาหลักแห่งชาติ-พ-ศ-2563.
Bohra V, Nair V. Gaucher’s disease. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2011;15(3):182-6.
Mehta A. Epidemiology and natural history of Gaucher’s disease. Eur J Intern Med. 2006;17 Suppl:S2-5.
National Gaucher Foundation. What is Gaucher di–sease? [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.gaucherdisease.org/about-gaucher-disease/what-is/.
มูลนิธิโรคพันธุกรรมแอลเอสดี. โรคพันธุกรรม LSD ชนิด Gaucher [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: http://www.lsdthailand.com/lsd/index.php/ct-menu-item-5/ct-menu-item-7.
Stirnemann J, Belmatoug N, Camou F, Serratrice C, Froissart R, Caillaud C, et al. A review of Gaucher disease pathophysiology, clinical presentation and treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(2):441.
Shawky RM, Elsayed SM. Treatment options for patients with Gaucher disease. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2016;17(3):281-5.
Biegstraaten M, Cox TM, Belmatoug N, Berger MG, Collin-Histed T, Vom Dahl S, et al. Management goals for type 1 Gaucher disease: An expert consensus document from the European working group on Gaucher disease. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2018;68:203-8.
Elstein D, Zimran A. Review of the safety and efficacy of imiglucerase treatment of Gaucher disease. Biologics. 2009;3:407-17.
Weinreb NJ. Imiglucerase and its use for the treatment of Gaucher’s disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9(11):1987-2000.
Educe Design & Innovation Inc. Imiglucerase [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 4]. Available from: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00053.
MIMS. Imiglucerase [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 4]. Available from: https://www.mims.com/thailand/drug/search?q=imiglucerase.
Genzyme Corporation. Cerezyme® (imiglucerase for injection) [Internet]. 2003 [cited 2021 Feb 5]. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2005/20367s066lbl.pdf.
Pastores GM. Recombinant glucocerebrosidase (imiglucerase) as a therapy for Gaucher disease. Bio–Drugs. 2010;24(1):41-7.
Phenix CP, Rempel BP, Colobong K, Doudet DJ, Adam MJ, Clarke LA, et al. Imaging of enzyme replacement therapy using PET. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(24):10842-7.
Freire E, Schön A, Hutchins BM, Brown RK. Chemical denaturation as a tool in the formulation optimization of biologics. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18(19-20):1007-13.
Genzyme Corporation. Cerezyme Preparation & Administration [Internet]. [cited 2021 Apr 19]. Available from: https://www.cerezyme.com/-/media/EMS/Conditions/RareDiseases/Brands/Cerezyme/pdf/Cerezyme%20Preperation%20and%20Administration.pdf?la=en.
Grabowski GA, Barton NW, Pastores G, Dambrosia JM, Banerjee TK, McKee MA, et al. Enzyme therapy in type 1 Gaucher disease: comparative efficacy of mannose-terminated glucocerebrosidase from natural and recombinant sources. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122(1):33-9.
Weinreb NJ, Charrow J, Andersson HC, Kaplan P, Kolodny EH, Mistry P, et al. Effectiveness of enzyme replacement therapy in 1028 patients with type 1 Gaucher disease after 2 to 5 years of treatment: a report from the Gaucher Registry. Am J Med. 2002;113(2):112-9.
Weinreb NJ, Camelo JS, Charrow J, McClain MR, Mistry P, Belmatoug N. Gaucher disease type 1 patients from the ICGG Gaucher Registry sustain initial clinical improvements during twenty years of imiglucerase treatment. Mol Genet Metab. 2021;132(2):100-11.
Raynor L, Batista J, Carloni L, Gudivada B, Lewis G, Sekulic D, et al. Real-world outcomes in pregnant imiglucerase-treated patients with Gaucher disease: Data from the global safety database and International Collaborative Gaucher Group (ICGG) Gaucher registry pregnancy sub-registry maintained by Sanofi Genzyme. Mol Genet Metab. 2019;126:S122.
Genzyme Corporation. Cerezyme: EPAR - Product Information [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 7]. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000157/WC500024112.pdf.
Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); 2006-. Imiglucerase. [Updated 2020 Apr 20]. [cited 2021 Feb 8]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501690/
Genzyme Corporation. Safety was evaluated in clinical trials and a long-term observational monitoring database [Internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 8]. Available from: https://www.cerezyme.com/hcp/about-cerezyme/safety.
Starzyk K, Richards S, Yee J, Smith SE, Kingma W. The long-term international safety experience of imiglucerase therapy for Gaucher disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2007;90(2):157-63.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Association of Hospital Pharmacy (Thailand)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

