The Impact of Lockdown during COVID-19 Pandemic on Physical and Mental Health of Adolescents
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/Smj.2022.105Keywords:
COVID-19 pandemic, adolescent, physical health, mental healthAbstract
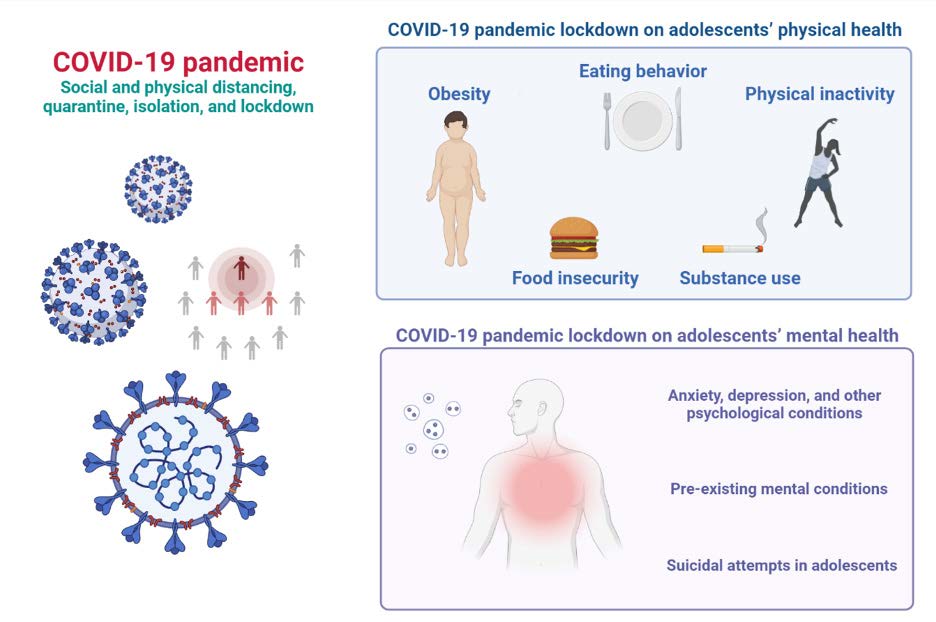
The COVID-19 pandemic is a once-in-a-lifetime incident whose impact touched everyone from all walks of life. Such an unparalleled global event warranted unprecedented measures to mitigate the imminent public health catastrophe and protect risk groups. However, these actions have inevitably marginalized the physical and mental health of adolescents who were at a lower threat of adverse physical outcomes from COVID-19 infection. Restrictive public health measures resulted in disruption of routines from the closure of the school and public spaces, social isolation, loneliness, lack of engagement, and boredom. These impacts culminated in physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle, eating disorders, and obesity and led to physical changes that have long-term implications. Equally, the substantial psychological stress of the pandemic resulted in an increased report of anxiety, depression, behavioral problems, and suicide attempts among adolescents in both previously healthy and those with pre-existing mental conditions. This narrative review provides a brief overview of the current evidence of the physical and mental impact of the pandemic lockdown on adolescent health and discussed interventional implications.
References
World Health Organization. 2022. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed 4 September 2022. [Available from: https://covid19.who.int/].
Ho FK, Petermann-Rocha F, Gray SR, Jani BD, Katikireddi SV, Niedzwiedz CL, et al. Is older age associated with COVID-19 mortality in the absence of other risk factors? General population cohort study of 470,034 participants. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0241824.
Ashwin A, Cherukuri SD, Rammohan A. Negative effects of COVID-19 pandemic on adolescent health: Insights, perspectives, and recommendations. J Glob Health. 2022;12:03009.
Singh S, Roy D, Sinha K, Parveen S, Sharma G, Joshi G. Impact of COVID-19 and lockdown on mental health of children and adolescents: A narrative review with recommendations. Psychiatry Res. 2020;293:113429.
