Integrative Health Promotion Model in Leprosy Prevention and Control Programs to Improve Quality of Life for Leprosy Survivors
Integrative Health Promotion Model in Leprosy Prevention
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v75i9.263011Keywords:
Leprosy survivors, quality of life, prevention and controlAbstract
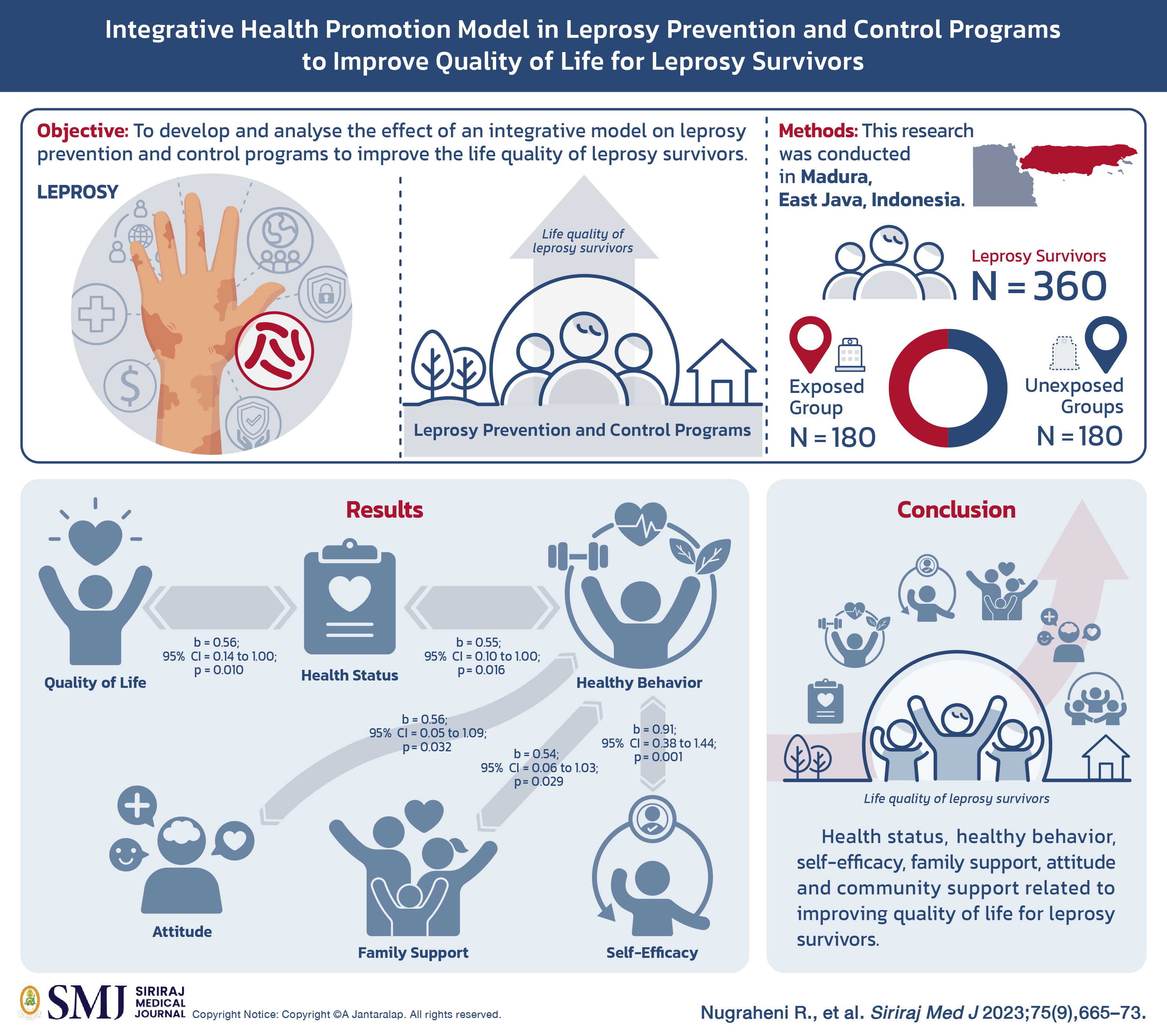
Objective: Leprosy is an infectious disease that causes highly complex problems from the medical aspect to social, economic, cultural, security, and national defence issues. This research aimed to develop and analyse the effect of an integrative model on leprosy prevention and control programs to improve the life quality of leprosy survivors.
Materials and Methods: This research was conducted in Madura, East Java, Indonesia. The study consists of 360 leprosy survivors. The exposed group in this study was a group of leprosy survivors living within the areas of the Ministry of Health's leprosy program, a total of 180 leprosy survivors. The unexposed groups were leprosy survivors living around the areas with the absence of Ministry of Health leprosy program, a total of 180 leprosy survivors.
