Human Travelling and COVID-19 Pandemic
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/Smj.2021.73Keywords:
Environment, travel, , COVID-19, nationwideAbstract
Objective: To determine whether there is a relationship between the extent of human travel and the number of COVID-19 cases in Thailand.
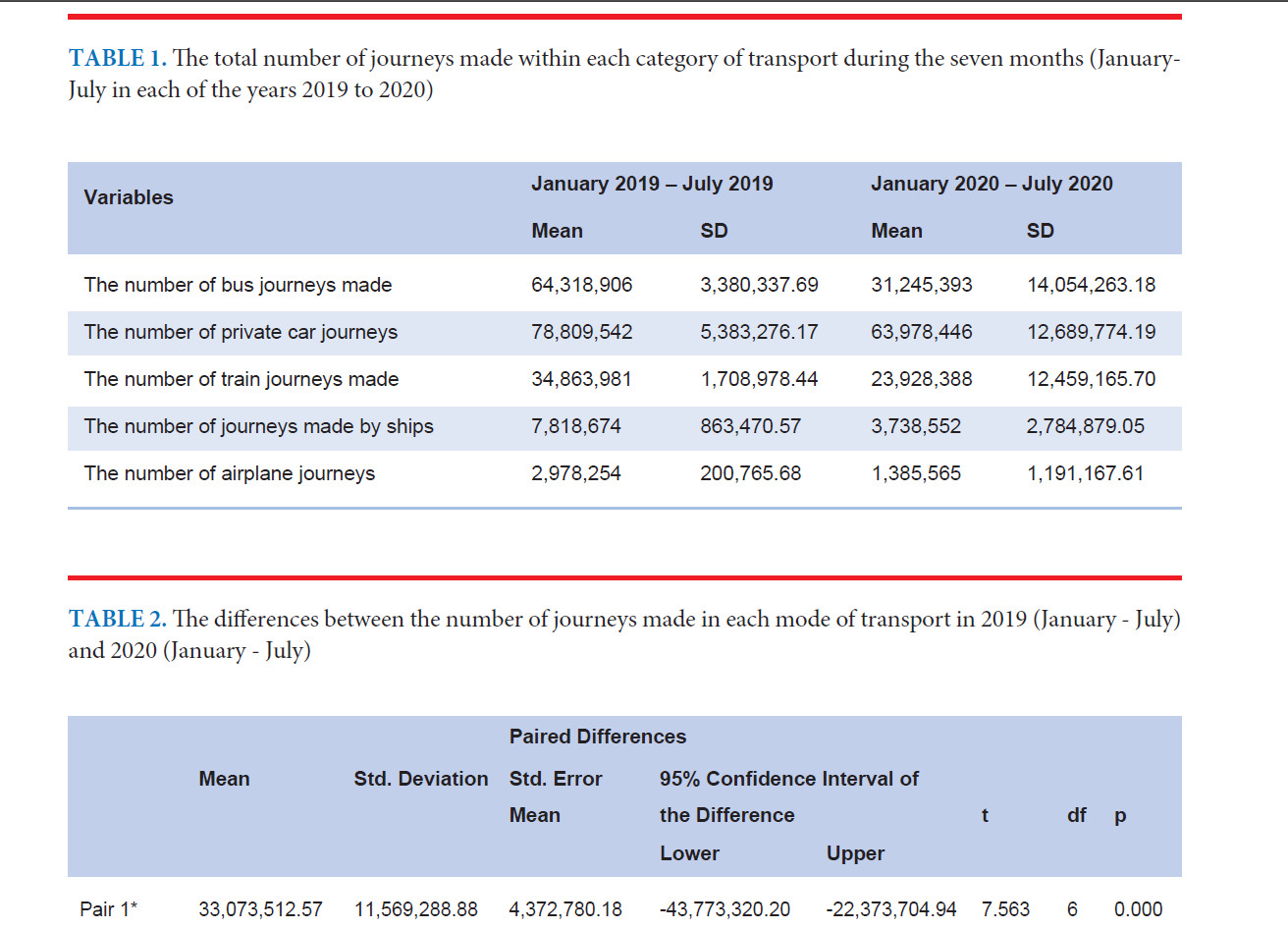
Materials and Methods: The data set on monthly COVID-19 in Thailand between January and July 2020 were retrieved from the Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. Data regarding people’s travel in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic and for the same period of 2019 were retrieved from Open Government Data of Thailand. A paired t-test was used to compare the differences between the number of journeys made in each mode of transport in 2019 (January - July) and 2020 (January - July). Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient was used to examine the relationships among studied variables.
