Incidences, Characteristics, Management and Outcomes of Different Subtypes of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients Admitted to the Surgical Intensive Care Unit: A Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i7.267145Keywords:
postoperative delirium, psychomotor subtype, surgical intensive care unitAbstract
Objective: Postoperative delirium (POD) has three subtypes: hyperactive, hypoactive, and mixed, with each having distinct features and implications. This study aimed to determine the incidence, management, and clinical outcomes of each POD subtype in elderly patients admitted to the surgical intensive care unit (SICU) after surgery.
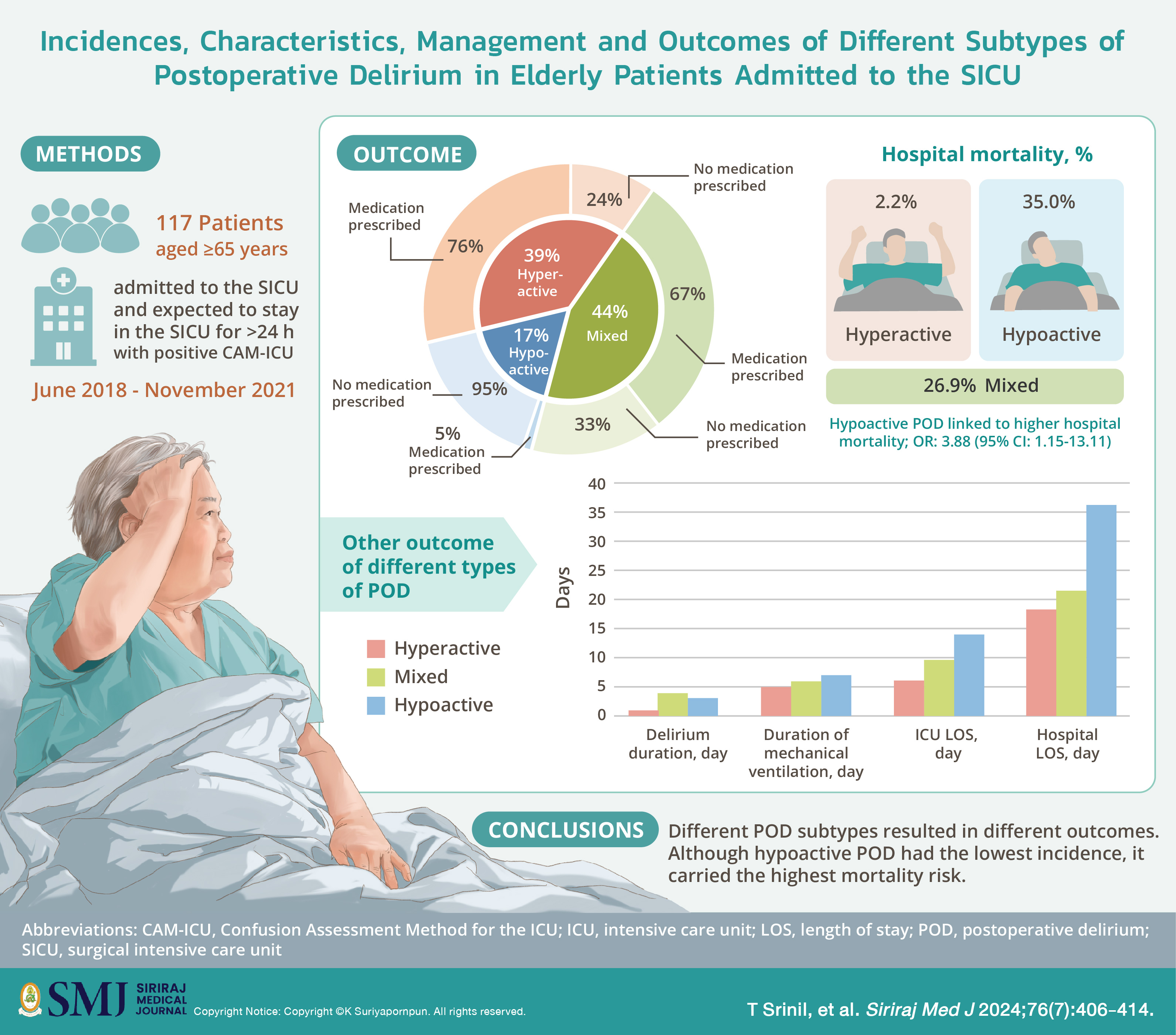
Materials and Methods: This was a secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study of POD in the SICU. Patients aged ≥65 years admitted to the SICU and expected to stay in the SICU for >24 h were recruited. POD was screened using the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU). Patients with positive CAM-ICU were defined as having POD and included in the analysis. The POD subtypes were categorized, pharmacological and nonpharmacological treatments were identified, and clinical outcomes were reported.
Results: Of the 300 included patients, 117 developed POD, with 20 (17.1%) having hypoactive, 45 (38.5%) hyperactive, and 52 (44.4%) mixed. Medications were prescribed in 1 (5.0%), 34 (75.6%), and 35 (67.3 %) in patients with hypoactive, hyperactive, and mixed POD, respectively (P <0.001). Patients with hypoactive POD had the longest duration of delirium, longest length of stay in both the SICU and hospital, and highest hospital mortality. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that hypoactive POD was significantly associated with increased hospital mortality (odds ratio, 3.88; 95% confidence interval, 1.15–13.11).
