An Assessment of the Validity and Reliability of the Social-Media Addiction Screening Scale (S-MASS)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v75i3.261044Keywords:
Assessment, Social Media, Addiction, Screening, TestAbstract
Objective: The excessive use of social media can lead to addiction among many vulnerable individuals. Hence, the utilization of a valid and reliable screening test to assess social media addiction is warranted.
Materials and Methods: The Social-Media Addiction Screening Scale (S-MASS) is a newly developed, self-report screening scale containing 16 items that assess the three main components of behavioral addiction: giving priority, impaired control, and negative consequences. The S-MASS reliability was measured using Cronbachs alpha. An exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) were employed to assess the S-MASS factorial validity. A latent profile analysis (LPA) was also carried out to identify the classes of problematic social media users.
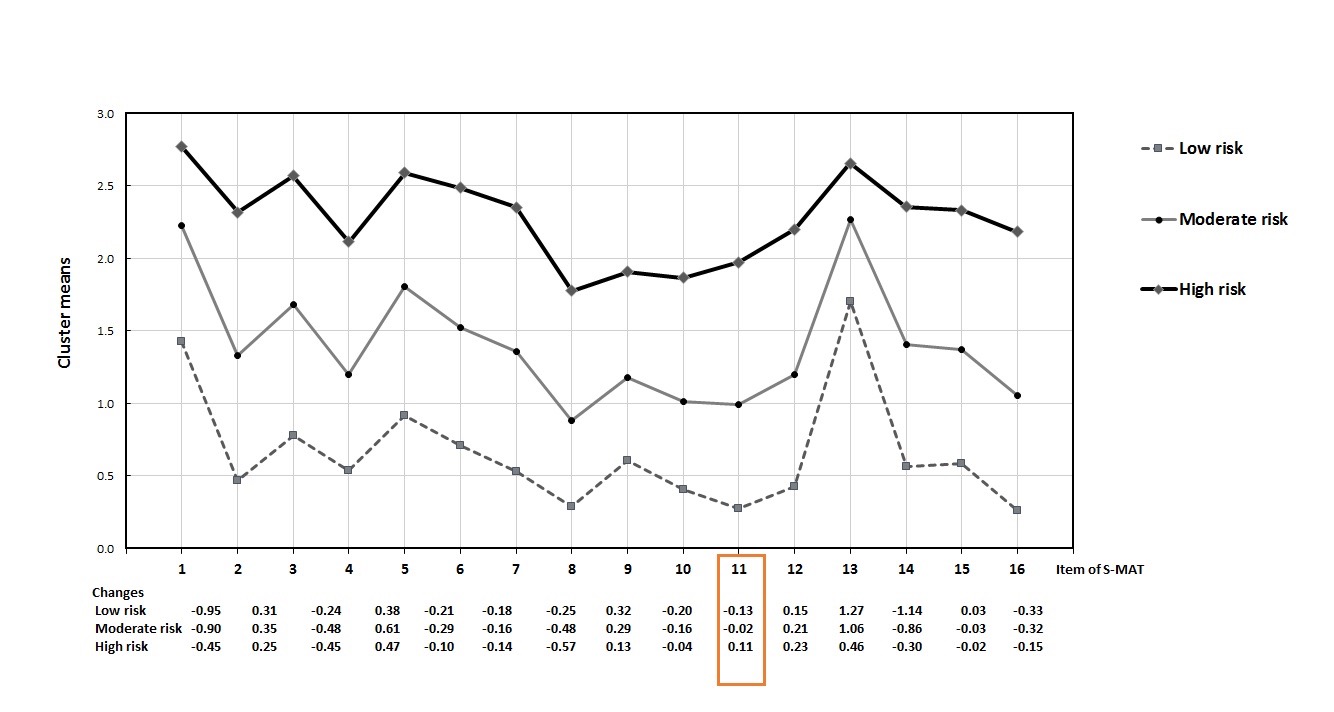
Results: In all, 5,068 participants aged 13 years were recruited from five high schools and an online survey. Cronbachs alpha for the S-MASS was 0.90 (95% CI: 0.890.90), indicating excellent test reliability. The EFA and CFA revealed a good factorial validity for the S-MASS. Based on the LPA, the participants were classed as “lowrisk” (n = 1,227; 24.2%), “moderate-risk” (n = 2,757; 54.4%), and “high-risk” (n = 1,084; 21.4%) problematic social media users. The key differences between these classes were gender, age, necessity to use social media for work, self-perception of addiction, and time spent on social media.
Conclusion: The S-MASS is a valid and reliable screening scale for social media addiction. The criterion validity of the S-MASS should be evaluated once formal diagnostic criteria for social media addiction become available.
References
Georgiev D. How Much Time Do People Spend on Social Media? 2022 [Available from: https://review42.com/how-much-time-do-people-spend-on-social-media/.
Andreassen CS. Online social network site addiction: A comprehensive review. Current Addiction Reports. 2015;2(2):175-84.
Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z. Social networking addiction: An overview of preliminary findings. In: Kenneth PR, Laura CF, editors. Behavioral Addictions: criteria, evidence, and treatment: Academic Press; 2014. p. 119-41.
Hou Y, Xiong D, Jiang T, Song L, Wang Q. Social media addiction: Its impact, mediation, and intervention. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace. 2019;13(1).
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, et al. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: A large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252-62.