Pai N, Vella SL. The physical and mental health consequences of social isolation and loneliness in the context of COVID-19. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2022;35(5):305-10.
Lou L, Zhang H, Tang B, Li M, Li Z, Cao H, et al. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis.medRxiv. 2021:2021.03.12.21253472. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.12.21253472
Carrillo-Diaz M, Ortega-Martínez AR, Romero-Maroto M, González-Olmo MJ. Lockdown impact on lifestyle and its association with oral parafunctional habits and bruxism in a
Spanish adolescent population. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2022;32(2):185-93.
Hossain MS, Deeba IM, Hasan M, Kariippanon KE, Chong KH, Cross PL, et al. International study of 24-h movement behaviors of early years (SUNRISE): a pilot study from Bangladesh. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021;7(1):176.
Medrano M, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Oses M, Arenaza L, Amasene M, Labayen I. Changes in lifestyle behaviours during the COVID-19 confinement in Spanish children: A longitudinal analysis from the MUGI project. Pediatr Obes. 2021;16(4):e12731.
Neville RD, Lakes KD, Hopkins WG, Tarantino G, Draper CE, Beck R, et al. Global Changes in Child and Adolescent Physical Activity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2022;176(9):886-94.
Pietiläinen KH, Kaprio J, Borg P, Plasqui G, Yki-Järvinen H, Kujala UM, et al. Physical inactivity and obesity: a vicious circle. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16(2):409-14.
Moynihan AB, van Tilburg WA, Igou ER, Wisman A, Donnelly AE, Mulcaire JB. Eaten up by boredom: consuming food to escape awareness of the bored self. Front Psychol. 2015;6:369.
Farello G, D’Andrea M, Quarta A, Grossi A, Pompili D, Altobelli E, et al. Children and Adolescents Dietary Habits and Lifestyle Changes during COVID-19 Lockdown in Italy. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):2135.
Rundle AG, Park Y, Herbstman JB, Kinsey EW, Wang YC. COVID-19–Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain Among Children. Obesity. 2020;28(6):1008-9.
Wang YC, Vine S, Hsiao A, Rundle A, Goldsmith J. Weight-Related Behaviors When Children Are in School Versus on Summer Breaks: Does Income Matter? J Sch Health. 2015;85(7):458-66.
von Hippel PT, Powell B, Downey DB, Rowland NJ. The Effect of School on Overweight in Childhood: Gain in Body Mass Index During the School Year and During Summer Vacation. Am J Public Health. 2007;97(4):696-702.
Franckle R, Adler R, Davison K. Accelerated Weight Gain Among Children During Summer Versus School Year and Related Racial/Ethnic Disparities: A Systematic Review. Prev Chronic Dis. 2014;11:E101.
Pujia R, Ferro Y, Maurotti S, Khoory J, Gazzaruso C, Pujia A, et al. The Effects of COVID-19 on the Eating Habits of Children and Adolescents in Italy: A Pilot Survey Study. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2641.
Heinberg LJ, Steffen K. Social Isolation and Loneliness During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact on Weight. Curr Obes Rep. 2021;10(3):365-70.
Bakaloudi DR, Jeyakumar DT, Jayawardena R, Chourdakis M. The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on snacking habits, fast-food and alcohol consumption: A systematic review of the evidence. Clin Nutr. 2021;S0261-5614(21)00212-0. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.020.
Gurnani M, Birken C, Hamilton J. Childhood Obesity: Causes, Consequences, and Management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2015;62(4):821-40.
Kansra AR, Lakkunarajah S, Jay MS. Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: A Review. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:581461.
Nittari G, Scuri S, Sagaro GG, Petrelli F, Grappasonni I. Epidemiology of Obesity in Children and Adolescents. In: Firstenberg MS, Stawicki SP, editor. Teamwork in Healthcare. London; 2020.