Conclusion: Different POD subtypes resulted in different outcomes. Although hypoactive POD had the lowest incidence, it carried the highest mortality risk.
References
Aldecoa C, Bettelli G, Bilotta F, Sanders RD, Audisio R, Borozdina A, et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology evidence-based and consensus-based guideline on postoperative delirium. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017;34(4):192-214.
Marcantonio ER. Postoperative delirium: a 76-year-old woman with delirium following surgery. JAMA. 2012;308(1):73-81.
Ansaloni L, Catena F, Chattat R, Fortuna D, Franceschi C, Mascitti P, et al. Risk factors and incidence of postoperative delirium in elderly patients after elective and emergency surgery. Br J Surg. 2010;97(2):273-80.
Olin K, Eriksdotter-Jönhagen M, Jansson A, Herrington MK, Kristiansson M, Permert J. Postoperative delirium in elderly patients after major abdominal surgery. Br J Surg. 2005;92(12):1559-64.
Ely EW, Shintani A, Truman B, Speroff T, Gordon SM, Harrell FE, Jr., et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA. 2004;291(14):1753-62.
Chaiwat O, Chanidnuan M, Pancharoen W, Vijitmala K, Danpornprasert P, Toadithep P, et al. Postoperative delirium in critically ill surgical patients: incidence, risk factors, and predictive scores. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019;19(1):39.
Ali M, Cascella M. ICU Delirium. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing
Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2023.
Meagher D. Motor subtypes of delirium: past, present and future. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21(1):59-73.
Peterson JF, Pun BT, Dittus RS, Thomason JW, Jackson JC, Shintani AK, et al. Delirium and its motoric subtypes: a study of 614 critically ill patients. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54(3):479-84.
Pandharipande P, Cotton BA, Shintani A, Thompson J, Costabile S, Truman Pun B, et al. Motoric subtypes of delirium in mechanically ventilated surgical and trauma intensive care unit patients. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(10):1726-31.
Robinson TN, Raeburn CD, Tran ZV, Brenner LA, Moss M. Motor subtypes of postoperative delirium in older adults. Arch Surg. 2011;146(3):295-300.
Pipanmekaporn T, Wongpakaran N, Mueankwan S, Dendumrongkul P, Chittawatanarat K, Khongpheng N, et al. Validity and reliability of the Thai version of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU). Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:879-85.
Page VJ, Casarin A, Ely EW, Zhao XB, McDowell C, Murphy L, et al. Evaluation of early administration of simvastatin in the prevention and treatment of delirium in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation (MoDUS): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(9):727-37.
Stransky M, Schmidt C, Ganslmeier P, Grossmann E, Haneya A, Moritz S, et al. Hypoactive delirium after cardiac surgery as an independent risk factor for prolonged mechanical ventilation. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25(6):968-74.
Suenghataiphorn T, Songwisit S, Tornsatitkul S, Somnuke P. An Overview on Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction; Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, Prevention and Treatment. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(10):705-13.
Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, Needham DM, Slooter AJC, Pandharipande PP, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Pain, Agitation/Sedation, Delirium, Immobility, and Sleep Disruption in Adult Patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(9):e825-e73.
Meagher DJ, O'Hanlon D, O'Mahony E, Casey PR, Trzepacz PT. Relationship between etiology and phenomenologic profile in delirium. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 1998;11(3):146-9; discussion 57-8.
Morita T, Tei Y, Tsunoda J, Inoue S, Chihara S. Underlying pathologies and their associations with clinical features in terminal delirium of cancer patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2001;22(6):997-1006.
Ross CA, Peyser CE, Shapiro I, Folstein MF. Delirium: phenomenologic and etiologic subtypes. Int Psychogeriatr. 1991;3(2):135-47.
Omichi C, Ayani N, Oya N, Matsumoto Y, Tanaka M, Morimoto T, et al. Association between discontinuation of benzodiazepine receptor agonists and post-operative delirium among inpatients with liaison intervention: A retrospective cohort study. Compr Psychiatry. 2021;104:152216.
Praditsuwan R. Current Knowledge in Geriatric Syndromes. Siriraj Med J. 2007;59(2):79-81.
Liptzin B, Levkoff SE. An empirical study of delirium subtypes. Br J Psychiatry. 1992;161:843-5.
O'Keeffe ST, Lavan JN. Clinical significance of delirium subtypes in older people. Age Ageing. 1999;28(2):115-9.
Miranda F, Gonzalez F, Plana MN, Zamora J, Quinn TJ, Seron P. Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM-ICU) for the diagnosis of delirium in adults in critical care settings. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;11(11):Cd013126.
Gusmao-Flores D, Salluh JI, Chalhub R, Quarantini LC. The confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU) and intensive care delirium screening checklist (ICDSC) for the diagnosis of delirium: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Crit Care. 2012;16(4):R115.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














