ขนาดวาร์ฟารินเริ่มต้นที่เหมาะสม และปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อขนาดวาร์ฟารินเริ่มต้นที่ทำให้ค่าไอเอ็นอาร์อยู่ในช่วงเป้าหมาย
คำสำคัญ:
ขนาดยาเริ่มต้น, วาร์ฟาริน, ไอเอ็นอาร์, ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อขนาดวาร์ฟารินบทคัดย่อ
ความเป็นมา วาร์ฟาริน เป็นยาต้านการแข็งตัวของเลือดชนิดรับประทานที่มีประสิทธิภาพดีในการรักษาโรคหัวใจและหลอดเลือดหลายชนิด โดยเฉพาะโรคหัวใจเต้นผิดจังหวะชนิด atrial fibrillation โรคหลอดเลือดสมองอุดตัน ภาวะลิ่มเลือดอุดตันในหลอดเลือดดำส่วนลึก และ โรคลิ่มเลือดอุดกั้นในปอด แต่วาร์ฟารินมีช่วงการรักษาแคบ มีเภสัชจลนศาสตร์และเภสัชพลศาสตร์ที่ซับซ้อน เกิดอันตรกิริยาระหว่างยาได้ง่าย และอาจเกิดอาการไม่พึงประสงค์
วัตถุประสงค์ เพื่อศึกษาขนาดวาร์ฟารินเริ่มต้นที่เหมาะสม ที่ทำให้ค่าไอเอ็นอาร์อยู่ในช่วงเป้าหมายการรักษา และหาปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อขนาดยาเริ่มต้นที่ทำให้ค่าไอเอ็นอาร์ของผู้ป่วยที่เริ่มใช้วาร์ฟารินอยู่ในช่วงเป้าหมาย
วิธีวิจัย ศึกษาแบบย้อนหลัง ณ โรงพยาบาลทั่วไป ขนาด 340 เตียง ในจังหวัดประจวบคีรีขันธ์ โดยรวบรวมข้อมูลผู้ป่วยที่เริ่มใช้วาร์ฟารินครั้งแรกที่โรงพยาบาลตั้งแต่ 1 ตุลาคม 2562 ถึง 30 กันยายน 2565 และติดตามค่าไอเอ็นอาร์ในช่วงการรักษาอย่างน้อย 1 ครั้งในช่วง 7 - 90 วันแรกหลังเริ่มยา
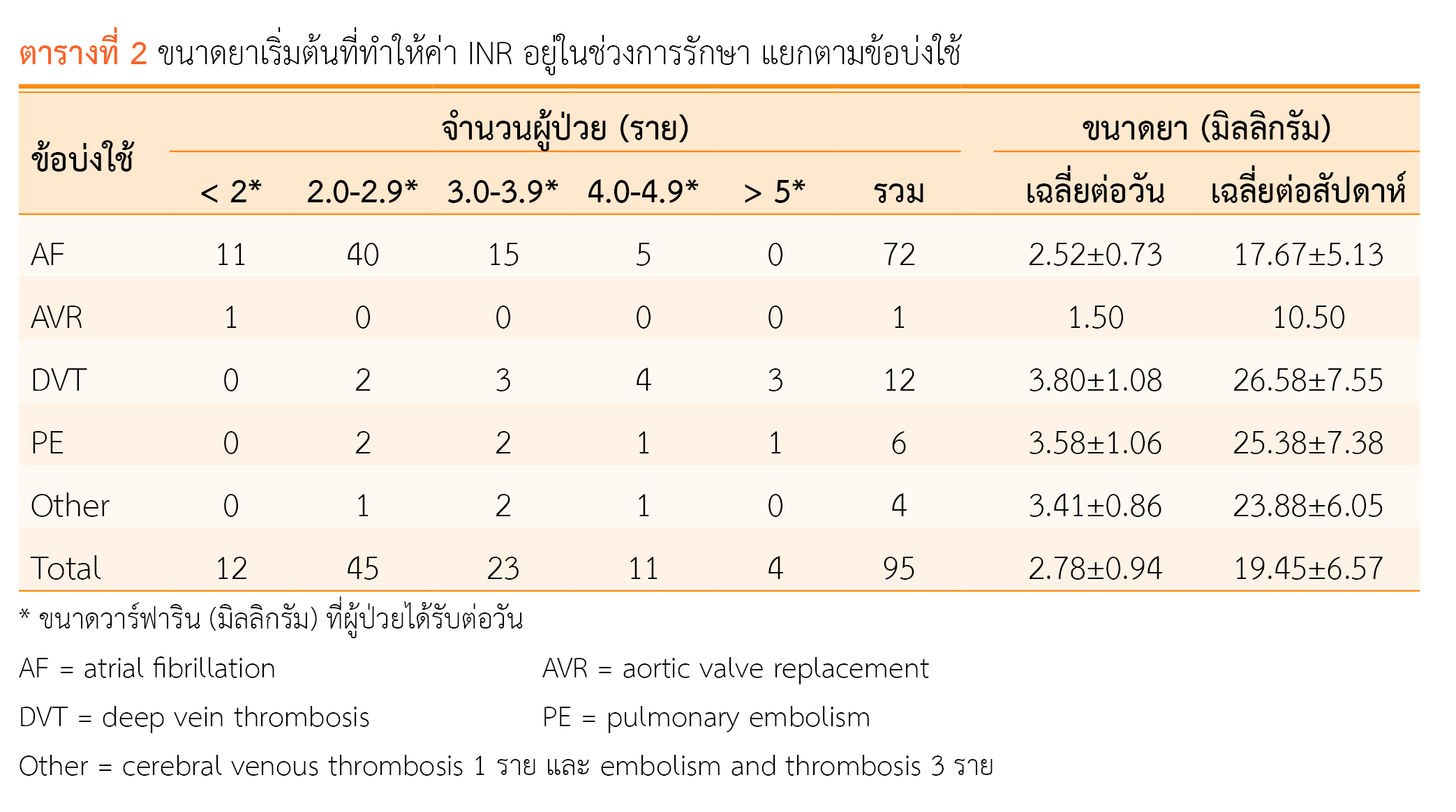
