Digoxin Intoxication
Keywords:
digoxin, digoxin intoxication, digitalis Fab fragmentAbstract
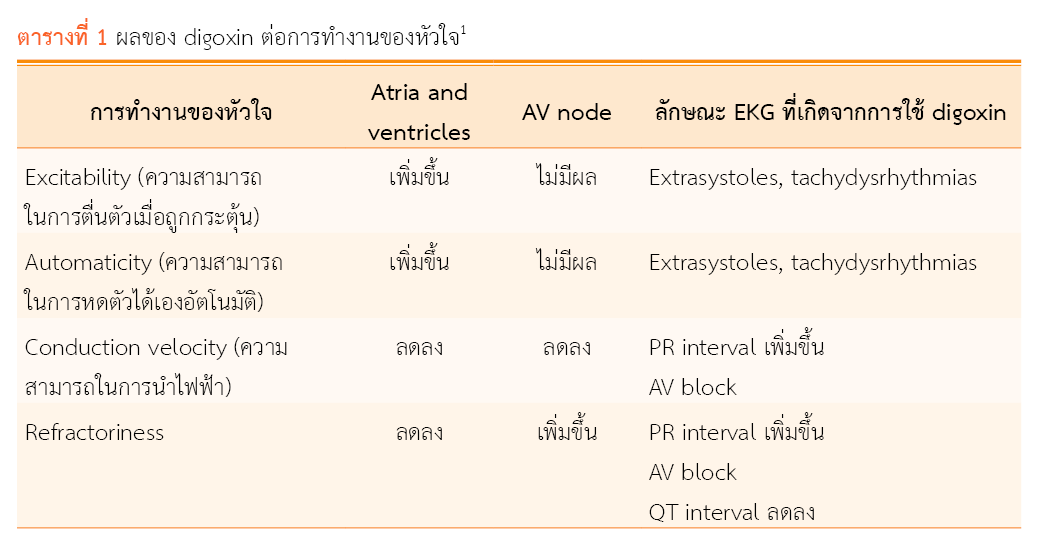
Digoxin is a medication used to treat heart failure and atrial fibrillation. It inhibits sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphate pumps, which raises calcium levels in myocardial cells, thereby increasing cardiac contraction. Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic range. Common symptoms of digoxin intoxication include nausea, vomiting, electrolyte imbalance, cardiac arrhythmias, and visual disturbances. The characteristics of digoxin intoxication can be divided into two types: acute toxicity and chronic toxicity. Hyperkalemia and bradycardia are more predominant in acute poisoning than in chronic poisoning. The general management of digoxin intoxication is symptomatic treatment. For example, calcium gluconate may be used in cases of hyperkalemia, and atropine may be used for bradycardia and heart block. In cases where atropine therapy is ineffective, the antidote digitalis Fab fragment should be considered. However, this antidote is not available in Thailand.
References
Hack JB. Cardioactive steroids. In: Hoffman RS, Howland MA, Lewin NA, Nelson LS, Goldfrank LR, Flomenbaum N, editors. Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies. 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019: 969-76.
Goldberger AL. Cardiac arrhythmias due to digoxin toxicity. In: UpToDate [Database on the internet]. Waltham (MA): UpToDate,Inc.; 2023 [cited 2023 July 3]. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com
National Library of Medicine. Digitalis Toxicity [Internet]. Bethesda: NCBI; updated 2023 [cited 2023 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459165/
สัมมน โฉมฉาย. ภาวะพิษจากดิจอกซิน. ใน: จารุวรรณ ศรีอาภา, บรรณาธิการ. ยาต้านพิษ 2. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ: สมาคมพิษวิทยาคลินิก, 2555. หน้า 37-41.
Benowitz NL. Digoxin and other cardiac glycosides In: Olson KR (ed). Poisoning & Drug Overdose. 7th ed. San Francisco: McGraw-Hill, 2018: 222-24.
MICROMEDEX® [Database on the internet]. Colorado: Thomson Reuters (Healthcare); c1974-2020. POISINDEX® System, Cardiac Glycosides; [cited 2023 Aug 31]. Available from: https://www.micromedexsolutions.com. Subscription required to view.
BMJ Best Practice. Digoxin Toxicity [Internet]. London: BMJ Publishing group; updated 2023 [cited 2023 Aug 31]. Available from: https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/3000257
Kearney TE. Digoxin-specific antibodies In: Olson KR (ed). Poisoning & Drug Overdose. 7th ed. San Francisco: McGraw-Hill, 2018: 542-4.
สัมมน โฉมฉาย. ดิจิทาลิส แฟบ แฟรคเมนท์. ใน: จารุวรรณ ศรีอาภา, บรรณาธิการ. ยาต้านพิษ 2. พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 1. กรุงเทพฯ: สมาคมพิษวิทยาคลินิก, 2555. หน้า 17-21.
Smith SW. and Howland MA. Digoxin-specific antibody fragments. In: Hoffman RS, Howland MA, Lewin NA, Nelson LS, Goldfrank LR, Flomenbaum N, editors. Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies. 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019: 977-84.
Collins SR. Digoxin immune FAB (ovine). In: Collins SR, editor. Elsevier’s 2023 intravenous medications. 39th ed. Missouri: Elsevier Inc; 2023. p. 431-3.
GlaxoSmithKline Manufacturing. Lanoxin [Package insert]. Bangkok: Invida (Thailand) Co., Ltd.; 2010.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Association of Hospital Pharmacy (Thailand)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
ข้อความภายในบทความที่ตีพิมพ์ในวารสารเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาลทั้งหมด รวมถึงรูปภาพประกอบ ตาราง เป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) การนำเนื้อหา ข้อความหรือข้อคิดเห็น รูปภาพ ตาราง ของบทความไปจัดพิมพ์เผยแพร่ในรูปแบบต่าง ๆ เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์ในเชิงพาณิชย์ ต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร (สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย)) อย่างเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษร
สมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) อนุญาตให้สามารถนำไฟล์บทความไปใช้ประโยชน์และเผยแพร่ต่อได้ โดยอยู่ภายใต้เงื่อนไขสัญญาอนุญาตครีเอทีฟคอมมอน (Creative Commons License: CC) โดย ต้องแสดงที่มาจากวารสาร – ไม่ใช้เพื่อการค้า – ห้ามแก้ไขดัดแปลง, Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
ข้อความที่ปรากฏในบทความในวารสารเป็นความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับสมาคมเภสัชกรรมโรงพยาบาล (ประเทศไทย) และบุคลากรในสมาคมฯ แต่อย่างใด ความรับผิดชอบองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดของบทความแต่ละเรื่องเป็นของผู้เขียนแต่ละท่าน หากมีความผิดพลาดใด ๆ ผู้เขียนแต่ละท่านจะรับผิดชอบบทความของตนเอง ตลอดจนความรับผิดชอบด้านเนื้อหาและการตรวจร่างบทความเป็นของผู้เขียน ไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับกองบรรณาธิการ


.png)

