Food-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Challenging Life-threatening Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i9.269446Keywords:
anaphylaxis, exercise, food allergy, food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis, gluten, challenge testAbstract
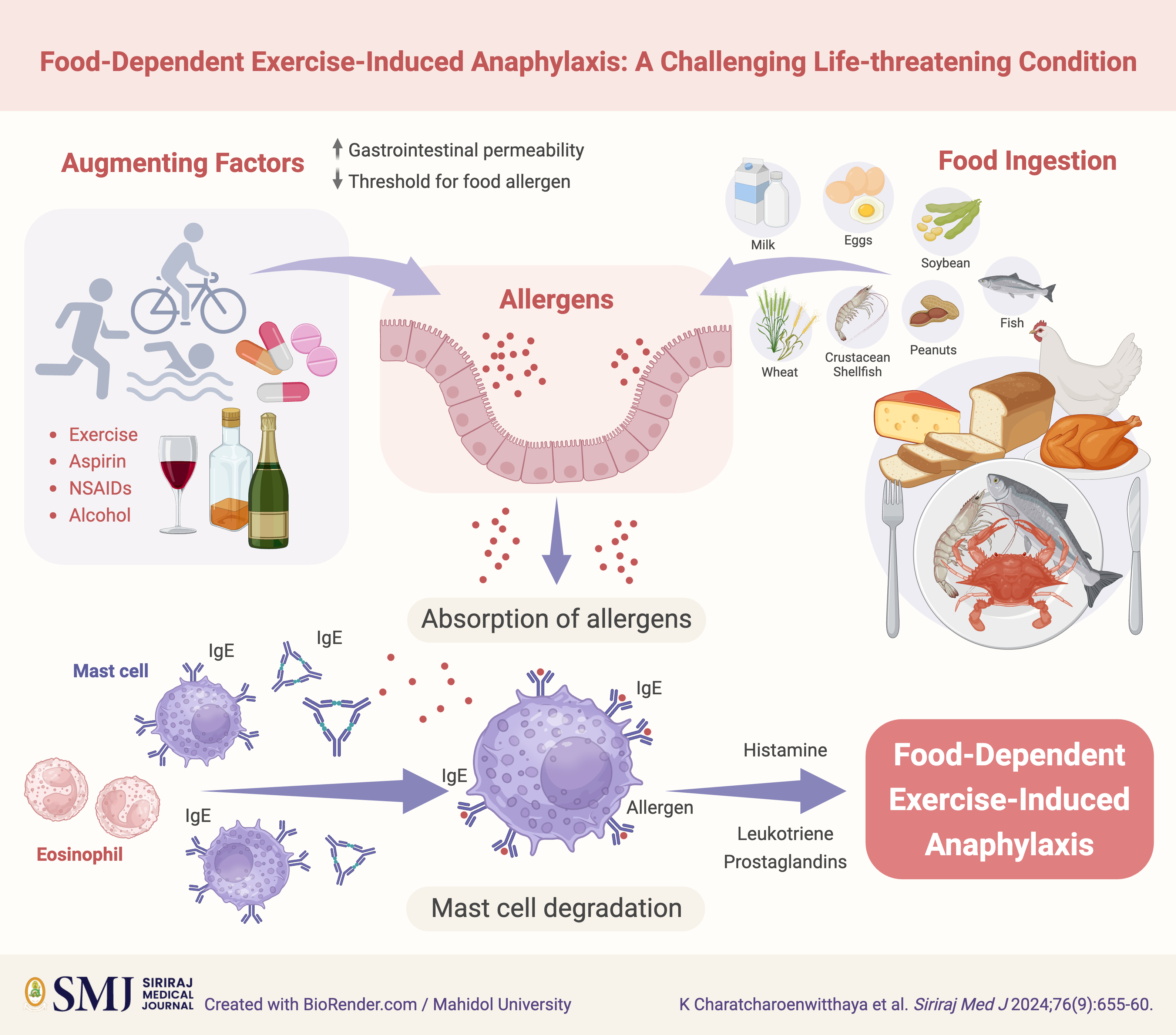
Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) is an uncommon but potentially life-threatening condition characterized by allergic reactions triggered by the combination of specific food ingestion and physical exertion. Despite its rarity, FDEIA poses significant diagnostic and management challenges due to its complex pathophysiology and variable clinical presentation. Diagnosis relies on careful evaluation of clinical history, symptomatology, and laboratory tests, with inherent difficulties in distinguishing FDEIA from other related conditions. Management of FDEIA involves comprehensive strategies to minimize the risk of allergic reactions through measures such as allergen avoidance, patient education, and timely administration of epinephrine. While existing treatment approaches primarily target acute reactions, ongoing research endeavors are crucial for validating emerging diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. This review offers a comprehensive overview of FDEIA, encompassing its epidemiology, underlying pathophysiology, clinical presentations, diagnostic challenges, and management approaches.