Results: A Paired Samples t-test showed that from January until July 2020, the number of journeys made by public buses, ships, and airplanes declined by more than 50% from the previous year (p < 0.05). Pearson correlation coefficients showed that the mean monthly number of COVID-19 cases was significantly and inversely correlated with the number of public bus journeys made (r = -0.897, p < 0.01), the number of train journeys (r = -0.834, p < 0.05), ship journeys (r = -0.890, p < 0.01), and airplane journeys (r = -0.911, p < 0.01). There was no significant relationship between the number of COVID-19 cases and private car journeys (r = -0.405, p = 0.367).
Conclusion: During the pandemic, the number of journeys has been decreased. Moreover, the correlation between the number of journeys and COVID-19 cases has been shown in our analysis.
References
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497-506.
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020.
Ludwig S, Zarbock A. Coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2. Anesth Analg In press doi.10.1213/ANE.0000000000004845
Guan W-j, Ni Z-y, Hu Y, Liang W-h, Ou C-q, He J-x, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. New England journal of medicine. 2020;382(18):1708-20.
COVID-19 CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC Worldometer: Worldometer; 2020. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?
Srichannil C. The COVID-19 pandemic and Thailand: A psychologist’s viewpoint. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy. 2020;12(5):485.
Shin MD, Shukla S, Chung YH, Beiss V, Chan SK, OrtegaRivera OA, et al. COVID-19 vaccine development and a potential nanomaterial path forward. Nature Nanotechnology. 2020;15(8):646-55.
Struyf T, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID‐19 disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020(7).
Tosepu R, Gunawan J, Effendy DS, Lestari H, Bahar H, Asfian P. Correlation between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Jakarta, Indonesia. Science of The Total Environment. 2020:138436.
Fauci AS, Lane HC, Redfield RR. Covid-19—navigating the uncharted. Mass Medical Soc; 2020.
Markus HS, Brainin M. COVID-19 and stroke—A global World Stroke Organization perspective. International journal of stroke. 2020;15(4):361-4.
Devi S. Travel restrictions hampering COVID-19 response. The Lancet. 2020;395(10233):1331-2.
Chinazzi M, Davis JT, Ajelli M, Gioannini C, Litvinova M, Merler S, et al. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science. 2020;368(6489):395-400.
Dalziel BD, Kissler S, Gog JR, Viboud C, Bjørnstad ON, Metcalf CJE, et al. Urbanization and humidity shape the intensity of influenza epidemics in US cities. Science. 2018;362(6410):75-9.
Group TWB. Thailand: The World Bank Group; 2020 [cited 2020]. Available from: https://data.worldbank.org/country/thailand.
Thailand TMoHo. Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19): The Ministry of Health of Thailand; 2020 [cited 2020]. Available from: The Ministry of Health of Thailand.
Government T. Open Government Data of Thailand. 2020.
Ratnasari D, Nazir F, Toresano L, Pawiro S, Soejoko DS, editors. The correlation between effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) with renal scintigraphy 99mTcDTPA study. Journal of Physics: Conference Series; 2016: IOP Publishing Ltd.
Coronavirus Disease National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Division of Viral Diseases; 2020 [cited 2020 11 December ]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/travelers/travel-risk.html.
Shen J, Duan H, Zhang B, Wang J, Ji JS, Wang J, et al. Prevention and control of COVID-19 in public transportation: experience from China. Environmental pollution. 2020:115291.
China N. New Coronavirus Pneumonia Prevention and Control Protocol. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; 2020.
Zou L, Ruan F, Huang M, Liang L, Huang H, Hong Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382(12):1177-9.
Bai Y, Yao L, Wei T, Tian F, Jin D-Y, Chen L, et al. Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA 2020;323(14):1406-7.
WHO. COVID-19: WHO Thailand situation reports 2020 [cited 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/thailand/emergencies/
novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














