Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of the ITM 68Ge/68Ga Generator After its Recommended Shelf-life
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v75i10.264289Keywords:
68Ge/68Ga Generator, 68Ge Breakthrough, 68Ge/68Ga Generator impurities, Gallium-68, 68Ge/68Ga Generator shelf-lifeAbstract
Objective: 68Ga can be routinely produced by a 68Ge/68Ga generator without the need for a cyclotron. It is recommended to replace the 68Ge/68Ga generator after 250 elutions or 12 months of shelf-life whichever endpoint is reached first. However, a 68Ge/68Ga generator that has gone past its recommended lifespan can still be further used as a 68Ga source for 68Ga-labeled radiopharmaceuticals for use in animal experiments. To ensure the quality of 68Ga eluates, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the ITM (Isotope Technologies München) 68Ge/68Ga generator in our institute after its recommended shelf-life.
Materials and Methods: A 21-month-old ITM 68Ge/68Ga generator was eluted using 4.0 ml of 0.05 M HCl. The 68Ga elution yields were calculated, and 68Ge breakthrough was measured at least 48 h after elution in an aliquot amount using a multichannel analyzer (MCA) with a high-purity germanium probe. Metal impurities in the 68Ga eluates were analyzed by ICP-MS.
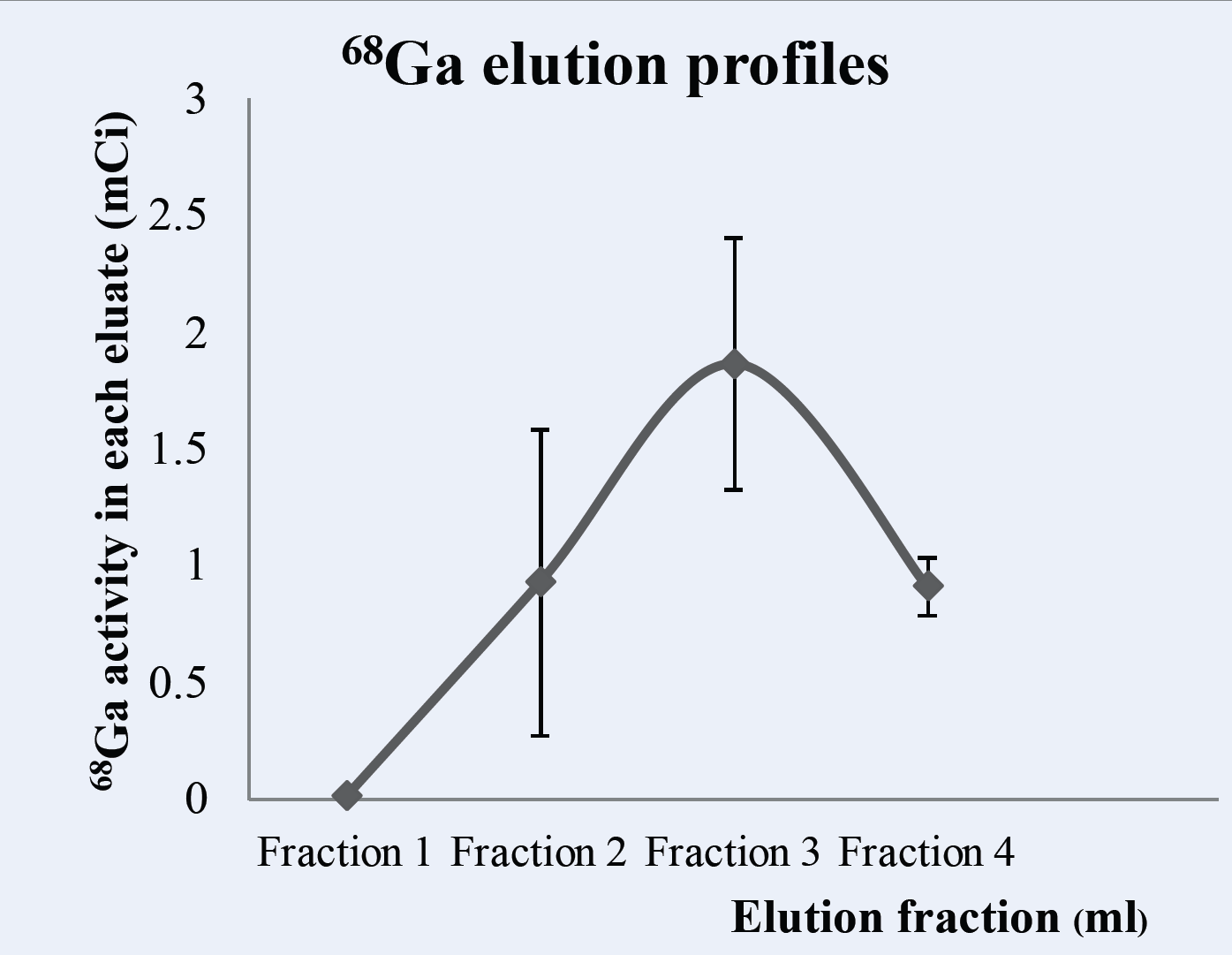
Results: The elution yield of 68Ga was 35.2 ± 8.1%; n = 5 (decay corrected). 68Ge breakthrough from the ITM 68Ge/68Ga generator was below the detectable level. The average amounts of the metallic ions 57Fe, 66Zn, 203Pb, 60Ni, and 63Cu were 18.60, 9.86, 2.42, 0.52, and 0.47 µg/GBq, respectively.