References
Sampson HA, Munoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF, Jr., Bock SA, Branum A, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report--Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:391-7.
Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979;63:433-4.
Feldweg AM. Food-Dependent, Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: Diagnosis and Management in the Outpatient Setting. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5:283-8.
Cardona V, Ansotegui IJ, Ebisawa M, El-Gamal Y, Fernandez Rivas M, Fineman S, et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ J. 2020;13:100472.
Tanaka S. An epidemiological survey on food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in kindergartners, schoolchildren and junior high school students. Asia Pac J Public Health. 1994;7:26-30.
Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Frequency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese junior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:1035-9.
Manabe T, Oku N, Aihara Y. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese elementary school children. Pediatr Int. 2018;60:329-33.
Jeong K, Ye YM, Kim SH, Kim KW, Kim JH, Kwon JW, et al. A multicenter anaphylaxis registry in Korea: Clinical characteristics and acute treatment details from infants to older adults. World Allergy Organ J. 2020;13:100449.
Wade JP, Liang MH, Sheffer AL. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: epidemiologic observations. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;297:175-82.
Rossi CM, Lenti MV, Di Sabatino A. Adult anaphylaxis: A state-of-the-art review. Eur J Intern Med. 2022;100:5-12.
Kulthanan K, Ungprasert P, Jirapongsananuruk O, Rujitharanawong C, Munprom K, Trakanwittayarak S, et al. Food-Dependent Exercise-Induced Wheals/Angioedema, Anaphylaxis, or Both: A Systematic Review of Phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023;11:1926-33.
Du Toit G. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007;18:455-63.
Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Stafylaraki C, Scibilia J, Mirone C, Pravettoni V, et al. Wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis caused by a lipid transfer protein and not by omega-5 gliadin. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;112:386-7.e1.
Scherf KA, Brockow K, Biedermann T, Koehler P, Wieser H. Wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46:10-20.
Zhu YQ, Wang DQ, Liu B, Hu Y, Shen YY, Xu JH, et al. Wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Chinese people: a clinical research on 33 cases with antigenic analysis of wheat proteins. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45:56-62.
Tanaka M, Nagano T, Yano H, Haruma K, Kato Y. Exercise-independent wheat-induced anaphylaxis caused by omega-5 gliadin in mice. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2011;156:434-42.
Matsuo H, Morimoto K, Akaki T, Kaneko S, Kusatake K, Kuroda T, et al. Exercise and aspirin increase levels of circulating gliadin peptides in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:461-6.
Yano H, Kato Y, Matsuda T. Acute exercise induces gastrointestinal leakage of allergen in lysozyme-sensitized mice. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;87:358-64.
Lee J, Kim SR, Park JH, Park KH, Jeong KY, Lee JH, et al. Evaluation of Allergenicity on a omega-5 Gliadin-Deficient Cultivar in Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022;14:379-92.
Robson-Ansley P, Toit GD. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;10:312-7.
Motomura C, Matsuzaki H, Ono R, Iwata M, Okabe K, Akamine Y, et al. Aspirin is an enhancing factor for food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in children. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017;47:1497-500.
Barg W, Medrala W, Wolanczyk-Medrala A. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11:45-51.
Jo EJ, Yang MS, Kim YJ, Kim HS, Kim MY, Kim SH, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis occurred only in a warm but not in a cold environment. Asia Pac Allergy. 2012;2:161-4.
Bito T, Kanda E, Tanaka M, Fukunaga A, Horikawa T, Nishigori C. Cows milk-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis under the condition of a premenstrual or ovulatory phase following skin sensitization. Allergol Int. 2008;57:437-9.
