The Effect of The Thai Herbal Wattana Formula on Platelet Aggregation and The Relationship with Innate Dhatu Chao Ruean
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v75i5.261536Keywords:
Thai Herbal Wattana formula, WNF, Herbal medicine, Platelet aggregation, innate Dhatu Chao RueanAbstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of the WNF on platelet aggregation and find a link between iDCR factors and platelet aggregation.
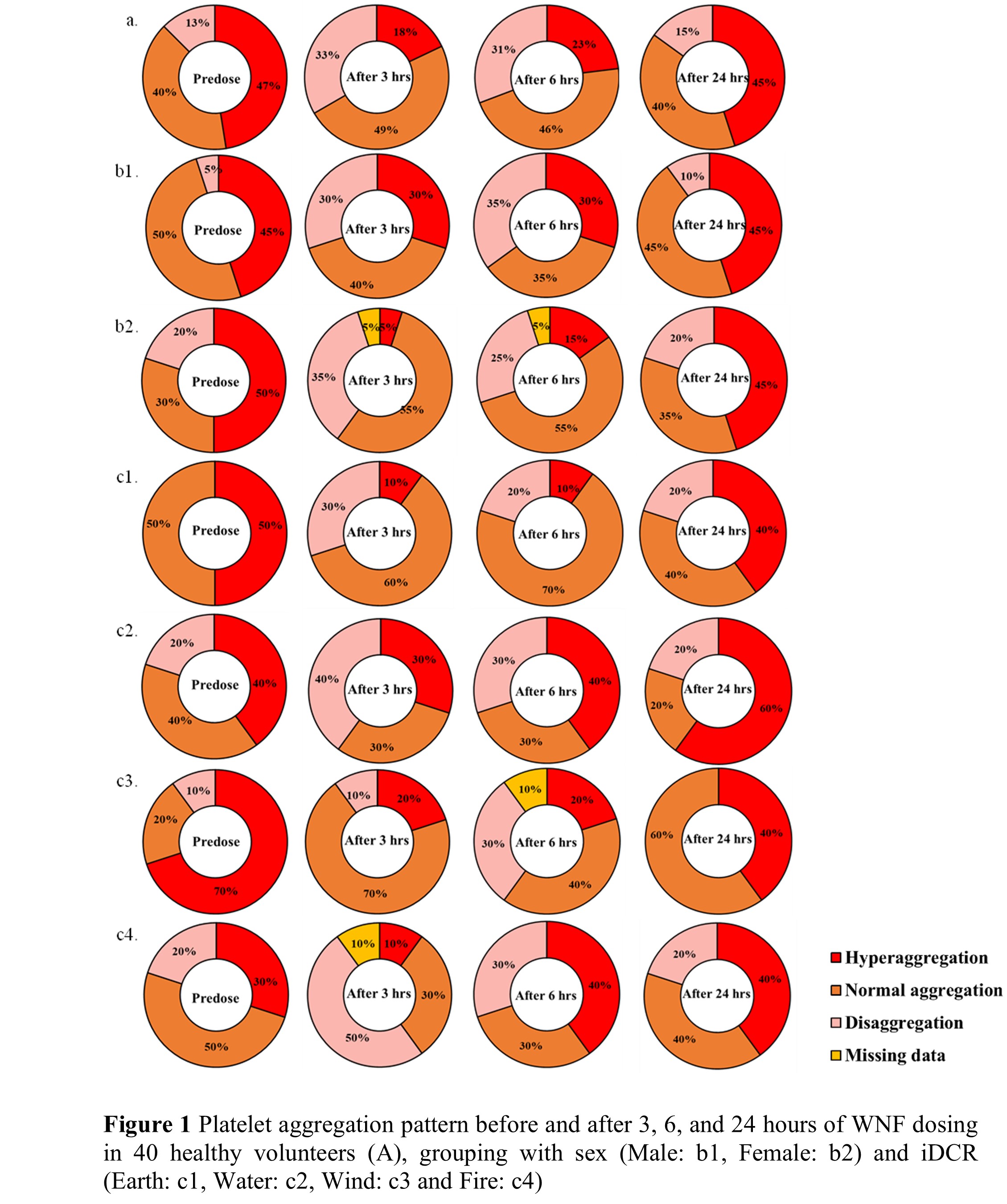
Materials and Methods: Forty healthy volunteers with different iDCRs (Earth, Water, Wind, and Fire) received a single dose of 1,000 mg WNF. A blood sample was taken before and after the WNF administration at 3, 6, and 24 hours for analysis of platelet aggregation by aggregometry. Epinephrine, adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and collagen were used as platelet agonists.
Results: The WNF affects platelet aggregation in some subjects, especially females with an Earth iDCR or Wind iDCR with hyperaggregation patterns at baseline. The result after WNF treatment revealed that the percentage of platelet aggregation significantly changed downward at 3 hours and then recovered to pre-dosing levels after 24 hours. Additionally, it also did not have any relationship to iDCR. There were no reported adverse drug events.
Conclusion: WNF should be used with caution in patients with blood diseases and a close eye should be kept on herb-drug interactions such as with aspirin or other NSAIDs.
