Asciminib: ทางเลือกใหม่สำหรับโรคมะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวชนิดเรื้อรังแบบมัยอีลอยด์
คำสำคัญ:
asciminib, ABL1 kinase inhibitor, โรคมะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวชนิดเรื้อรังแบบมัยอีลอยด์ในระยะเรื้อรังบทคัดย่อ
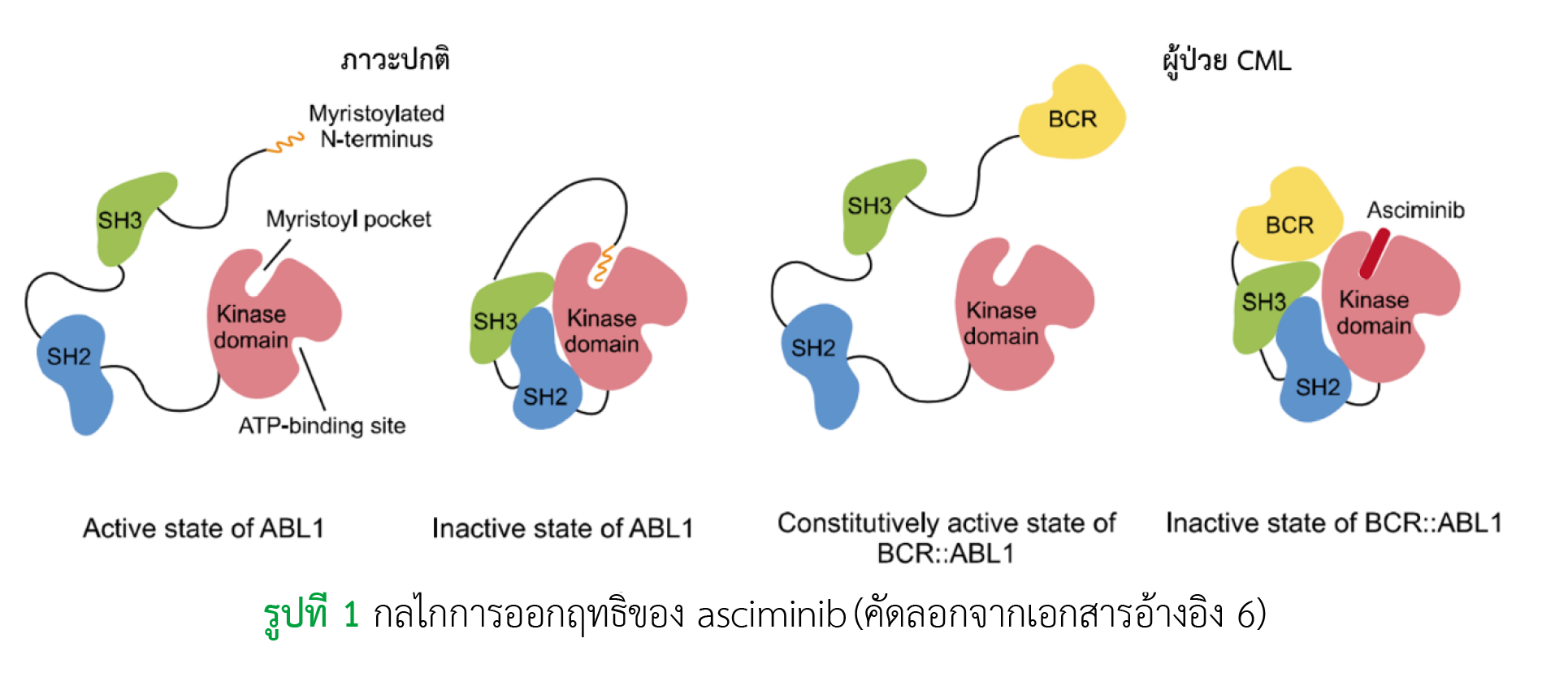
Asciminib เป็นยาตัวแรกในกลุ่ม ABL1 kinase inhibitor ที่ได้รับการขึ้นทะเบียนโดยองค์การอาหารและยาแห่งประเทศสหรัฐอเมริกา ในวันที่ 29 ตุลาคม ค.ศ.2021 สำหรับการรักษาโรคมะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวชนิดเรื้อรังแบบมัยอีลอยด์ระยะเรื้อรังในผู้ป่วยที่ผ่านการรักษาด้วยยากลุ่ม tyrosine kinase inhibitor มาแล้วอย่างน้อย 2 ชนิดและเป็นผู้ป่วยที่พบ T315I mutation กลไกการออกฤทธิ์คือ ยาจะไปยับยั้ง ABL1 kinase โดยไปจับกับ myristol pocket ซึ่งจากการศึกษาในหลอดทดลองและสัตว์ทดลองพบว่า ยามีผลต่อโปรตีน wild-type BCR-ABL1 และโปรตีนชนิดที่มีการกลายพันธุ์ต่าง ๆ รวมถึง T315I mutation จากการทบทวนวรรณกรรมอย่างเป็นระบบพบว่า ผู้ป่วยสามารถทนต่อยาได้ดีและยามีข้อมูลความปลอดภัยสูง สำหรับอาการไม่พึงประสงค์ที่พบบ่อย ได้แก่ การติดเชื้อที่ทางเดินหายใจส่วนบน ปวดกล้ามเนื้อและกระดูก อ่อนล้า คลื่นไส้ ผื่นขึ้น และท้องเสีย ส่วนผลผิดปกติทางห้องปฏิบัติการที่พบบ่อย ได้แก่ การเพิ่มขึ้นของระดับ triglyceride, creatine kinase, alanine aminotransferase, lipase และ amylase รวมทั้งมีการลดลงของ hemoglobin จำนวน platelet และจำนวน neutrophils
เอกสารอ้างอิง
แสงสุรีย์ จูฑา, อุดมศักดิ์ บุญวรเศรษฐ์, ธีรยา พัววิไล, ต้นตนัย นำเบญจพล, วีระศักดิ์ นาวารวงศ์, อานุภาพ เลขะกุล, และคณะ. แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติสำหรับโรคมะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวเรื้อรังชนิดมัยอีลอยด์ พ.ศ. 2554 [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. กรุงเทพมหานคร: สมาคมโลหิตวิทยาแห่งประเทศไทย; 2554 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ก.ย. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก http://www.tsh.or.th/files_news/newsFile_20110509164226.pdf
เอกรัฐ รัฐฤทธิ์ธำรง. โรคมะเร็งเม็ดเลือดขาวชนิดเรื้อรัง [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. กรุงเทพมหานคร: สมาคมโลหิตวิทยาแห่งประเทศไทย; 2562 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ก.ย. 2566]. สืบค้นจากhttp://www.tsh.or.th/Knowledge/Details/67
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Silver RT, Schiffer C, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2020;34(4):966-84. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0776-2.
Hochhaus A, Saussele S, Rosti G, Mahon FX, Janssen JJWM, Hjorth-Hansen H, et al. Chronic myeloid leukaemia: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(suppl_4):iv41-51. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx219.
Deininger MW, Shah NP, Altman JK, Berman E, Bhatia R, Bhatnagar B, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020;18(10):1385-415. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0047.
