Depression, Social Support, and Coping Strategies in Individuals with Spinal Injury Depression with Spinal Injury Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/Smj.2021.67Keywords:
Spinal cord injury, depression, social support, coping strategies, SCIAbstract
Objective: To investigate the prevalence of and factors associated with depression, the social support received by, and the coping strategies used by spinal cord injury (SCI) patients.
Materials and Methods: SCI patients who received follow-up evaluation at the Siriraj Hospital during 2016 to 2018. The instruments used included a general information, the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale(Thai version), the Social Provisions Scale, and the Spinal Cord Lesion-Related Coping Strategies Questionnaire (Thai version).
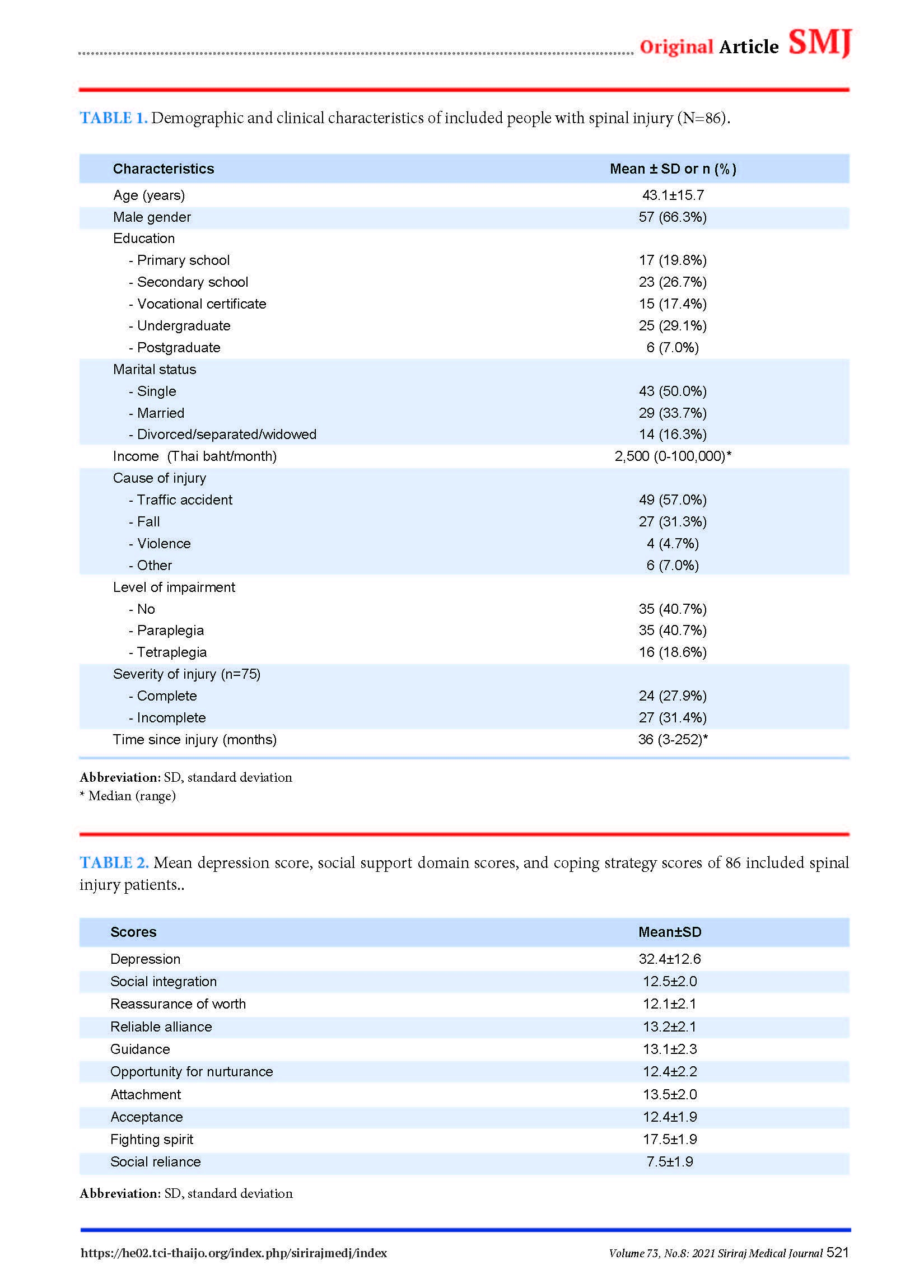
Results: Eighty-six SCI patients (age: 43.1±15.7 years, 66.3% male) were included, and 59.3% had some level of permanent impairment. The prevalence of depression was 55.8%. Depression was found to be negatively associated with all social support domains. Regarding coping, depression was shown to be negatively associated with the acceptance strategy, but positively associated with the social reliance strategy. Multivariate analysis by multiple logistic regression showed level of impairment (p=0.005), guidance provision (p=0.040), fighting spirit strategy (p=0.031), and the social reliance strategy (p=0.032) to be independently associated with depression.
Conclusion: The prevalence of depression among SCI was 55.8%. The results revealed the types of social support received, and the coping strategies used by SCI patients after hospital discharge. These findings will improve follow-up care and patient quality of life.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














