Distribution of Foot Arch Type and Associated Symptoms in Medical Students at Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i6.267251Keywords:
Prevalence, Flatfoot, Talipes cavus, Students medical, PainAbstract
Objective: To determine the distribution of foot arch type, associated symptoms, and factors associated with moderate to severe pain
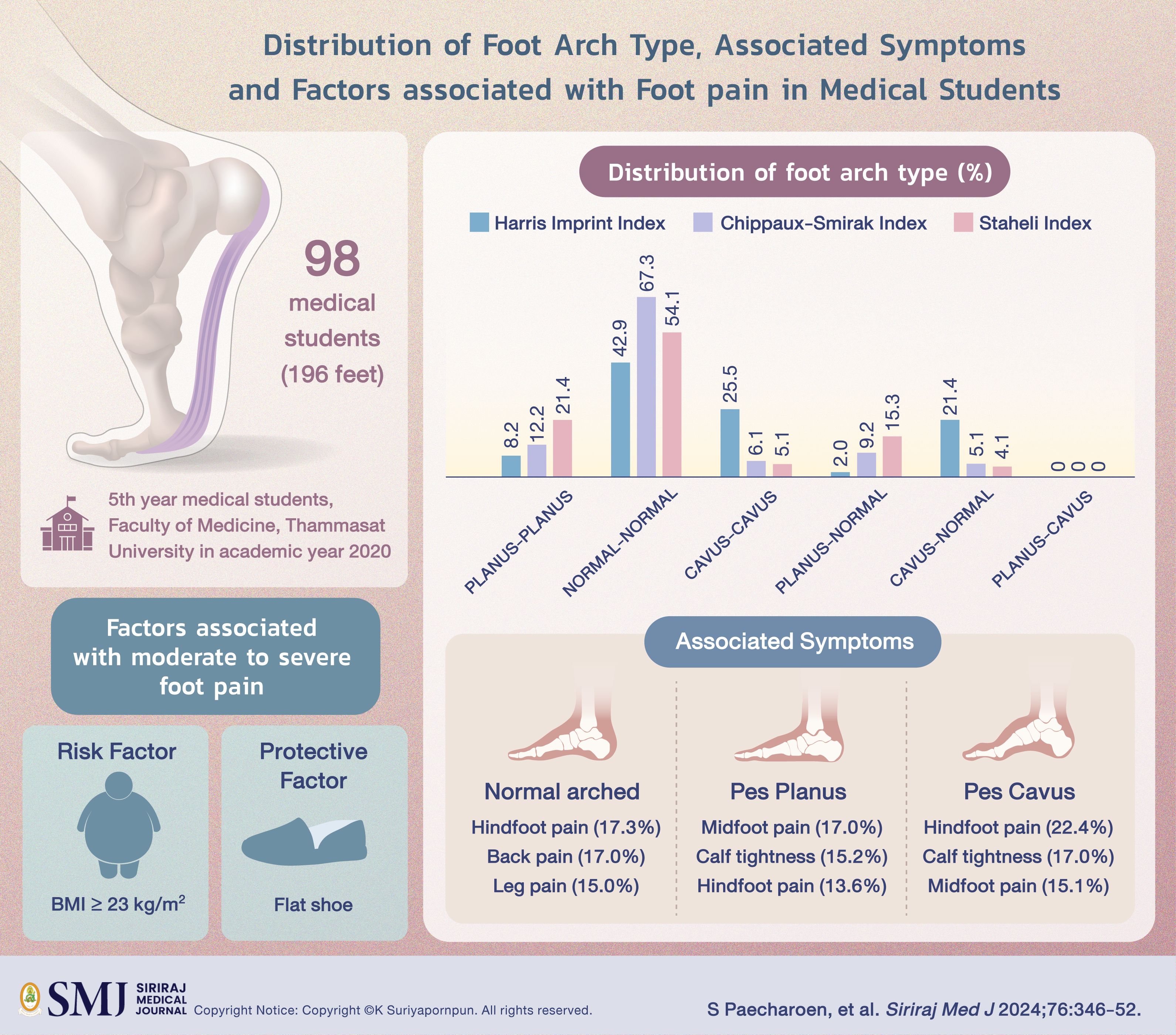
Materials and Methods: The cross-sectional study was collected data from 5th year medical students, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University in academic year 2020. The distribution of foot arch type used the footprint and classified by Harris imprint index (HII), Chippaux-Smirak index (CSI), Staheli index (SI). The associated symptoms were collected into pain and tightness. Pain score was rated by the volunteer using numeric rating scale (NRS) at each foot/leg separately.