References
Laohapand T and Jaturatamrong U, Thai Traditional Medicine in the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Ayurved Thamrong School, Center of Applied Thai Traditional Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University. Bangkok: Supavanich Press; 2009.
Panich U, Pluemsamran T, Tangsupa-a-nan V, Wattanarangsan J, Phadungrakwittaya R, Akarasereenont P, et al. Protective effect of AVS073, a polyherbal formula, against UVA-induced melanogenesis through a redox mechanism involving glutathione-related antioxidant defense. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013;13:159.10 page.
Duangsa-ard S, Wongkajornsilp A, Akarasereenont P, Huabprasert S, Chongputtharaksa T, Laohapand T. The effects of Ayurved Siriraj Wattana recipe on splenocytes in Wistar rat. Siriraj Med J. 2013;65(3):73-6.
Wongkajornsilp A, Numchaisermsuk N, Sa-ngiamsuntorn K, Akarasereenont P, Wamanuttajinda V, Kasetsinsombat K, et al. Effects of the Ayurved Siriraj Wattana recipe on functional and phenotypic characterization of cytokine-induced killer cells and dendritic cells in vitro. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16(489):11 page.
Htoo HH, Limsuvan S, Thamsermsang O, Hernandez JF, Checler F, Govitrapong P, Pakaprot N, Akarasereenont P, Vincent B. The Polyherbal Wattana Formula Displays Anti-Amyloidogenic Properties by Increasing α-Secretase Activities. Plos One. 2017;1-17.
Charoenkij P, Palo T, Chotewuttakorn S, Limsuvan S, Laohapand T, Akarasereenont P. The effect of Ayurved Siriraj Wattana Recipe (AVS073) on LPS induced COX-2 expression in human PBMC. Siriraj Med J. 2016;68(2):90-6.
Pengkhum T, Chatsiricharoenkul S, Akarasereenont P, Charoencholvanich K. Phase II clinical trial of Ayurved Siriraj Wattana recipe for symptomatic relief in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012; 95(3):452-60.
Schafer AI. Effects of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs on platelet function and systemic hemostasis. J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;35(3):209-19.
Cattaneo M. Light Transmission Aggregometry and ATP Release for the Diagnostic Assessment of Platelet Function. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2009;35:158–67.
Ketsa-Ard K, Poungvarin N, Juengchareon M, Jarerat S, Kittigul L. Clinical study on antithrombotic effects of ticlopidine in ischemic stroke. J Med Assoc Thai. 1991 Jun;74(6):331-9.
Akarasereenont P, Tripatara P, Chotewuttakorn S, Palo T, Thaworn A. The effects of estrone, estradiol and estriol on platelet aggregation induced by adrenaline and adenosine diphosphate. Platelets. 2006 Jan 1;17(7):441-7.
Femia EA, Scavone M, Lecchi A, Cattaneo M. Effect of platelet count on platelet aggregation measured with impedance aggregometry (multiplate analyzer) and with light transmission aggregometry. J Thromb Haemost. 2013; 11:2193–6.
Yee DL, Bergeron AL, Sun CW, Dong JF, Bray PF. Platelet hyperreactivity generalizes to multiple forms of stimulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2006 Sep;4(9):2043-50.
Sirikarin T, Palo T, Chotewuttakorn S, Chandranipapongse W, Limsuvan S, Akarasereenont P. The Effects of Andrographis paniculata on Platelet Activity in Healthy Thai Volunteers. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Aug 6; 2018:2458281.
Huang D, Lu Y, Shi L, Zhang J, Shen J, Bao M, et al. Effect of safflower yellow on platelet activating factor mediated platelet activation in patients with coronary heart disease. Bangladesh J Pharmacol. 2012; 7:140-4.
Lu PH, Kuo CY, Chan CC, Wang LK, Chen ML, Tzeng IS, Tsai FM. Safflower Extract Inhibits ADP-Induced Human Platelet Aggregation. Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 11;10(6):1192.
Li HX, Han SY, Wang XW, Ma X, Zhang K, Wang L, Ma ZZ, Tu PF. Effect of the carthamins yellow from Carthamus tinctorius L. on hemorheological disorders of blood stasis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009 Aug;47(8):1797-802.
Chang Y, Huang SKH, Lu WJ, Chung CL, Chen WL, Lu SH, et al. Brazilin isolated from Caesalpinia sappan L. acts as a novel collagen receptor agonist in human platelets. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20(4):11 page.
Seo EJ, Lee DU, Kwakf JH, Lee SM, Kimg YS, Jung YS. Antiplatelet effects of Cyperus rotundus and its component (+)-nootkatone. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;135(1):48-54.
Son DJ, Akiba S, Hong JT, Yun YP, Hwang SY, Park YH, Lee SE. Piperine Inhibits the Activities of Platelet Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 and Thromboxane A2 Synthase without Affecting Cyclooxygenase-1 Activity: Different Mechanisms of Action Are Involved in the Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation and Macrophage Inflammatory Response. Nutrients. 2014:6:3336-52.
Haq MZU, Shahid SA, Ahmed S, Ahmad S, Qayum M, Khan I. Anti-platelet activity of methanolic extract of Grewia asiatica L. leaves and Terminalla chebula Retz. fruits. J Med Plants Res. 2012;6(10):2029-32.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














