Comparative Evaluation of Imaging Modalities for Eligibility in Endovascular Treatment of Delayed Onset Acute Anterior Circulation Ischemic Stroke in Siriraj Hospital: A Retrospective Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i9.268564Keywords:
stroke, MultiphaseCTA, CTperfusion, Acute ischemic stroke, Mechanical thrombectomyAbstract
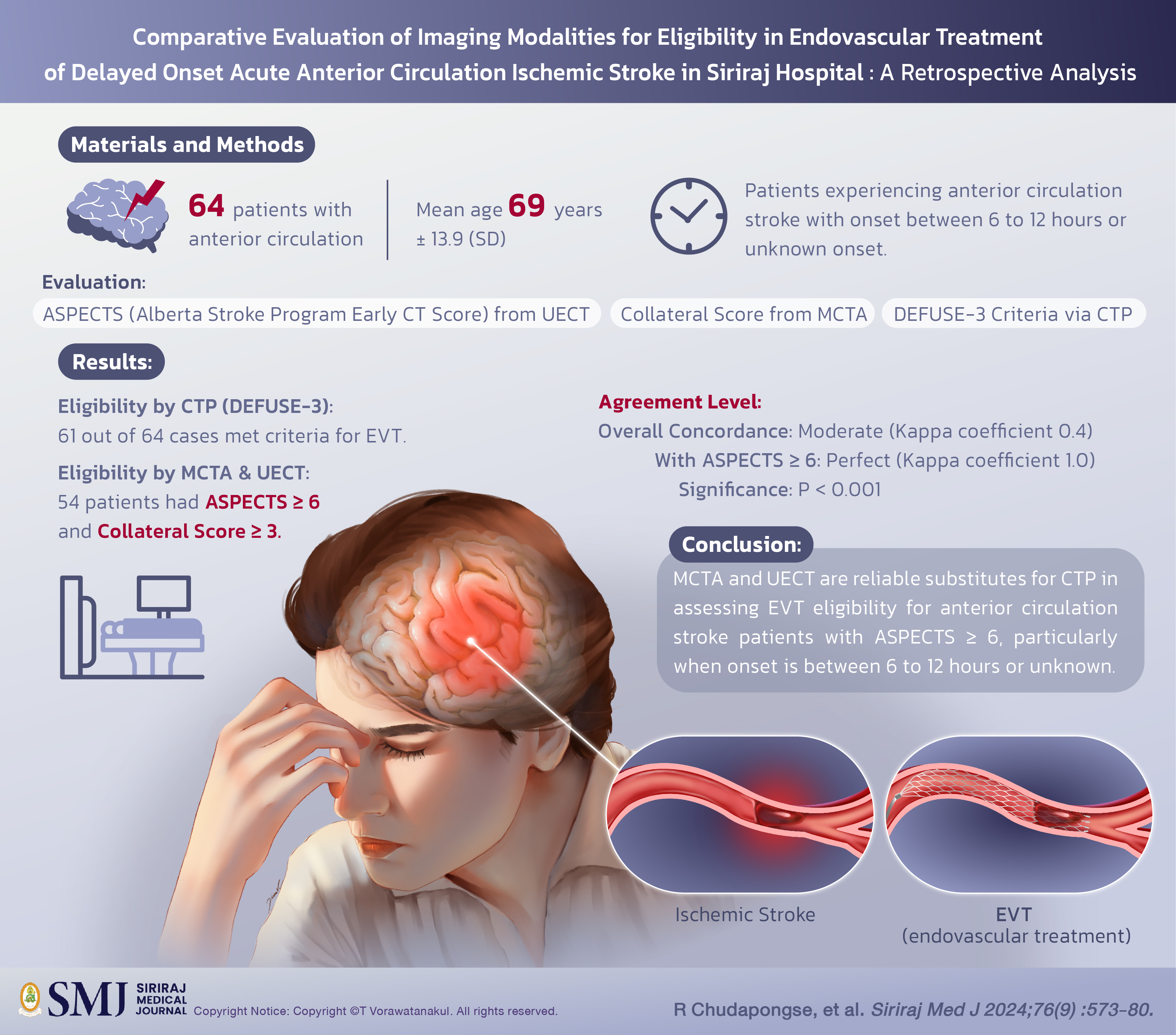
Objective: The goal of this study is to evaluate the consistency between CTP according to the endovascular therapy following imaging evaluation for ischemic stroke (DEFUSE-3) criteria and other standard computed tomography (CT) imaging modalities, such as multi-phase CT angiography (MCTA) and unenhanced computed tomography (UECT), in assessing patient eligibility for EVT as determined by neurointerventionists evaluations.