ผลการวิจัย พบว่ามีผู้ป่วยที่เริ่มใช้วาร์ฟารินครั้งแรกตามเกณฑ์คัดเข้าทั้งหมด 95 คน อายุเฉลี่ย 62.78 ปี ระยะเวลาเฉลี่ยที่ผู้ป่วยมีค่าไอเอ็นอาร์อยู่ในช่วงการรักษาครั้งแรกเท่ากับ 35.28±26.15 วัน ในผู้ป่วยโรคหัวใจเต้นผิดจังหวะชนิด atrial fibrillation ขนาดยาเริ่มต้นที่เหมาะสมอยู่ในช่วง 2.0-2.9 มิลลิกรัม/วัน ขณะที่ผู้ป่วยภาวะลิ่มเลือดอุดตันในหลอดเลือดดำส่วนลึกได้รับขนาดยาที่สูงกว่า คือ 3.0-5.0 มิลลิกรัม/วัน ผลการวิเคราะห์แบบ multiple linear regression พบว่าปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อการเริ่มให้ขนาดวาร์ฟาริน ได้แก่ อายุ การมีภาวะลิ่มเลือดอุดตันในหลอดเลือดดำส่วนลึก และการได้ค่าไอเอ็นอาร์ที่สามารถเข้าช่วงเป้าหมายภายใน 7 วัน ล้วนมีผลต่อขนาดวาร์ฟารินเริ่มต้น
สรุปผล ควรมีการนำสมการขนาดยาเริ่มต้นที่ได้จากการศึกษาไปศึกษาเพิ่มเติมเพื่อหาขนาดยาที่เหมาะสม และเก็บข้อมูลเปรียบเทียบกับการเริ่มยาแบบปกติต่อไป
เอกสารอ้างอิง
สมาคมแพทย์โรคหัวใจแห่งประเทศไทย. แนวทางการรักษาผู้ป่วยด้วยยาต้านการแข็งตัวของเลือดชนิดรับประทาน พ.ศ. 2553. กรุงเทพฯ: สมาคมแพทย์โรคหัวใจแห่งประเทศไทยในพระบรมราชูปถัมภ์; 2553.
สุภารัตน์ วัฒนสมบัติ. ยาต้านการแข็งตัวของเลือด. ไทยไภษัชยนิพนธ์. 2553;5(1): 87–98. doi: 10.14456/tbps.2010.6
Ansell J, Hirsh J, Hylek E, Jacobson A, Crowther M, Palareti G. Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):160S-98S. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0670.
กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข. แนวทางการจัดการด้านยาตาม service plan สาขาโรคหัวใจและไต. นนทบุรี: กองบริหารการสาธารณสุข สำนักงานปลัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข; 2563. หน้า 5-18.