Results: The quality of life has a direct and positive relationship with health status (b= 0.56 ; 95% CI = 0.14 to 1.00; p=0.010), health status has a direct and positive relationship with healthy behavior (b= 0.55 ; 95% CI = 0.10 to 1.00; p=0.016), healthy behavior has a direct and positive relationship with self-efficacy (b= 0.91 ; 95% CI = 0.38 to 1.44; p=0.001), healthy behavior has a direct and positive relationship with family support (b= 0.54; 95% CI = 0.06 to 1.03; p=0.029), healthy behavior has a direct and positive relationship with attitude (b= 0.56 ; 95% CI = 0.05 to 1.09; p=0.032).
Conclusion: Health status, healthy behavior, self-efficacy, family support, attitude and community support related to improving quality of life for leprosy survivors.
References
Joseph G, Rao P. Impact of Leprosy on The Quality of Life. Bull World Health Organ. 1999;77(6):515-7.
Pattanaprichakul P, Chayangsu O, Lertrujiwanit K, Chairatchaneeboon M, Bunyaratavej S. Assessment of Non-Dermatologists’ Knowledge Regarding Clinical Diagnosis of Leprosy and Practice in Slit-Skin Smear as a Basic Investigation. Siriraj Med J. 2015;67(2):66-71.
Tosepu R, Gunawan J, Effendy DS, Fadmi FR. Stigma and increase of leprosy cases in SouthEast Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. Afr Health Sci. 2018;18(1):29-31.
Dwikurniarini D, Dewi IM. PENYAKIT KUSTA DI BANGKALAN PADA ABAD KE-20. MOZAIK J Ilmu-Ilmu Sos dan Hum. 2018;9(1). Available from: https://journal.uny.ac.id/index.php/mozaik/article/view/19406
Correia JC, Golay A, Lachat S, Singh SB, Manandhar V, Jha N, et al. “If you will counsel properly with love, they will listen”: A qualitative analysis of leprosy affected patients’ educational needs and caregiver perceptions in Nepal. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0210955.
Scollard DM. Unfinished business - Leprosy still not defeated. Indian J Med Res [Internet]. 2019;149(1):1-4. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23144490
Nugraheni R. Analisis Konsep Diri Terhadap Kualitas Hidup Penderita Kusta Yang Mengalami Kecacatan Di Rumah Sakit Kusta Kediri. Prev Indones J Public Heal. 2016;1(2). Available from: http://journal2.um.ac.id/index.php/preventia/article/view/2743
RI K. Strategi nasional riset implementasi/operasional untuk mendukung pencegahan dan pengendalian Tuberkulosis, Malaria dan Neglected Tropical Diseases 2016-2019. 2016;39.
Rejeski WJ, Fanning J. Models and theories of health behavior and clinical interventions in aging: A contemporary, integrative approach. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:1007-19.
Rinadewi A., Wieke T, dan SL. Kualitas hidup pasien kusta. Univ Indones. 2018;1(1).
Tsutsumi A, Izutsu T, Md Islam A, Maksuda AN, Kato H, Wakai S. The quality of life, mental health, and perceived stigma of leprosy patients in Bangladesh. Sos Sci Med. 2007;64(12):2443-53.
Muntasir M, Salju E V, Rulianti LP. Studi Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Penyakit Kusta Pada Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Bakunase Kota Kupang Tahun 2017. J INFO Kesehat. 2018;16(2). Available from: https://jurnal.poltekeskupang.ac.id/index.php/infokes/article/view/223
Palant A, Himmel W. Are there also negative effects of social support? A qualitative study of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. BMJ Open. 2019;9(1):e022642.
Mostafavi F, Masoudi R, Hassanzadeh A, Rabiei L. The effect of family-based intervention on empowerment of the elders. J Educ Health Promot. 2013;2:24.
Jimenez DE, Thomas L, Bartels SJ. The role of serious mental illness in motivation, participation and adoption of health behavior change among obese/sedentary Latino adults. Ethn Health. 2019;24(8):889-96.
Hoffman AJ. Enhancing Self-Efficacy for Optimized Patient Outcomes through the Theory of Symptom Self-Management. Cancer Nurs [Internet]. 2013;36(1):E16-E26. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3624763/pdf/nihms412728.pdf
Williams D, Rhodes RE. The Confounded Self-Efficacy Construct: Conceptual Analysis, and Recommendations for Future Research. Health Psychol Rev. 2016;10(2):113-28.