Choi EJ. Asciminib: the first-in-class allosteric inhibitor of BCR::ABL1 kinase. Blood Res. 2023;58(S1):S29-36. doi: 10.5045/br.2023.2023017.
สำนักงานหลักประกันสุขภาพแห่งชาติ สำนักสนับสนุนคุณภาพและมาตรฐานหน่วยบริการ. คู่มือแนวทางการรักษาโรคมะเร็งโลหิตวิทยาในผู้ใหญ่ พ.ศ. 2561 เพื่อขอรับค่าบริการสาธารณสุข ในระบบหลักประกันสุขภาพแห่งชาติ [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. กรุงเทพมหานคร: สำนักงานหลักประกันสุขภาพแห่งชาติ; 2561 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 1 ก.ย. 2566]. สืบค้นจาก https://www.nhso.go.th/storage/files/shares/PDF/Protocol_UC02.pdf
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. SCEMBLIX® (asciminib) tablets, for oral use [Internet]. East Hanover (New Jersey): Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 1]. Available from: https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/scemblix.pdf
Hughes TP, Mauro MJ, Cortes JE, Minami H, Rea D, DeAngelo DJ, et al. Asciminib in chronic myeloid leukemia after ABL kinase inhibitor failure. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(24):2315-26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1902328.
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122(6):872-84. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-05-501569.
Réa D, Mauro MJ, Boquimpani C, Minami Y, Lomaia E, Voloshin S, et al. A phase 3, open-label, randomized study of asciminib, a STAMP inhibitor, vs bosutinib in CML after 2 or more prior TKIs. Blood. 2021;138(21):2031-41. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009984.
Mauro MJ, Minami Y, Rea D, Hochhaus A, Lomaia E, Voloshin S, et al. Efficacy and safety results from ascembl, a multicenter, open-label, phase 3 study of asciminib, a first-in-class STAMP inhibitor, vs bosutinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase after ≥2 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors: update after 48 weeks. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):310. doi: 10.1182/blood-2021-152561.
Pérez-Lamas L, Luna A, Boque C, Xicoy B, Giraldo P, Pérez López R, et al. Toxicity of asciminib in real clinical practice: analysis of side effects and cross-toxicity with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(4):1045. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041045.
Wylie AA, Schoepfer J, Jahnke W, Cowan-Jacob SW, Loo A, Furet P, et al. The allosteric inhibitor ABL001 enables dual targeting of BCR-ABL1. Nature. 2017;543(7647):733-7. doi: 10.1038/nature21702.
Eide CA, Zabriskie MS, Savage Stevens SL, Antelope O, Vellore NA, Than H, et al. Combining the allosteric inhibitor asciminib with ponatinib suppresses emergence of and restores efficacy against highly resistant BCR-ABL1 mutants. Cancer Cell. 2019;36(4):431–43:e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.08.004.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล(ประเทศไทย)

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

