Developing Cerebral Palsy Screening of Functional Abilities in School (CPS –FAS)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i8.267459Keywords:
Cerebral palsy, Functional ability, Special education schoolAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to determine the psychometric property of a newly developed functional abilities screening tool for children with cerebral palsy (CP) in special education units.
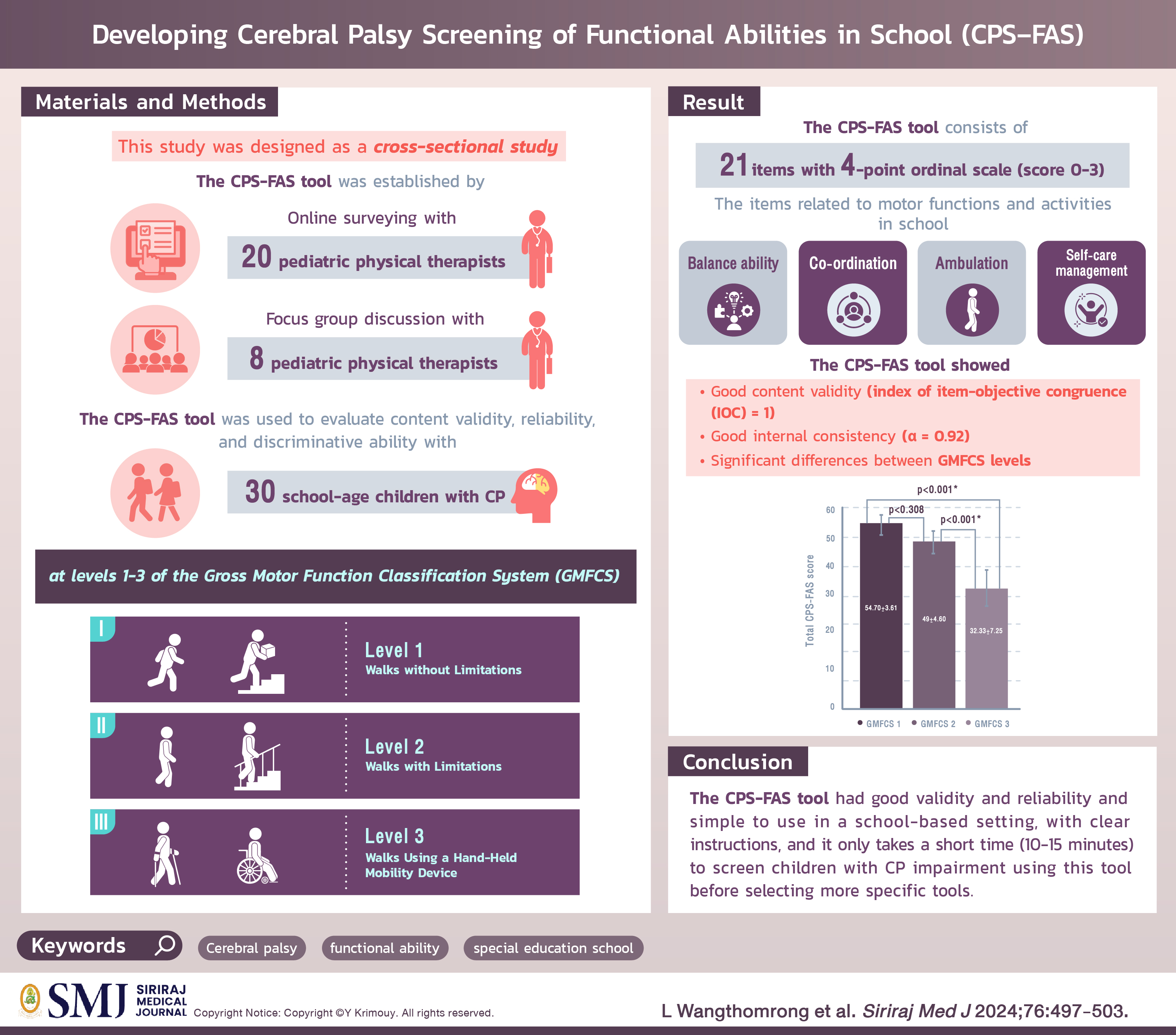
Materials and Methods: This study was designed as a cross-sectional study. The tool for cerebral palsy screening of functional abilities in school (CPS-FAS) was established by surveying 28 pediatric physical therapists and holding focus group discussions with them. The CPS-FAS tool was used to evaluate content validity, reliability, and discriminative ability with 30 school-age children with CP at levels 1-3 of the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS).
