Use of Child Restraint Systems in Thailand and Factors associated with it: A Cross-Sectional Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i11.269751Keywords:
Car seats, Caregiver knowledge, Child restraint systems, ThailandAbstract
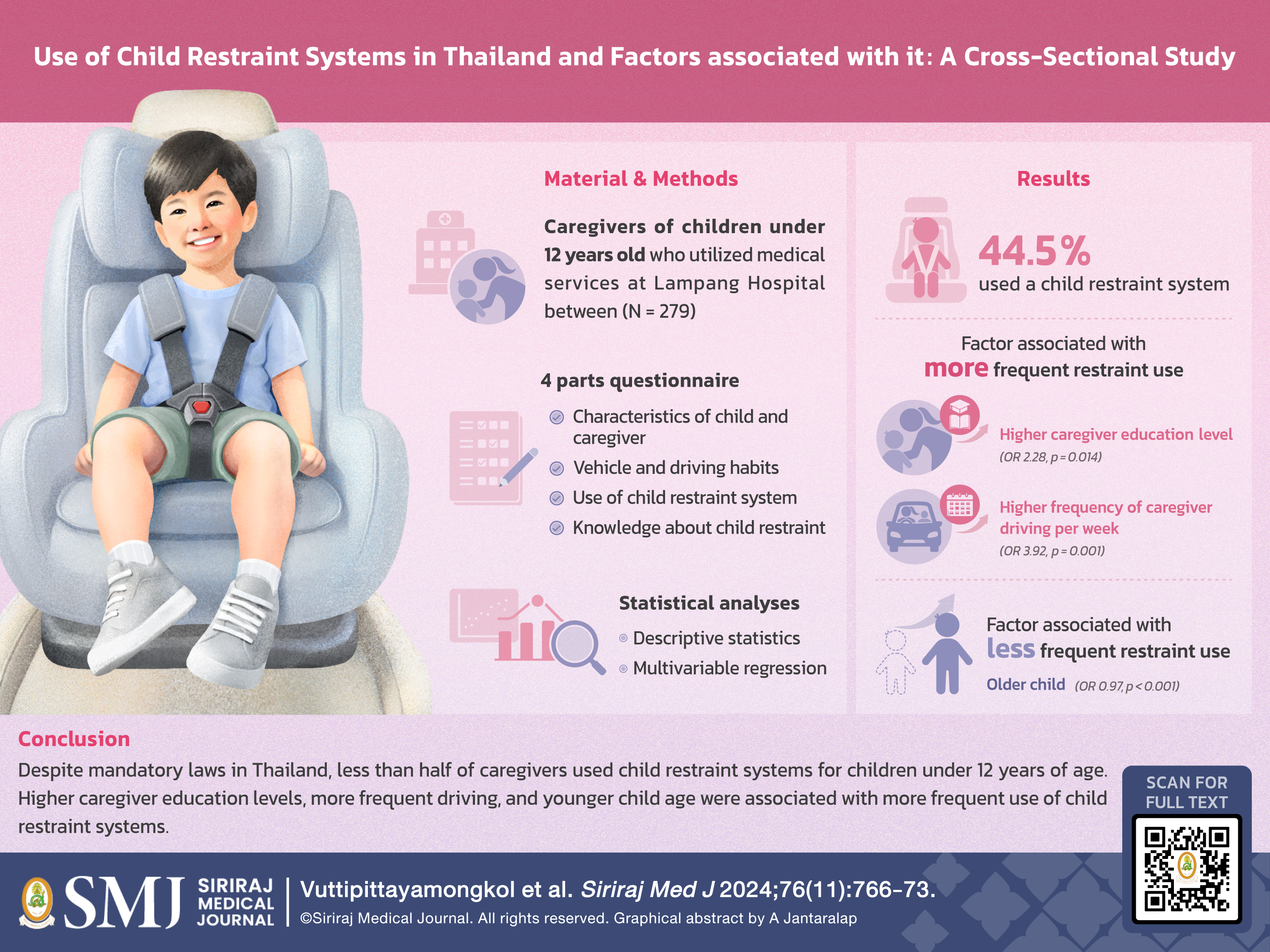
Objective: To determine the use of child restraint systems among caregivers of children in Thailand and to identify factors associated with it.
Materials and Methods: Caregivers of children under 12 years old who utilized medical services at Lampang Hospital between March 2023 and March 2024 were asked to participate in this cross-sectional study. Data on characteristics of child and caregiver, driving behavior, and knowledge about child restraint systems were collected via a questionnaire. Multivariable regression was applied to analyze associated factors.