Jia P, Zhang L, Yu W, Yu B, Liu M, Zhang D, et al. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on activity patterns and weight status among youths in China: the COVID-19 Impact on Lifestyle Change Survey (COINLICS). Int J Obes (Lond). 2021;45(3):695-9.
Jenssen BP, Kelly MK, Powell M, Bouchelle Z, Mayne SL, Fiks AG. COVID-19 and Changes in Child Obesity. Pediatrics. 2021;147(5):e2021050123.
Chang TH, Chen YC, Chen WY, Chen CY, Hsu WY, Chou Y, et al. Weight Gain Associated with COVID-19 Lockdown in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13(10):3668.
La Fauci G, Montalti M, Di Valerio Z, Gori D, Salomoni MG, Salussolia A, et al. Obesity and COVID-19 in Children and Adolescents: Reciprocal Detrimental Influence-Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(13):7603.
Agha AEA, Alharbi RS, Almohammadi OA, Yousef SY, Sulimani AE, Alaama RA. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic control in children and adolescents. Saudi Medical Journal. 2021;42(1):44.
Azoulay E, Yackobovitch-Gavan M, Yaacov H, Gilboa I, Lopez A, Sheppes T, et al. Weight Status and Body Composition Dynamics in Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:707773.
Brooks CG, Spencer JR, Sprafka JM, Roehl KA, Ma J, Londhe AA, et al. Pediatric BMI changes during COVID-19 pandemic: An electronic health record-based retrospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine. 2021;38:101026.
Ghozy S, Abdelaal A, Shah J, Parker KE, Islam SMS. COVID-19 and physical inactivity: Teetering on the edge of a deadlier pandemic? J Glob Health. 2021;11:03031.
Popkin BM, Du S, Green WD, Beck MA, Algaith T, Herbst CH, et al. Individuals with obesity and COVID-19: A global perspective on the epidemiology and biological relationships. Obes Rev. 2020;21(11):e13128.
Gold MS, Sehayek D, Gabrielli S, Zhang X, McCusker C, Ben-Shoshan M. COVID-19 and comorbidities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Postgrad Med. 2020;132(8):749-55.
Shuvo SD, Hossain MS, Riazuddin M, Mazumdar S, Roy D. Factors influencing low-income households’ food insecurity in Bangladesh during the COVID-19 lockdown. PLoS One. 2022;17(5):e0267488.
Baird S, Jones N, Goel N, Dutton R, Oakley E, Presler-Marshall E, Yadete W. Adolescent well-being in the time of COVID-19. Adolescent Well-being: Background Papers for Multi-stakeholder Consultations Geneva: Partnership for Maternal, Newborn & Child Health. 2021.
Laborde D, Martin W, Swinnen J, Vos R. COVID-19 risks to global food security. Science. 2020;369(6503):500-2.
Rezaul Karim KM, Tasnim T. Impact of lockdown due to COVID-19 on nutrition and food security of the selected lowincome households in Bangladesh. Heliyon. 2022;8(5):e09368.
Gundersen C, Ziliak JP. Food Insecurity And Health Outcomes. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(11):1830-9.
Hawke LD, Szatmari P, Cleverley K, Courtney D, Cheung A, Voineskos AN, et al. Youth in a pandemic: a longitudinal examination of youth mental health and substance use concerns during COVID-19. BMJ Open. 2021;11(10):e049209.
Layman HM, Thorisdottir IE, Halldorsdottir T, Sigfusdottir ID, Allegrante JP, Kristjansson AL. Substance Use Among Youth During the COVID-19 Pandemic: a Systematic Review. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2022;24(6):307-24.
Temple JR, Baumler E, Wood L, Guillot-Wright S, Torres E, Thiel M. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Adolescent Mental Health and Substance Use. J Adolesc Health. 2022;71(3):277-84.
Kaplow JB, Curran PJ, Dodge KA. Child, parent, and peer predictors of early-onset substance use: a multisite longitudinal study. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2002;30(3):199-216.