Abdel-Aziz MI, Ali MA, Hassan AK, Elfaham TH. Factors influencing warfarin response in hospitalized patients. Saudi Pharm J. 2015;23(6):642-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.02.004.
สิระ ชวรัศมิ์, ชนัชชา อุปฮาด. ปัจจัยที่มีผลต่อค่า INR ของผู้ใช้ยาวาร์ฟาริน โรงพยาบาลเบญจลักษณ์เฉลิมพระเกียรติ 80 พรรษา. วารสารอนามัยสิ่งแวดล้อมและสุขภาพชุมชน [อินเตอร์เนต]. 2565 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 ส.ค. 2566];7(1):137-46. สืบค้นจาก: https://he03.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ech/article/view/519
กรรณิกา เหมือนจันทร์แจ่ม. ขนาดยาวาร์ฟารินที่เหมาะสมและปัจจัยทางคลินิกที่มีผลต่อขนาดยาวาร์ฟารินในขนาดคงที่ ที่โรงพยาบาลราชบุรี. วารสารหัวหินสุขใจไกลกังวล [อินเตอร์เนต]. 2563 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 29 พ.ค. 2566];5(1):18-29. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/hhsk/article/view/240517
กิตติศักดิ์ พนมพงศ์, พัชริยา โทนหงษา. ปัจจัยทำนายขนาดยาวาร์ฟารินและปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับระดับไอเอ็นอาร์ของผู้ป่วย ที่ได้รับยาวาร์ฟาริน โรงพยาบาลหนองพอก จังหวัดร้อยเอ็ด. วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนานวัตกรรมทางสุขภาพ [อินเตอร์เนต]. 2564 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 ส.ค. 2566];2(3):109-20. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/jrhi/article/view/252824
Pongbangli N, Phrommintikul A, Wongcharoen W. Simplified warfarin dosing formula to guide the initiating dose in Thai patients. J Med Assoc Thai [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2022 May 29];102(9):957-61. Available from: http://www.jmatonline.com/index.php/jmat/article/view/10030#
Suwanawiboon B, Rotchanapanya W, Mahaprom K, Thongnoppakhun W, Lalerd Y, Limwongse C, et al. The efficacy of low-dose warfarin initiation (3 mg versus 5 mg) in newly diagnosed venous thromboembolism patients among a population with a high prevalence of warfarin-sensitive haplotype of the VKORC1 gene: a randomized controlled trial. Hematology. 2022;27(1):95-104. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2021.2019891.
Gao W, Zhang Z, Guan Z, Chen W, Li Z. Developing Chinese race-specific warfarin dose prediction algorithms. Int J Clin Pharm. 2023;45(3):731-8. doi: 10.1007/s11096-023-01565-1.
Yang W, Ma J, Hu W, Dai H, Xu H. Associated factors and safety of the rapidly achieving first therapeutic target of warfarin in hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Clin Pharm. 2022;44(4):939-46. doi: 10.1007/s11096-022-01404-9.
Suwanawiboon B, Kongtim P, Chinthammitr Y, Ruchutrakool T, Wanachiwanawin W. The efficacy of 3-mg warfarin initiating dose in adult Thai patients, who required long-term anticoagulant therapy. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011;94(Suppl 1):S225-31. PMID: 21721451.
ระวิวรรณ หลิมศิโรรัตน์. ผลการให้บริการทางเภสัชกรรมสำหรับผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาวอร์ฟารินครั้งแรกในหอผู้ป่วยอายุรกรรมและศัลยกรรม [วิทยานิพนธ์ปริญญาเภสัชศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต]. สงขลา:มหาวิทยาลัยสงขลานครินทร์; 2560.
นาตยา หวังนิรัติศัย, สกนธ์ สุภากุล, ภูขวัญ อรุณมานะกุล. ผลของการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาวาร์ฟาริน ของคลินิกวาร์ฟาริน โรงพยาบาลสวรรค์ประชารักษ์. วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2561 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 ส.ค. 2566];10(1):120-8. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJPP/article/view/171018
ศุภกร อ่อนงาม. ผลลัพธ์ของการบริบาลทางเภสัชกรรมกรรมในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับยาวาร์ฟารินขณะพักรักษาตัวในโรงพยาบาลชุมชน.วารสารเภสัชกรรมไทย [อินเทอร์เน็ต]. 2560 [สืบค้นเมื่อ 14 ส.ค. 2566];9(2):433-46. สืบค้นจาก: https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/TJPP/article/view/170897
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2024 สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล(ประเทศไทย)

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

