Paradigm Shift from Open Surgery to Minimally Invasive Surgery in Three Approaches for Radical Prostatectomy: Comparing Outcomes and Learning Curves
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/Smj.2022.73Keywords:
Radical prostatectomy, Laparoscopic, Robotic, Localized prostate cancer, Learning curveAbstract
Objective: Radical prostatectomy (RP) can be performed by several approaches, such as open retropubic radical prostatectomy (RRP), laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP), and robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP). This study investigated and shared the differences in the surgical techniques, learning curves, and outcomes of each approach of RP.
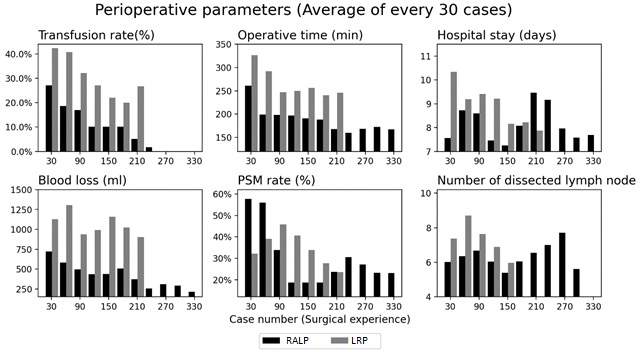
Materials and Methods: The data of patients who received RP given by one of the authors between January 2002 to June 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. We compared perioperative and postoperative outcomes among approaches, searched for predictors of a positive surgical margin (PSM), and assess the learning curves of the two minimally invasive approaches.
Results: 527 patients underwent RP during January 2002 to June 2016 including 42 RRP, 198 LRP, and 327 RALP. RALP had the highest negative surgical margin (68.8%) and lowest multifocal positive surgical margin (10.7%). PSM predictors were the Gleason score and pathological T staging. The learning curve showed that RALP needed one-hundred-cases experience to achieve the lowest PSM rate and 200 cases to master bleeding control. In the first 100 cases in each group, the PSM rate in LRP was lower than in RALP.
Conclusion: Minimally invasive approach in radical prostatectomy showed significant improvements over RRP, especially the RALP approach. RALP would take a surgeon 100 and 200 cases to reach the plateau on the learning curve for achieving the desired oncologic and perioperative outcome efficiencies, respectively. However, LRP and RRP are still feasible in a service setting and for training purposes.
References
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Pineros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J Cancer. 2021.
Sivilaikul S, Soontrapa S. Epidemiology of Genitourinary Tract Carcinoma in Siriraj Hospital During 1990-1995. Siriraj Med J. 2020;53(3):130-7.
Costello AJ. Considering the role of radical prostatectomy in 21st century prostate cancer care. Nat Rev Urol. 2020;17(3):177-88.
Arenas-Gallo C, Shoag JE, Hu JC. Optimizing Surgical Techniques in Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. Urol Clin North Am. 2021;48(1):1-9.
Chopra S, Srivastava A, Tewari A. Robotic radical prostatectomy: The new gold standard. Arab J Urol. 2012;10(1):23-31.
Faria EF, Maciel CVM, Berger A, Mitre A, Dauster B, Freitas CH, Jr., et al. Recommendations on robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: a Brazilian experts’ consensus. J Robot Surg. 2021.
Huynh LM, Ahlering TE. Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: A Step-by-Step Guide. J Endourol. 2018;32(S1):S28-S32.
Martini A, Tewari AK. Anatomic robotic prostatectomy: current best practice. Ther Adv Urol. 2019;11:1756287218813789.
Minafra P, Carbonara U, Vitarelli A, Lucarelli G, Battaglia M, Ditonno P. Robotic radical perineal prostatectomy: tradition and evolution in the robotic era. Curr Opin Urol. 2021;31(1):11-7.
Cao L, Yang Z, Qi L, Chen M. Robot-assisted and laparoscopic vs open radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer: perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(22):e15770.