Results: A total of ninety-eight medical students (196 feet) were recruited and analyzed. The distribution of foot arch type by HII, CSI and SI were 1) bilateral normal arched feet: 42.9%, 67.3%, 54.1% 2) bilateral pes planus: 8.2%, 12.2%, 21.4% 3) bilateral pes cavus: 25.5%, 6.1%, 5.1% 4) unilateral pes planus: 2%, 9.2%,15.3% 5) unilateral pes cavus: 21.4%, 5.1%, 4.1%, respectively. The most commonly associated symptom of pes planus was midfoot pain (17%) while pes cavus and normal arched foot were hindfoot pain (22.4% and 17.3%). The factor associated with moderate to severe pain was BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 (OR = 3.23, 95%CI 1.63 - 6.41, p-value = 0.001).
Conclusion: Bilateral normal arched feet were mostly found. Midfoot pain in pes planus and hindfoot pain in pes cavus and normal arched foot were the greatest symptoms. BMI was a risk factor.
References
Toullec E. Adult flatfoot. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S11-7.
Riskowski J, Dufour A, Hagedorn T, Hillstrom H, Casey V, Hannan M. Associations of foot posture and function to lower extremity pain: the Framingham foot study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2013;65(11):1804-12.
Coughlin MJ, Saltzman CL, Anderson RB. Mann’s surgery of the foot and ankle. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2014.
Shariff S, Manaharan T, Shariff A, Merican A. Evaluation of foot arch in adult women: comparison between five different footprint parameters. Sains Malays. 2017;46:1839-48.
Tantaopas W, Jitchanvichai J, Laisiriroengrai T, Jenjai N, Julphakee T, Theera-Umpon N, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of flatfoot in third-year medical students at Chiang Mai University. Chula Med J. 2018;62:627-37.
Zhai JN, Qiu YS, Wang J. Effects of orthotic insoles on adults with flexible flatfoot under different walking conditions. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(11):3078-83.
Burns J, Crosbie J, Ouvrier R, Hunt A. Effective orthotic therapy for the painful cavus foot: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006;96(3):205-11.
Paecharoen S, Arunakul M, Tantivangphaisal N. Diagnostic accuracy of Harris Imprint Index, Chippaux-Smirak Index, Staheli Index compared with talar-first metatarsal angle for screening arch of foot. Ann Rehabil Med. 2023;47(3):222-7.
Boonstra AM, Stewart RE, Koke AJA, Oosterwijk RFA, Swaan JL, Schreurs KMG, et al. Cut-off points for mild, moderate, and severe pain on the numeric rating scale for pain in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: variability and influence of sex and catastrophizing. Front Psychol. 2016;7:1-9.
Shah DK, Khatun S. Pes planus foot among the first and second year medical students of a medical college: A descriptive cross-sectional study. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2021;59(236):327-30.
Ashraf T, Asif M, Abdul S, Khalfe H, Hafiza A, Mehmood, et al. Prevalence of flat foot and high arch foot among undergraduate physical therapy students by using navicular drop test. Int J Sci Eng Res. 2017;8(10):1126-34.
Ganapathy A, Sadeesh T, Sudha R. Morphometric analysis of foot in young adult individuals. World J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;4(8):980-93.
Tejashree B, Deepak B, Abhijit D. Prevalence of flat foot among 18 -25 years old physiotherapy students: cross sectional study. Int J Biol Med Res. 2014;3(4):272-8.
Jonely H, Brismée JM, Sizer PS, James CR. Relationships between clinical measures of static foot posture and plantar pressure during static standing and walking. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(8):873-9.
Buldt AK, Allan JJ, Landorf KB, Menz HB. The relationship between foot posture and plantar pressure during walking in adults: A systematic review. Gait Posture. 2018;62:56-67.
Kosashvili Y, Fridman T, Backstein D, Safir O, Bar Ziv Y. The correlation between pes planus and anterior knee or intermittent low back pain. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29(9):910-3.
Menz HB, Dufour AB, Riskowski JL, Hillstrom HJ, Hannan MT. Foot posture, foot function and low back pain: the Framingham Foot Study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(12):2275-82.
Martins GC, Fraga PHG, Teixeira LB, Valle BRG, Martins Filho LF, Gama M de P. Functional evaluation and pain symptomatology of the foot and ankle in individuals with severe obesity - controlled transversal study. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2021;56(2):235-43.
Dufour AB, Losina E, Menz HB, LaValley MP, Hannan MT. Obesity, foot pain and foot disorders in older men and women. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2017;11(4):445-53.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