Results: Of the 322 eligible caregivers, 279 (86.6%) participated, of which 127(44.5%) used a child restraint system. A higher caregiver education level (odds ratio [OR] 2.28, 95% CI 1.18; 4.39), and driving 3–7 days per week (OR 3.92, 95% CI 1.82; 8.40) were associated with more frequent restraint use. A higher age of the child (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.96; 0.98) was associated with less frequent restraint use.
Conclusion: Fewer than half of the caregivers utilized child restraint systems. Higher caregiver education levels and more frequent driving were associated with more frequent use, while older child age was associated with less frequent use of child restraint systems. Targeted interventions are needed to improve the use of child restraint systems.
References
World Health Organization. Global status report on road safety 2023. Available from: https://assets.bbhub.io/dotorg/sites/64/2023/12/WHO-Global-status-report-on-road-safety-2023.pdf
Chen SY, Garcia I, Ourshalimian S, Lowery C, Chaudhari PP, Spurrier RG. Childhood opportunity and appropriate use of child safety restraints in motor vehicle collisions. World J Pediatr Surg. 2024;7(2):e000703.
Durbin DR, Hoffman BD, Agran PF, Denny SA, Hirsh M, Johnston B, Lee LK, Monroe K, Schaechter J, Tenenbein M, Zonfrillo MR. Child passenger safety. Pediatrics. 2018;142(5):e2018246.
Rok Simon M, Korosec A, Bilban M. The influence of parental education and other socio-economic factors on child car seat use. Zdr Varst. 2017;56(1):55-64.
Li Y, Zhao T, Kang N, Wang W, Liu Q, Namgung M. Analysis of the factors influencing parents’ support for child safety seat legislation in Nanjing. Traffic Inj Prev. 2022;23(4):187-92.
Armouti I. Factors affecting the use of Child Car Seats for nursery school travel. A study in Athens. In: Transportation Research Board 95th Annual Meeting 2016.
Termworasin P, Lumbiganon D, Prueksapraopong C. Car Seat Knowledge and Car Seat Use among Parents of Preschool Children in Bangkok, Thailand. Vajira Med J. 2021;65(2):95-106.
Kim SH, Park SW, Lee YK, Ko SY, Shin SM. Use of child safety seats during transportation of newborns. Korean J Pediatr. 2018;61(8):253-7.
AlSallum GA, Alwassel AA, Alshushan AM, Abaalkhail AK, Alhasoon MA, Aldamigh AS. Parent’s knowledge, attitude, and practice about children car seats at Unaizah city, KSA. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019;8(3):805-11.
Jones AT, Hoffman BD, Gallardo AR, Gilbert TA, Carlson KF. Rear-facing car safety seat use for children 18 months of age: prevalence and determinants. J Pediatr. 2017;189:189-195.e9.
Dissanayake S, Amarasingha N. Restraint usage characteristics and other factors associated with safety of children involved in motor vehicle crashes. J Civil Eng Archit. 2016;10(1):81-95.
Bangkok Media and Broadcasting [Internet]. Recommendations for choosing a “Car Seat” for children to reduce “injury and death” from accidents; 2021 [cited 2024 Jun 7]. Available from: https://www.pptvhd36.com/automotive/news/172026
Kannika Pusara. Road Traffic Act (No. 13), B.E. 2565, and the Requirement for Children to Sit in Car Seats. Senate Journal [Internet]. November 2022 [cited 2024 Jun 7]. Available from: https://www.senate.go.th/assets/portals/93/fileups/253/files/Analysis/65/11_66_1.pdf
A Situation Study Report: Car Seat in Thailand. Report No: 296-2015-16. [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 June 6]. Available from: http://kb.hsri.or.th/dspace/handle/11228/4326?locale-attribute-th
Wannapaschaiyong P, Penphattarakul A, Rojmahamongkol P, Sutchritpongsa S. The Relationship Between Primary Caregivers’ Psychosocial Factors and Self Esteem in Children and Adolescents with ADHD: An Exploratory Crossectional Study. Siriraj Med J. 2023;75(8):584-91.
Sauber-Schatz EK, Ederer DJ, Dellinger AM. Vital Signs: Motor Vehicle Injury Prevention - United States and 19 Comparison Nations. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(26):672-7.
Lee G, Pope CN, Nwosu A, McKenzie LB, Zhu M. Child passenger fatality: Child restraint system usage and contributing factors among the youngest passengers from 2011 to 2015. J Safety Res. 2019;70:33-8.
Sayed I, Abdelgawad H, Said D. Studying driving behavior and risk perception: a road safety perspective in Egypt. J Eng Appl Sci. 2022;69(22).
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