Conclusion: The ITM 68Ge/68Ga generator demonstrated consistent and reliable 68Ga elution profiles with an absence of either 68Ge breakthrough or other metal contaminants in the eluent samples as verified by the manufacturer. The use of the ITM 68Ge/68Ga generator could be extended past its recommended shelf-life to prepare 68Ga radiopharmaceuticals that are considered safe and suitable for use in animal experimentation and other applications.
References
Sarko D, Eisenhut M, Haberkorn U, Mier W. Bifunctional chelators in the design and application of radiopharmaceuticals for oncological diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(17):2667-88.
Schuhmacher J, Zhang H, Doll J, Mäcke HR, Matys R, Hauser H, et al. GRP receptor-targeted PET of a rat pancreas carcinoma xenograft in nude mice with a 68Ga-labeled bombesin(6-14) analog. J Nucl Med. 2005;46(4):691-9.
Jeong JM, Hong MK, Chang YS, Lee Y-S, Kim YJ, Cheon GJ, et al. Preparation of a promising angiogenesis PET imaging agent: 68Ga-labeled c(RGDyK)-isothiocyanatobenzyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid and feasibility studies in mice. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(5):830.
Mier W, Hoffend J, Krämer S, Schuhmacher J, Hull WE, Eisenhut M, et al. Conjugation of DOTA Using Isolated Phenolic Active Esters: The Labeling and Biodistribution of Albumin as Blood Pool Marker. Bioconjug Chem. 2005;16(1):237-40.
Hoffend J, Mier W, Schuhmacher J, Schmidt K, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Strauss LG, et al. Gallium-68-DOTA-albumin as a PET blood-pool marker: experimental evaluation in vivo. Nucl Med Biol. 2005;32(3):287-92.
Baum RP, Prasad V, Müller D, Schuchardt C, Orlova A, Wennborg A, et al. Molecular imaging of HER2-expressing malignant tumors in breast cancer patients using synthetic 111In- or 68Ga-labeled affibody molecules. J Nucl Med. 2010;51(6):892-7.
Werner RA, Bluemel C, Allen-Auerbach MS, Higuchi T, Herrmann K. 68Gallium- and 90Yttrium-/ 177Lutetium: "theranostic twins" for diagnosis and treatment of NETs. Ann Nucl Med. 2015;29(1):1-7.
Eiber M, Weirich G, Holzapfel K, Souvatzoglou M, Haller B, Rauscher I, et al. Simultaneous (68)Ga-PSMA HBED-CC PET/MRI Improves the Localization of Primary Prostate Cancer. Eur Urol. 2016;70(5):829-36.
Prasad V, Steffen IG, Diederichs G, Makowski MR, Wust P, Brenner W. Biodistribution of [(68)Ga]PSMA-HBED-CC in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Characterization of Uptake in Normal Organs and Tumour Lesions. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016;18(3):428-36.
Cytawa W, Seitz AK, Kircher S, Fukushima K, Tran-Gia J, Schirbel A, et al. (68)Ga-PSMA I&T PET/CT for primary staging of prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020;47(1):168-77.
Derlin T, Weiberg D, von Klot C, Wester HJ, Henkenberens C, Ross TL, et al. (68)Ga-PSMA I&T PET/CT for assessment of prostate cancer: evaluation of image quality after forced diuresis and delayed imaging. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(12):4345-53.
Antunes P, Ginj M, Zhang H, Waser B, Baum RP, Reubi JC, et al. Are radiogallium-labelled DOTA-conjugated somatostatin analogues superior to those labelled with other radiometals? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34(7):982-93.
