Vitamin D Deficiency as a Factor Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i1.265476Keywords:
Cognitive impairment, type 2 diabetes mellitus, vitamin DAbstract
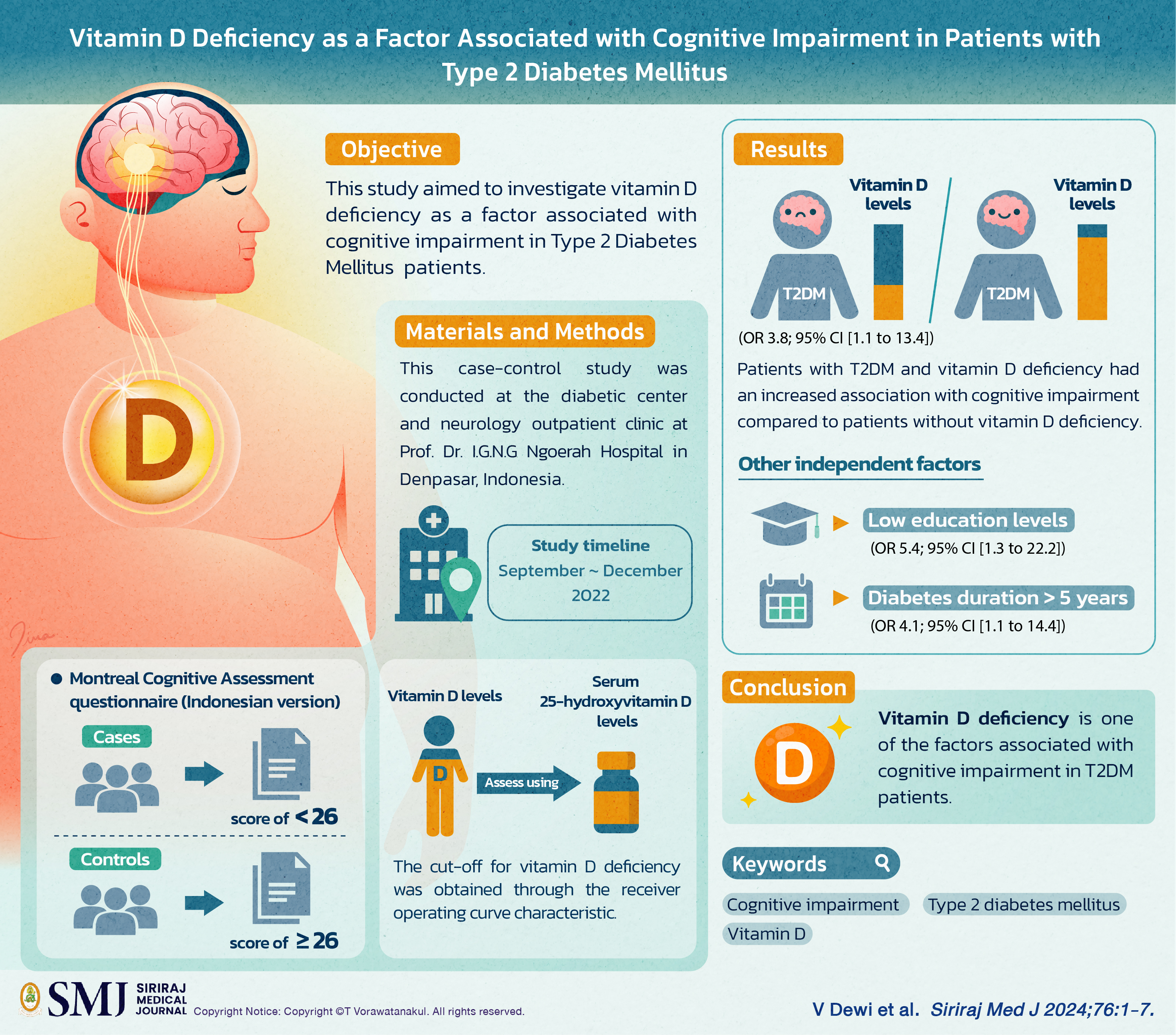
Objective: Vitamin D as an essential nutrient is increasingly being studied and reported to have roles in diabetes and cognitive function through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective functions. This study aimed to investigate vitamin D deficiency as a factor associated with cognitive impairment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients.
Materials and Methods: This case-control study was conducted at the diabetic center and neurology outpatient clinic at Prof. Dr. I.G.N.G Ngoerah Hospital in Denpasar, Indonesia between September and December 2022. Cases had a score of < 26 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment questionnaire (Indonesian version) controls had a score ≥26. Vitamin D levels were assessed using serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. The cut-off for vitamin D deficiency was obtained through the receiver operating curve characteristic.
Results: In total 31 cases and 31 controls were included. The cut-off for vitamin D deficiency was <24.6 ng/ml. Patients with T2DM and vitamin D deficiency had an increased association with cognitive impairment (OR 3.8; 95% CI [1.1 to 13.4]) compared to patients without vitamin D deficiency. Other independent factors associated with cognitive impairment in T2DM were low education levels (OR 5.4; 95% CI [1.3 to 22.2]) and diabetes duration of more than 5 years (OR 4.1; 95% CI [1.1 to 14.4]).
Conclusion: Vitamin D deficiency is one of the factors associated with cognitive impairment in T2DM patients.
References
Mehrabian S, Raycheva M, Gateva A, Todorova G, Angelova P, Traykova M, et al. Cognitive dysfunction profile and arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes. J Neurol Sci 2012;322:152-156.
Saedi E, Gheini MR, Faiz F, Arami MA. Diabetes mellitus and cognitive impairments. World J Diabetes 2016;7:412-422.