Jones EAK, Mitra AK, Bhuiyan AR. Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health in Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(5):2470.
Liu JJ, Bao Y, Huang X, Shi J, Lu L. Mental health considerations for children quarantined because of COVID-19. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2020;4(5):347-9.
Loades ME, Chatburn E, Higson-Sweeney N, Reynolds S, Shafran R, Brigden A, et al. Rapid Systematic Review: The Impact of Social Isolation and Loneliness on the Mental Health of Children and Adolescents in the Context of COVID-19. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2020;59(11):1218-39.e3.
Orgilés M, Morales A, Delvecchio E, Mazzeschi C, Espada JP. Immediate Psychological Effects of the COVID-19 Quarantine in Youth From Italy and Spain. Front Psychol. 2020;11:579038.
Qin Z, Shi L, Xue Y, Lin H, Zhang J, Liang P, et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated With Self-reported Psychological Distress Among Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic in China. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2035487.
Panda PK, Gupta J, Chowdhury SR, Kumar R, Meena AK, Madaan P, et al. Psychological and Behavioral Impact of Lockdown and Quarantine Measures for COVID-19 Pandemic on Children, Adolescents and Caregivers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Trop Pediatr. 2021;67(1):fmaa122.
Bobo E, Lin L, Acquaviva E, Caci H, Franc N, Gamon L, et al. How do children and adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) experience lockdown during the COVID-19 outbreak?. Encephale. 2020;46(3s):S85-S92.
Zijlmans J, Teela L, van Ewijk H, Klip H, van der Mheen M, Ruisch H, et al. Mental and Social Health of Children and Adolescents With Pre-existing Mental or Somatic Problems During the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:692853.
Charpignon M-L, Ontiveros J, Sundaresan S, Puri A, Chandra J, Mandl KD, et al. Evaluation of Suicides Among US Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Pediatr. 2022;176(7):724-6.
Goto R, Okubo Y, Skokauskas N. Reasons and trends in youth’s suicide rates during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2022;27:100567.
Kazi F, Mushtaq A. Adolescents navigating the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2021;5(10):692-3.
Lantos JD, Yeh H-W, Raza F, Connelly M, Goggin K, Sullivant SA. Suicide Risk in Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pediatrics. 2022;149(2):e2021053486.
Arundell L, Salmon J, Timperio A, Sahlqvist S, Uddin R, Veitch J, et al. Physical activity and active recreation before and during COVID-19: The Our Life at Home study. J Sci Med Sport. 2022;25(3):235-41.
Bakaloudi DR, Barazzoni R, Bischoff SC, Breda J, Wickramasinghe K, Chourdakis M. Impact of the first COVID-19 lockdown on body weight: A combined systematic review and a metaanalysis. Clin Nutr. 2021;S0261-5614(21)00207-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.015.
Garagiola ER, Lam Q, Wachsmuth LS, Tan TY, Ghali S, Asafo S, et al. Adolescent Resilience during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of the Impact of the Pandemic on Developmental Milestones. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022;12(7):220.
Panchal U, Salazar de Pablo G, Franco M, Moreno C, Parellada M, Arango C, et al. The impact of COVID-19 lockdown on child and adolescent mental health: systematic review. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021:1-27.
Prati G, Mancini AD. The psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns: a review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies and natural experiments. Psychol Med. 2021;51(2):201-11.
Robinson E, Sutin AR, Daly M, Jones A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. J Affect Disord. 2022;296:567-76.
CDC. Post-COVID Conditions. 2021. Accessed 12 September 2022. [Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.
Zimmermann P, Pittet LF, Curtis N. Long covid in children and adolescents. BMJ. 2022;376:o143.
Evans YN, Golub S, Sequeira GM, Eisenstein E, North S. Using Telemedicine to Reach Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J Adolesc Health. 2020;67(4):469-71.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