Gonzalez-Quintela A, Vidal C, Gude F. Alcohol, IgE and allergy. Addict Biol. 2004;9:195-204.
Christensen MJ, Eller E, Mortz CG, Brockow K, Bindslev-Jensen C. Wheat-Dependent Cofactor-Augmented Anaphylaxis: A Prospective Study of Exercise, Aspirin, and Alcohol Efficacy as Cofactors. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:114-21.
Simons FE, Ardusso LR, Bilo MB, El-Gamal YM, Ledford DK, Ring J, et al. World allergy organization guidelines for the assessment and management of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ J. 2011;4:13-37.
Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;47:109-17.
Srisuwatchari W, Kanchanaphoomi K, Nawiboonwong J, Thongngarm T, Sompornrattanaphan M. Food-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis: A Distinct Form of Food Allergy-An Updated Review of Diagnostic Approaches and Treatments. Foods. 2023;12(20):3768.
Lertvipapath P, Jameekornrak Taweechue A, Wongsa C, Thongngarm T, Uawattanasakul W, Sompornrattanaphan M. Concomitant chronic spontaneous urticaria treatment might hinder the diagnosis of occupational latex-induced anaphylaxis: A case report. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021. doi: 10.12932/AP-050521-1126.
Tewari A, Du Toit G, Lack G. The difficulties of diagnosing food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in childhood -- a case study and review. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2006; 17:157-60.
Mahakittikun V, Bunnag C, Vichyanond P, Komoltri C, Wongkamchai S, Tunsuriyawong P, et al. A Comparative Study of the Major Allergenic Components in House Dust Mite Extracts between Siriraj and Commercially Prepared Extracts. Siriraj Med J. 2003;55:283-93.
Brockow K, Kneissl D, Valentini L, Zelger O, Grosber M, Kugler C, et al. Using a gluten oral food challenge protocol to improve diagnosis of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:977-84.e4.
Sampson HA, Aceves S, Bock SA, James J, Jones S, Lang D, et al. Food allergy: a practice parameter update-2014. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:1016-25.e43.
Asaumi T, Yanagida N, Sato S, Shukuya A, Nishino M, Ebisawa M. Provocation tests for the diagnosis of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2016;27:44-9.
Srisuwatchari W, Sompornrattanaphan M, Jirapongsananuruk O, Visitsunthorn N, Pacharn P. Exercise-food challenge test in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2024;42:43-9.
Aihara M, Miyazawa M, Osuna H, Tsubaki K, Ikebe T, Aihara Y, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: influence of concurrent aspirin administration on skin testing and provocation. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146:466-72.
Christensen MJ, Eller E, Mortz CG, Brockow K, Bindslev-Jensen C. Exercise Lowers Threshold and Increases Severity, but Wheat-Dependent, Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis Can Be Elicited at Rest. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:514-20.
Thongngarm T, Wongsa C, Pacharn P, Piboonpocanun S, Sompornrattanaphan M. Clinical Characteristics and Proposed Wheat-Cofactor Challenge Protocol with a High Diagnostic Yield in Adult-Onset IgE-Mediated Wheat Allergy. J Asthma Allergy. 2020;13:355-68.
Muraro A, Worm M, Alviani C, Cardona V, DunnGalvin A, Garvey LH, et al. EAACI guidelines: Anaphylaxis (2021 update). Allergy. 2022;77:357-77.
Del Giacco SR, Carlsen KH, Du Toit G. Allergy and sports in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012;23:11-20.
Moore LE, Kemp AM, Kemp SF. Recognition, treatment, and prevention of anaphylaxis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2015;35:363-74.
Nurmatov UB, Rhatigan E, Simons FE, Sheikh A. H2-antihistamines for the treatment of anaphylaxis with and without shock: a systematic review. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014;112:126-31.
Gabrielli S, Clarke A, Morris J, Eisman H, Gravel J, Enarson P, et al. Evaluation of Prehospital Management in a Canadian Emergency Department Anaphylaxis Cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7:2232-8.e3.
Simons FE, Gu X, Johnston LM, Simons KJ. Can epinephrine inhalations be substituted for epinephrine injection in children at risk for systemic anaphylaxis? Pediatrics. 2000;106:1040-4.
Foong RX, Giovannini M, du Toit G. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;19:224-8.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