Robinson A, Bonnette A, Howard K, Ceballos N, Dailey S, Lu Y, et al. Social comparisons, social media addiction, and social interaction: An examination of specific social media behaviors related to major depressive disorder in a millennial population. Journal of Applied Biobehavioral Research. 2019;24(1):e12158.
Shensa A, Sidani JE, Dew MA, Escobar-Viera CG, Primack BA. Social media use and depression and anxiety symptoms: A cluster analysis. Am J Health Behav. 2018;42(2):116-28.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
World Health Organization. ICD-11 for mortality and morbidity statistics 2018 [Available from: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/1448597234.
Karim R, Chaudhri P. Behavioral Addictions: An Overview. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2012;44(1):5-17.
Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Instagram addiction and the Big Five of personality: The mediating role of self-liking. J Behav Addict. 2018;7(1):158-70.
Smith MA. Social learning and addiction. Behav Brain Res. 2021;398:112954.
Wang X. Mobile SNS Addiction as A Learned Behavior: A Perspective from Learning Theory. Media Psychology. 2020;23(4):461-92.
Wilson K, Fornasier S, White KM. Psychological predictors of young adults' use of social networking sites. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2010;13(2):173-7.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2011;14(11):631-5.
Andreassen C, Torsheim T, Brunborg G, Pallesen S. Utvikling av en Facebook-avhengighetsskala. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501-17.
Turel O, Serenko A. The benefits and dangers of enjoyment with social networking websites. European Journal of Information Systems. 2012;21(5):512-28.
Wolniczak I, Caceres-DelAguila JA, Palma-Ardiles G, Arroyo KJ, Solís-Visscher R, Paredes-Yauri S, et al. Association between Facebook dependence and poor sleep quality: a study in a sample of undergraduate students in Peru. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59087.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2013;16(4):279-84.
Wu AM, Cheung VI, Ku L, Hung EP. Psychological risk factors of addiction to social networking sites among Chinese smartphone users. J Behav Addict. 2013;2(3):160-6.
Al-Menayes J. Psychometric properties and validation of the Arabic social media addiction scale. J Addict. 2015;2015:291743.
Phanasathit M, Manwong M, Hanprathet N, Khumsri J, Yingyeun R. Validation of the Thai version of Bergen Facebook addiction scale (Thai-BFAS). J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98:108-17.
Dantlgraber M, Wetzel E, Schützenberger P, Stieger S, Reips U-D. Simple construct evaluation with latent class analysis: An investigation of Facebook addiction and the development of a short form of the Facebook Addiction Test (F-AT). Behav Res Methods. 2016;48(3):869-79.
van den Eijnden RJ, Lemmens JS, Valkenburg PM. The Social Media Disorder Scale. Computers in Human Behavior. 2016;61:478-87.
Monacis L, De Palo V, Griffiths MD, Sinatra M. Social networking addiction, attachment style, and validation of the Italian version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale. J Behav Addict. 2017;6(2):178-86.
Chung-Ying Lin AB, Per Nilsen, Mark D Griffiths, Amir H Pakpour. Psychometric validation of the Persian Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale using classic test theory and Rasch models. J Behav Addict. 2017;6(4):620-9.
Liu C, Ma J. Development and validation of the Chinese social media addiction scale. Personality and Individual Differences. 2018;134:55-9.
Savci M, Ercengiz M, Aysan F. Turkish adaptation of the Social Media Disorder Scale in adolescents. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2018;55(3):248-55.
Bouna-Pyrrou P, Aufleger B, Braun S, Gattnar M, Kallmayer S, Wagner H, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal evaluation of the social network use disorder and internet gaming disorder criteria. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:692.
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JM, et al. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive behavior instruments among Hong Kong university students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117-28.
Fung SF. Cross-cultural validation of the Social Media Disorder scale. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2019;12:683-90.
Bendayan R, Blanca Mena MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook intrusion questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204-9.
Shahnawaz MG, Rehman U. Social Networking Addiction Scale. Cogent Psychology. 2020;7(1):1832032.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®): American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Ko CH, Yen JY, Chen SH, Wang PW, Chen CS, Yen CF. Evaluation of the diagnostic criteria of Internet gaming disorder in the DSM-5 among young adults in Taiwan. J Psychiatr Res. 2014;53:103-10.
Tavakol M, Dennick R. Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. Int J Med Educ. 2011;2:53-5.
Brown TA. Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research: Guilford publications; 2015.
Griffiths M. A ‘components’ model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. Journal of Substance Use. 2005;10(4):191-7.
Kaiser HF, Rice J. Little Jiffy, Mark IV. Educational and psychological measurement. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1974;34(1):111-7.
Young K. Internet addiction: diagnosis and treatment considerations. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy. 2009;39(4):241-6.
Tang CS-K, Koh YYW. Online social networking addiction among college students in Singapore: Comorbidity with behavioral addiction and affective disorder. Asian J Psychiatr. 2017;25:175-8.
Khumsri J, Yingyeun R, Mereerat M, Hanprathet N, Phanasathit M. Prevalence of Facebook Addiction and Related Factors Among Thai High School Students. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98:S51-60.
Bányai F, Zsila Á, Király O, Maraz A, Elekes Z, Griffiths MD, et al. Problematic Social Media Use: Results from a Large-Scale Nationally Representative Adolescent Sample. PloS One. 2017;12(1):e0169839.
Cheng C, Lau Y-C, Chan L, Luk JW. Prevalence of social media addiction across 32 nations: Meta-analysis with subgroup analysis of classification schemes and cultural values. Addict Behav. 2021;117:106845.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