Ilic D, Evans SM, Allan CA, Jung JH, Murphy D, Frydenberg M. Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted versus open radical prostatectomy for the treatment of localised prostate cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;9:CD009625.
Hung S-C, Ou Y-C, Cheng C-L, Hung S-W, Ho H-C, Chiu K-Y, et al. Standardized procedure of robotic assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy from case 1 to case 1200. Urological Science. 2016;27(4):199-207.
Haga N, Takinami R, Tanji R, Onagi A, Matsuoka K, Koguchi T, et al. Comprehensive approach for post-prostatectomy incontinence in the era of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2017;63(2):46-56.
Kark AE, Kurzer M. Groin hernias in women. Hernia. 2008;12(3):267-70.
Walsh PC, Donker PJ. Impotence Following Radical Prostatectomy: Insight Into Etiology and Prevention. Journal of Urology. 1982;128(3):492-7.
Ballantyne GH, Moll F. The da Vinci telerobotic surgical system: the virtual operative field and telepresence surgery. Surgical Clinics of North America. 2003;83(6):1293-304.
Feng T, Heulitt G, Lee JJ, Liao M, Li HF, Porter JR. Randomised comparison of techniques for control of the dorsal venous complex during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2020;126(5):586-94.
Saksirisampant P, Nualyong C, Srinualnad S, Leewansangtong S, Taweemonkongsap T, Jitpraphai S, et al. Positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy: Associated risk factors in Thai prostate cancer patients. J Med Assoc Thai. 2020;103(5):68-74.
Kotamarti S, Williams T, Silver M, Silver DA, Schulman AA. Rethinking the need for overnight admission after roboticassisted laparoscopic prostatectomy. J Robot Surg. 2020;14(6):913-5.
Nason GJ, Kim JK, HeeTan G, Ajib K, Nam RK. Single-night stay for open radical prostatectomy. Can Urol Assoc J. 2021;15(3):E130-E4.
Lin C, Wan F, Lu Y, Li G, Yu L, Wang M. Enhanced recovery after surgery protocol for prostate cancer patients undergoing laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Int Med Res. 2019;47(1):114-21.
Xu Y, Liu A, Chen L, Huang H, Gao Y, Zhang C, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) pathway optimizes outcomes and costs for minimally invasive radical prostatectomy. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(6):300060520920072.
Zhao Y, Zhang S, Liu B, Li J, Hong H. Clinical efficacy of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2020;18(1):131.
Song W, Lee SW, Chung JH, Kang M, Sung HH, Jeon HG, et al. Relationship between robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy and retropubic radical prostatectomy in the learning curve of a single surgeon as a novice in radical prostatectomy: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2020;81:74-9.
Kongchareonsombat W. Perioperative Outcomes and the Learning Curve for Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy in Thailand by a Single Surgeon: Six Years’ Experience in Ramathibodi Hospital. J Med Assoc Thai. 2019;102(9):951-6.
Secin FP, Savage C, Abbou C, de La Taille A, Salomon L, Rassweiler J, et al. The Learning Curve for Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: An International Multicenter Study. Journal of Urology. 2010;184(6):2291-6.
Coughlin GD, Yaxley JW, Chambers SK, Occhipinti S, Samaratunga H, Zajdlewicz L, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy versus open radical retropubic prostatectomy: 24-month outcomes from a randomised controlled study. The Lancet Oncology. 2018;19(8):1051-60.
Pereira R, Joshi A, Roberts M, Yaxley J, Vela I. Open retropubic radical prostatectomy. Transl Androl Urol. 2020;9(6):3025-35.
Yaxley JW, Coughlin GD, Chambers SK, Occhipinti S, Samaratunga H, Zajdlewicz L, et al. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy versus open radical retropubic prostatectomy: early outcomes from a randomised controlled phase 3 study. The Lancet. 2016;388(10049):1057-66.
Tobias-Machado M, Mitre AI, Rubinstein M, Costa EF, Hidaka AK. Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy learning curve for experienced laparoscopic surgeons: does it really exist? Int Braz J Urol. 2016;42(1):83-9.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