Mudanayasa IK. Diabetes Melitus Tipe 2 sebagai Faktor Risiko Gangguan Fungsi Kognitif pada Usia Dewasa Muda. 2012.
Mathieu C. Vitamin D and diabetes: where do we stand? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;108:201-209.
Vondra K, Hampl R. Vitamin D and new insights into pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 2021;42:203-208.
Berridge MJ. Vitamin D deficiency and diabetes. Biochem J 2017;474:1321-1332.
Rui-Hua C, Yong-de P, Xiao-Zhen J, Chen J, Bin Z. Decreased levels of serum IGF-1 and vitamin D are associated with cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am J Alzheimers Dis Dementias® 2019;34:450-456.
Sultan S, Taimuri U, Basnan SA, Ai-Orabi WK, Awadallah A, Almowald F, et al. Low vitamin D and its association with cognitive impairment and dementia. J Aging Res 2020;2020.
Geng T, Lu Q, Wan Z, Guo J, Liu L, Pan A, et al. Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations with risk of dementia among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A cohort study in the UK Biobank. PLoS Med 2022;19:e1003906.
Ong PA, Muis A, Rambe AS, Widjojo FS, Laksmidewi AA, Pramono A, et al. Panduan Praktik klinik diagnosis dan penatalaksanaan demensia. Jkt Perhimpun Dr Spes Saraf Indones 2015.
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:695-699.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). Philadelphia: American Psychiatric Pub; 2013. 2013.
Grimm MO, Thiel A, Lauer AA, Winkler J, Lehmann J, Regner L, et al. Vitamin D and its analogues decrease amyloid-β (Aβ) formation and increase Aβ-degradation. Int J Mol Sci 2017;18:2764.
Filipović N, Ferhatović L, Marelja I, Puljak L, Grković I. Increased vitamin D receptor expression in dorsal root ganglia neurons of diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 2013;549:140-145.
Hosseinpour F, Wikvall K. Porcine microsomal vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase (CYP2D25): catalytic properties, tissue distribution, and comparison with human CYP2D6. J Biol Chem 2000;275:34650-34655.
Balabanova S, Richter H-P, Antoniadis G, Homoki J, Kremmer N, Hanle J, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, 24, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D and 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D in human cerebrospinal fluid. Klin Wochenschr 1984;62:1086-1090.
Przybelski RJ, Binkley NC. Is vitamin D important for preserving cognition? A positive correlation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration with cognitive function. Arch Biochem Biophys 2007;460:202-205.
Naveilhan P, Neveu I, Wion D, Brachet P. 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3, an inducer of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroreport 1996;7:2171-2175.
Ibi M, Sawada H, Nakanishi M, Kume T, Katsuki H, Kaneko S, et al. Protective effects of 1α, 25-(OH) 2D3 against the neurotoxicity of glutamate and reactive oxygen species in mesencephalic culture. Neuropharmacology 2001;40:761-771.
Wilson RS, Yu L, Lamar M, Schneider JA, Boyle PA, Bennett DA. Education and cognitive reserve in old age. Neurology 2019;92:e1041-e1050.
Brucki SMD, Nitrini R. Cognitive impairment in individuals with low educational level and homogeneous sociocultural background. Dement Neuropsychol 2014;8:345-350.
Sun L, Diao X, Gang X, Lv Y, Zhao X, Yang S, et al. Risk factors for cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2020;2020.
Munshi M, Grande L, Hayes M, Ayres D, Suhl E, Capelson R, et al. Cognitive dysfunction is associated with poor diabetes control in older adults. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1794-1799.
Launer LJ, Miller ME, Williamson JD, Lazar RM, Gerstein HC, Murray AM, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering on brain structure and function in people with type 2 diabetes (ACCORD MIND): a randomised open-label substudy. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:969-977.
Rizzo MR, Marfella R, Barbieri M, Boccardi V, Vestini F, Lettieri B, et al. Relationships between daily acute glucose fluctuations and cognitive performance among aged type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2010;33:2169-2174.
Suh S, Kim JH. Glycemic variability: how do we measure it and why is it important? Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:273-282.
Feinkohl I, Price JF, Strachan MW, Frier BM. The impact of diabetes on cognitive decline: potential vascular, metabolic, and psychosocial risk factors. Alzheimers Res Ther 2015;7:1-22.
Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Budge M, Young J. Body mass index in midlife and late-life as a risk factor for dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Obes Rev 2011;12:e426-e437.
Xiu S, Liao Q, Sun L, Chan P. Risk factors for cognitive impairment in older people with diabetes: a community-based study. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 2019;10:2042018819836640.
Chen G, Cai L, Chen B, Liang J, Lin F, Li L, et al. Serum level of endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation end products and other factors in type 2 diabetic patients with mild cognitive impairment. Diabetes Care 2011;34:2586-2590.
Ghoshal S, Allred ND, Freedman BI. The contribution of kidney disease to cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 2020;20:1-10.
Tantanokit T, Bosittipichet T, Leesri T. The study of prevalence and associated factors of dementia in the elderly. Siriraj Med J 2021;73:224-235.
Espeland MA, Carmichael O, Yasar S, Hugenschmidt C, Hazzard W, Hayden KM, et al. Sex-related differences in the prevalence of cognitive impairment among overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes. Alzheimers Dement 2018;14:1184-1192.
Chatterjee S, Peters SA, Woodward M, Mejia Arango S, Batty GD, Beckett N, et al. Type 2 diabetes as a risk factor for dementia in women compared with men: a pooled analysis of 2.3 million people comprising more than 100,000 cases of dementia. Diabetes Care 2016;39:300-307.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