Wong ML. Designing Programmes to address stigma in leprosy: Issues and challenges. Asia Pacific Disability Rehabilitation Journal. 2004;15(2):3-12.
Sulaeman ES. Model dan Teori Perilaku Kesehatan. Surakarta: UNS Press; 2019.
Taylor DL, Kahawita TM, Cairncross S, Ensink JHJ. The impact of water, sanitation and hygiene interventions to control cholera: A systematic review. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0135676.
Yang C, Xia M, Li T, Zhou Y. How Do Specific Social Supports (Family, Friend, and Specialist) Reduce Stress in Patients With Substance Use Disorders: A Multiple Mediation Analysis. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:618576.
Fink L, Strassner C, Ploeger A. Exploring External Factors Affecting the Intention-Behavior Gap When Trying to Adopt a Sustainable Diet: A Think Aloud Study. Front Nutr. 2021;8:511412.
Wang C, Liu J, Pu R, Li Z, Guo W, Feng Z, et al. Determinants of Subjective Health, Happiness, and Life Satisfaction among Young Adults (18-24 Years) in Guyana. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:9063808.
Liu L, Liu YP, Wang J, An LW, Jiao JM. Use of a knowledge-attitude-behaviour education programme for Chinese adults undergoing maintenance haemodialysis: Randomized controlled trial. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(3):557-68.
Oza BB, Patel BM, Malhotra SD, Patel VJ. Health related quality of life in hypertensive patients in a tertiary care teaching hospital. J Assoc Physicians India. 2014;62(10):22-9.
Zheng Q, Peng Z, Ding S. Financial literacy, health engagement and residents’ health: Evidence from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8):4202.
Yen CF, Cheng CC, Yu L, Tang T-C, Ko C-H, Yen J-Y. Association bertween quality of life and self stigma, insight, and adverse effects of medication in patients with depressive disorder. Depress Anxiety. 2019;26(11):1033-9.
Hammer CC, Brainard J, Hunter PR. Risk factors and risk factor cascades for communicable disease outbreaks in complex humanitarian emergencies: A qualitative systematic review. BMJ Glob Health. 2018;3(4):e000647.
Gill B, Hayes S, Senior C. The effects of family support and gender on mature student engagement in higher education. Front Psychol. 2015;6:156.
Solikhah S, Perwitasari DA, Irham LM, Matahari R. Social Support in Quality of Life among Breast Cancer Patients after Diagnosis : A Bibliometric Analysis. Siriraj Med J. 2023;75(7):529-37.
Anderson EW, White KM. “This Is What Family Does”: The Family Experience of Caring for Serious Illness. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2018;35(2):348-54.
Gopalakrishnan S, Grace GA, Sujitha P, Eashwar VMA. Knowledge, attitude, and health seeking behavior on leprosy among urban adults in Kancheepuram district of Tamil Nadu: A Community‑based cross‑sectional study. J Fam Med Prim Care. 2021;10(5):18951-903.
Kodner DL, Spreeuwenberg C. Integrated care: meaning, logic, applications, and implications – a discussion paper. Int J Integr Care. 2002;2:e12.
Raina SK, Kumar R, Bhota S, Gupta G, Kumar D, Chauhan R, et al. Does temperature and humidity influence the spread of Covid-19?: A preliminary report. J Fam Med Prim Care. 2020;9(4):1811-4.
Menaldi SL, Harini M, Nelfidayani N, Irawati Y, Setiono S, Wahyuni LK, et al. Functional activity limitation of leprosy cases in an endemic area in Indonesia and recommendations for integrated participation program in society. PLoS Negl Trop Dis [Internet]. 2022;16(8):1–13. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0010646
Martos-Casado G, Vives-Cases C, Gil-González D. Community intervention programmes with people affected by leprosy: Listening to the voice of professionals. PLoS Negl Trop Dis [Internet]. 2022;16(3):1–17. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0010335
Abdela SG, van Henten S, Abegaz SH, Bayuh FB, Zewdu FT, Berhe FT, et al. Activity limitation and social participation restriction among leprosy patients in Boru Meda Hospital, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis [Internet]. 2020;14(9):1–12. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0008702
Marahatta SB, Amatya R, Adhikari S, Giri D, Lama S, Kaehler N, et al. Perceived stigma of leprosy among community members and health care providers in Lalitpur district of Nepal: A qualitative study. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0209676.
Thanakiatpinyo T, Dajpratham P, Kovindha A, Kuptniratsaikul V. Quality of Life of Stroke Patients at One Year after Discharge from Inpatient Rehabilitation: A Multicenter Study. Siriraj Med J. 2021;73(4):213-6.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