Materials and Methods: This retrospective analysis included 64 patients with anterior circulation stroke and onset between 6 to 12 hours or unknown onset. Two neuro-interventionalists independently reviewed images and assessed eligibility for EVT based on the Alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS) derived from UECT and collateral score obtained from MCTA. The results were then compared to CTP, utilizing the DEFUSE-3 criteria.
Results: Out of the 64 cases analyzed (mean age: 69 years ± 13.9 [SD]), 61 met DEFUSE-3 criteria for EVT by CTP, while 54 were deemed eligible based on an ASPECTS ≥ 6 and collateral score ≥ 3. Agreement between the modalities was moderate (Kappa coefficient score 0.4). When patients with ASPECTS score < 6 were excluded, concordance improved to perfect (Kappa coefficient score 1.0). Hence, concordance was significantly associated with ASPECTS scores ≥ 6 (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: In patients experiencing anterior circulation stroke with onset between 6 to 12 hours or unknown onset, excluding an ASPECTS score of 6 or higher, MCTA and UECT proved to be reliable for assessing endovascular treatment eligibility. These modalities may serve as substitutes for CTP and offer support in the clinical decisionmaking process.
References
Dharmasaroja P, Ratanakorn D, Nidhinandana S, Singhara Na Ayudhaya S, Churojana A, Suwatcharangkoon S. Thai guidelines of endovascular treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Thai Stroke Soc. 2019;18(2):52-75.
Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, et al. 2021 guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52(7):e364-e467.
Kim JT, Goyal M, Levy EI, Liebeskind D, Jahan R, Pereira VM, et al. Onset to reperfusion time as a determinant of outcomes across a wide range of ASPECTS in endovascular thrombectomy: pooled analysis of the SWIFT, SWIFT PRIME, and STAR studies. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020;12(3):240-5.
Warner JJ, Harrington RA, Sacco RL, Elkind MS. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke. Am Heart Assoc; 2019. p. 3331-2.
Churojana A, Mongkolratnan A, Sangpetngam B, Aurboonyawat T, Chankaew E, Withayasuk P, et al. A Comparison of Mechanical Thrombectomy for Large Vessel Occlusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke between Patients with and without Atrial Fibrillation. Siriraj Med J. 2018;70(4):278-83.
Roubec M, Kuliha M, Procházka V, Krajča J, Czerný D, Jonszta T, et al. A controlled trial of revascularization in acute stroke. Radiology. 2013;266(3):871-8.
Golnari P, Nazari P, Ansari SA, Hurley MC, Shaibani A, Potts MB, et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischemic stroke: utilization, outcomes, and readmissions across the United States. Radiology. 2021;299(1):179-89.
Kim BJ, Menon BK, Kim JY, Shin DW, Baik SH, Jung C, et al. Endovascular Treatment After Stroke Due to Large Vessel Occlusion for Patients Presenting Very Late From Time Last Known Well. JAMA Neurol. 2020;78(1):21-9.
Nael K, Sakai Y, Khatri P, Prestigiacomo CJ, Puig J, Vagal A. Imaging-based selection for endovascular treatment in stroke. Radiographics. 2019;39(6):1696-713.
Demeestere J, Wouters A, Christensen S, Lemmens R, Lansberg MG. Review of Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke: From Time to Tissue. Stroke. 2020;51(3):1017-24.
Menon BK, d’Esterre CD, Qazi EM, Almekhlafi M, Hahn L, Demchuk AM, et al. Multiphase CT angiography: a new tool for the imaging triage of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Radiology. 2015;275(2):510-20.
Singer OC, Berkefeld J, Nolte CH, Bohner G, Reich A, Wiesmann M, et al. Collateral vessels in proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion: the ENDOSTROKE study. Radiology. 2015;274(3):851-8.
Kim BM, Baek JH, Heo JH, Nam HS, Kim YD, Yoo J, et al. Collateral status affects the onset-to-reperfusion time window for good outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018;89(9):903-9.
Albers GW, Marks MP, Kemp S, Christensen S, Tsai JP, Ortega-Gutierrez S, et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):708-18.
Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RF, Bhuva P, et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(1):11-21.
Nael K, Sakai Y, Larson J, Goldstein J, Deutsch J, Awad AJ, et al. CT Perfusion collateral index in assessment of collaterals in acute ischemic stroke with delayed presentation: Comparison to single phase CTA. J Neuroradiol. 2022;49(2):198-204.
Pozzi-Mucelli RA, Furlanis G, Caruso P, Lugnan C, Zdjelar A, Degrassi F, et al. A Novel Fast CT Perfusion Core-Penumbra Mismatch Score: Correlation With Stroke Outcome. Neurologist. 2021;26(2):41-6.
Vaclavik D, Volny O, Cimflova P, Svub K, Dvornikova K, Bar M. The importance of CT perfusion for diagnosis and treatment of ischemic stroke in anterior circulation. J Integr Neurosci. 2022;21(3):92.
Wannamaker R, Buck B, Butcher K. Multimodal CT in Acute Stroke. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):63.
Wintermark M. Brain perfusion-CT in acute stroke patients. Eur Radiol. 2005;15 Suppl 4:D28-31.
Cortijo E, Garcia-Bermejo P, Calleja AI, Perez-Fernandez S, Gomez R, del Monte JM, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis in ischemic stroke with unknown onset using CT perfusion. Acta Neurol Scand. 2014;129(3):178-83.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-74.
Nguyen TN, Abdalkader M, Nagel S, Qureshi MM, Ribo M, Caparros F, et al. Noncontrast Computed Tomography vs Computed Tomography Perfusion or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Selection in Late Presentation of Stroke With Large-Vessel Occlusion. JAMA Neurol. 2022;79(1):22-31.
Wang Z, Xie J, Tang TY, Zeng CH, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, et al. Collateral Status at Single-Phase and Multiphase CT Angiography versus CT Perfusion for Outcome Prediction in Anterior Circulation Acute Ischemic Stroke. Radiology. 2020;296(2):393-400.
Reidler P, Thierfelder KM, Rotkopf LT, Fabritius MP, Puhr-Westerheide D, Dorn F, et al. Attenuation Changes in ASPECTS Regions: A Surrogate for CT Perfusion-based Ischemic Core in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Radiology. 2019;291(2):451-8.
Siegler JE, Messe SR, Sucharew H, Kasner SE, Mehta T, Arora N, et al. Noncontrast CT versus Perfusion-Based Core Estimation in Large Vessel Occlusion: The Blood Pressure after Endovascular Stroke Therapy Study. J Neuroimaging. 2020;30(2):219-26.
Nannoni S, Ricciardi F, Strambo D, Sirimarco G, Wintermark M, Dunet V, et al. Correlation between ASPECTS and Core Volume on CT Perfusion: Impact of Time since Stroke Onset and Presence of Large-Vessel Occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42(3):422-8.
Dhillon PS, Butt W, Podlasek A, McConachie N, Lenthall R, Nair S, et al. Association between time to treatment and clinical outcomes in endovascular thrombectomy beyond 6 hours without advanced imaging selection. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023;15(4):336-42.
Diestro JDB. Rethinking the role of CT perfusion in the management of emergent large vessel ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023;15(9):833-4.
Kobeissi H, Ghozy S, Adusumilli G, Bilgin C, Tolba H, Amoukhteh M, et al. CT Perfusion vs Noncontrast CT for Late Window Stroke Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurology. 2023;100(22):e2304-e11.
Nannoni S, Cereda CW, Sirimarco G, Lambrou D, Strambo D, Eskandari A, et al. Collaterals are a major determinant of the core but not the penumbra volume in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology. 2019;61(9):971-8.
Voleti S, Aziz YN, Vidovich J, Corcoran B, Zhang B, Mistry E, et al. Association Between CT Angiogram Collaterals and CT Perfusion in Delayed Time Windows for Large Vessel Occlusion Ischemic Strokes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;31(3):106263.
Fiehler J. Do we need CT perfusion for stroke patients? Define your terms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2022;14(9):847-8.
Pirson FAV, Hinsenveld WH, Goldhoorn R-JB, Staals J, de Ridder IR, van Zwam WH, et al. MR CLEAN-LATE, a multicenter randomized clinical trial of endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke in The Netherlands for late arrivals: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2021;22(1):160.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