Reubi JC, Schär JC, Waser B, Wenger S, Heppeler A, Schmitt JS, et al. Affinity profiles for human somatostatin receptor subtypes SST1-SST5 of somatostatin radiotracers selected for scintigraphic and radiotherapeutic use. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000;27(3):273-82.
Hofmann M, Maecke H, Börner R, Weckesser E, Schöffski P, Oei L, et al. Biokinetics and imaging with the somatostatin receptor PET radioligand (68)Ga-DOTATOC: preliminary data. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001;28(12):1751-7.
Kowalski J, Henze M, Schuhmacher J, Mäcke HR, Hofmann M, Haberkorn U. Evaluation of positron emission tomography imaging using [68Ga]-DOTA-D Phe(1)-Tyr(3)-Octreotide in comparison to [111In]-DTPAOC SPECT. First results in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Mol Imaging Biol. 2003;5(1):42-8.
Wild D, Mäcke HR, Waser B, Reubi JC, Ginj M, Rasch H, et al. 68Ga-DOTANOC: a first compound for PET imaging with high affinity for somatostatin receptor subtypes 2 and 5. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32(6):724.
Wild D, Schmitt JS, Ginj M, Mäcke HR, Bernard BF, Krenning E, et al. DOTA-NOC, a high-affinity ligand of somatostatin receptor subtypes 2, 3 and 5 for labelling with various radiometals. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30(10):1338-47.
Kratochwil C, Flechsig P, Lindner T, Abderrahim L, Altmann A, Mier W, et al. (68)Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(6):801-5.
Spreckelmeyer S, Balzer M, Poetzsch S, Brenner W. Fully-automated production of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-46 for clinical application. EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry. 2020;5(1):31.
Lin M, Waligorski GJ, Lepera CG. Production of curie quantities of (68)Ga with a medical cyclotron via the (68)Zn(p,n)(68)Ga reaction. Appl Radiat Isot. 2018;133:1-3.
Rodnick ME, Sollert C, Stark D, Clark M, Katsifis A, Hockley BG, et al. Cyclotron-based production of (68)Ga, [(68)Ga]GaCl(3), and [(68)Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 from a liquid target. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2020;5(1):25.
Velikyan I. 68Ga-Based radiopharmaceuticals: production and application relationship. Molecules. 2015;20(7):12913-43.
Romero E, Martínez A, Oteo M, Ibañez M, Santos M, Morcillo MÁ. Development and long-term evaluation of a new 68Ge/68Ga generator based on nano-SnO2 for PET imaging. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12756.
M. Harfensteller, R. Henkelmann, J. Moreno, O. Leib, T. August, O. Buck, T. Nikula. Gallium-68 a candidate for use in clinical routine. February 3, 2010, CERN.
Eppard E, Loktionova NS, Rösch F. Quantitative online isolation of68Ge from68Ge/68Ga generator eluates for purification and immediate quality control of breakthrough. Appl Radiat Isot 2013;82:45-48.
Chakravarty R, Chakraborty S, Ram R, Vatsa R, Bhusari P, Shukla J, et al. Detailed evaluation of different (68)Ge/(68)Ga generators: an attempt toward achieving efficient (68)Ga radiopharmacy. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2016;59(3):87-94.
Uğur A, Yaylali O, Yüksel D. Examination of metallic impurities of 68Ge/68Ga generators used for radioactive labeling of peptides in clinical PET applications. Nucl Med Commun. 2021;42(1):81-85.
Amor-Coarasa A, Kelly JM, Gruca M, Nikolopoulou A, Vallabhajosula S, Babich JW. Continuation of comprehensive quality control of the itG 68Ge/68Ga generator and production of 68Ga-DOTATOC and 68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC for clinical research studies. Nucl Med Biol. 2017;53:37-39.
Asti M, De Pietri G, Fraternali A, Grassi E, Sghedoni R, Fioroni F, et al. Validation of 68Ge/68Ga generator processing by chemical purification for routine clinical application of 68Ga-DOTATOC. Nucl Med Biol. 2008;35:721-4.
Amor-Coarasa A, Milera A, Carvajal D, Gulec S, McGoron AJ. Lyophilized Kit for the Preparation of the PET Perfusion Agent [(68)Ga]-MAA. Int J Mol Imaging. 2014;2014:269365.
Lückerath K, Stuparu AD, Wei L, Kim W, Radu CG, Mona CE, et al. Detection Threshold and Reproducibility of 68Ga-PSMA11 PET/CT in a Mouse Model of Prostate Cancer. J Nucl Med. 2018;59(9):1392-7.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