Results: The CPS-FAS generation process established 21 activity-problem screening items for children with CP, which had good content validity (index of item-objective congruence (IOC) = 1), good internal consistency (α = 0.92), and showed significant differences between GMFCS levels 1 and 3 (p > 0.001) and GMFCS levels 2 and 3 (p > 0.001).
Conclusion: The CPS-FAS tool can be applied to school-age children with CP in a special education unit to screen such children for activity problems that affect school living without environmental obstruction and language barriers, and it only takes a short time (10-15 minutes) to complete.
References
McIntyre S, Goldsmith S, Webb A, Ehlinger V, Hollung SJ, McConnell K, et al. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2022;64(12):1494-506.
Eunson P. Aetiology and epidemiology of cerebral palsy. Paediatrics and Child Health. 2012;22(9):361-6.
Patel DR, Neelakantan M, Pandher K, Merrick J. Cerebral palsy in children: a clinical overview. Transl Pediatr. 2020;9(Suppl 1):S125-S35.
Aisen ML, Kerkovich D, Mast J, Mulroy S, Wren TAL, Kay RM, et al. Cerebral palsy: clinical care and neurological rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(9):844-52.
Barrett RS, Lichtwark GA. Gross muscle morphology and structure in spastic cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010;52(9):794-804.
Fluss J, Lidzba K. Cognitive and academic profiles in children with cerebral palsy: A narrative review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2020;63(5):447-56.
Imms C. Children with cerebral palsy participate: A review of the literature. Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(24):1867-84.
Stadskleiv K. Cognitive functioning in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2020;62(3):283-9.
Bourke-Taylor HM, Cotter C, Lalor A, Johnson L. School success and participation for students with cerebral palsy: a qualitative study exploring multiple perspectives. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;40(18):2163-71.
Mei C, Reilly S, Reddihough D, Mensah F, Green J, Pennington L, et al. Activities and participation of children with cerebral palsy: parent perspectives. Disabil Rehabil. 2015;37(23):2164-73.
Dirk-Wouter S, Marjolijn K, Jan Willem G, Petra, Annet D, Marian J, et al. Development of daily activities in school-age children with cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2011;32(1):222-34.
Korzeniewski SJ, Slaughter J, Lenski M, Haak P, Paneth N. The complex aetiology of cerebral palsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(9):528-43.
Schenker R, Coster W, Parush S. Participation and activity performance of students with cerebral palsy within the school environment. Disabil Rehabil. 2005;27(10):539-52.
Pratt B, Baker K, Gaebler D. Participation of the child with cerebral palsy in the home, school, and community: A review of the literature. J Pediatr Rehabil Med. 2008;1:101-11.
Pratt B, Peterson M. The Role of Physical Therapists in Advancing Special Education. 2015;30:47-66.
Wannapakhe J, Kunloetchariya T, Jaiphian P, Sinwech P, Parnfaung N. Surveying the requirements of physical abilities assessments and social participation of children with cerebral palsy who studied in Srisangwan School: Srinakariwirot university; 2019.
World Health O. International classification of functioning, disability and health: children and youth version: ICF-CY. World Health Organization; 2007.
Bureau SE. Study of guidelines for setting up a service unit of special education centers. In: Commission OotBE, editor. 2016.
Gehrmann FE, Coleman A, Weir KA, Ware RS, Boyd RN. School readiness of children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014;56(8):786-93.
Maciver D, Rutherford M, Arakelyan S, Kramer J, Richmond J, Todorova L, et al. Participation of children with disabilities in school: A realist systematic review of psychosocial and environmental factors. Plos One. 2019;14(1):e0210511.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice: Pearson/Prentice Hall; 2015.
Netto A, Wiesiolek C, Brito P, Rocha G, Tavares R, Lambertz K. Functionality, school participation and quality of life of schoolchildren with cerebral palsy. Fisioterapia em Movimento. 2020;33.
Palee S, Ploypetch T, Pajareya K, Timdang S. Goal-Directed Therapy to Improve Gross Motor Function and the Quality of Life of Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(1):1-10.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














