Improvement in the Youthfulness of Facial Skin after a Single Treatment with Platelet Rich Plasma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i11.270077Keywords:
Youthfulness, Platelet-rich Plasma, Facial Skin, Aging Face, ImprovementAbstract
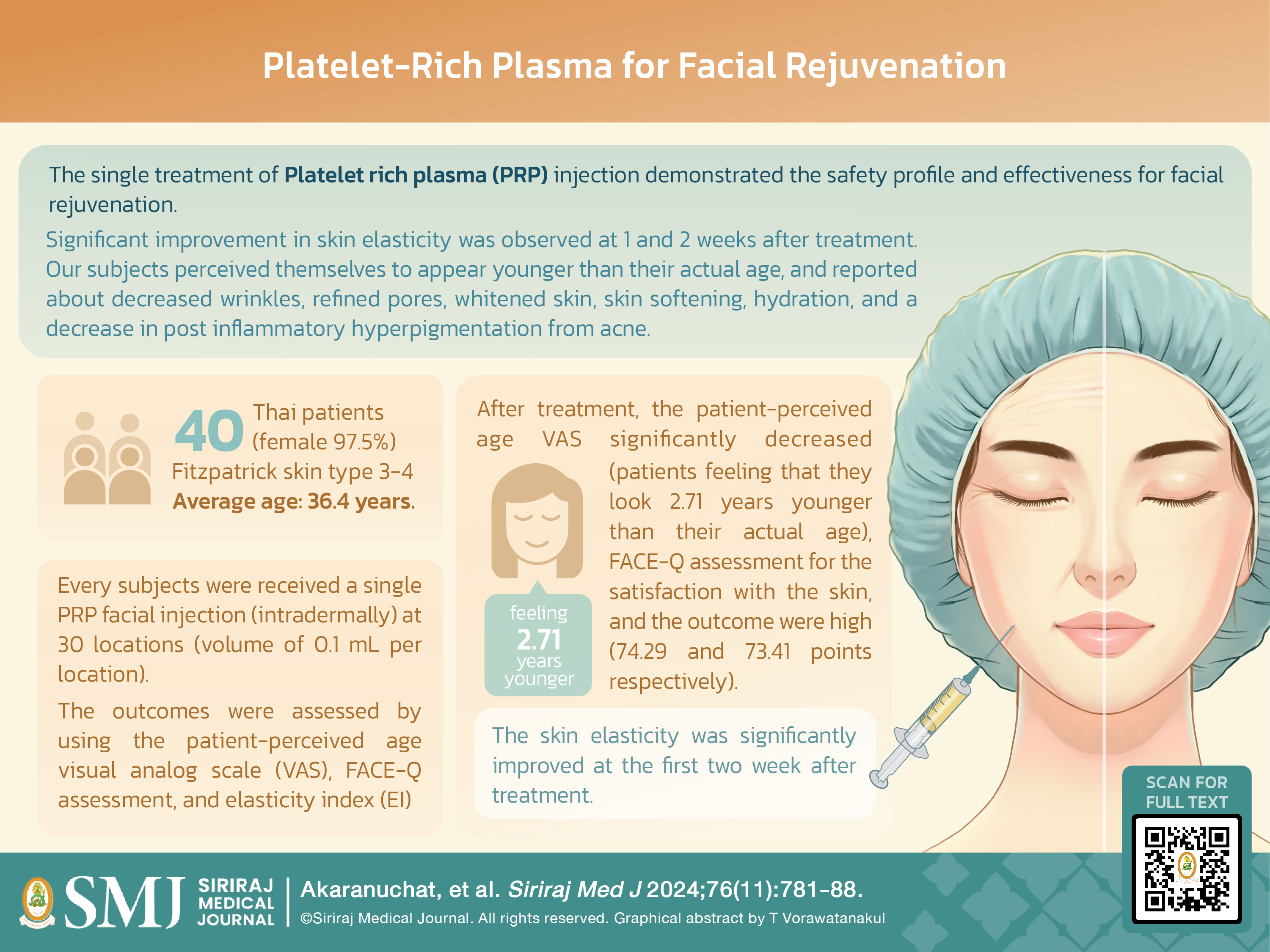
Objective: Platelet rich plasma (PRP) is an autologous substance widely used to stimulate dermal collagen synthesis. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of a single PRP treatment for facial rejuvenation.
Materials and Methods: This study was conducted at the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand from August 2020 to March 2021. Enrolled patients underwent a single intradermal injection treatment of 0.1 mL PRP at 30 locations on the face. Outcomes were assessed at 1, 2, and 4 weeks post-intervention using the patient-perceived age visual analog scale (VAS), FACE-Q assessment, and elasticity index (EI) with a Cutometer.
Results: Forty Thai patients with an average age of 36.4 years, Fitzpatrick skin type 3-4 were enrolled. The mean Patient-perceived Age VAS significantly decreased one month after treatment (-2.71±2.42, p<0.001). FACE-Q satisfaction with facial skin was 74.29±14.49, and satisfaction with the outcome was 73.41±16.26 (scale 0-100). The PRP significantly affected skin EI, with the peak improvement observed at 1-2 weeks post-injection, predominantly at the cheek, crow’s feet, and perioral area (all p<0.05). All patients had an overall improvement in satisfaction scores throughout the study.
Conclusion: A single treatment of PRP injection resulted in overall satisfaction in facial skin rejuvenation as measured by patient-perceived age VAS and FACE-Q assessment. The PRP showed positive outcomes in EI with peak performance at 1-2 weeks post-treatment.
References
Alexiades-Armenakas MR, Dover JS, Arndt KA. The spectrum of laser skin resurfacing: nonablative, fractional, and ablative laser resurfacing. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):719-37; quiz 738-40.
Borrione P, Fagnani F, Di Gianfrancesco A, Mancini A, Pigozzi F, Pitsiladis Y. The Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Muscle Healing. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2017;16(6):459-63.
Cervelli V, Nicoli F, Spallone D, Verardi S, Sorge R, Nicoli M, et al. Treatment of traumatic scars using fat grafts mixed with platelet-rich plasma, and resurfacing of skin with the 1540 nm nonablative laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2012;37(1):55-61.
Ince B, Yildirim MEC, Dadaci M, Avunduk MC, Savaci N. Comparison of the Efficacy of Homologous and Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for Treating Androgenic Alopecia. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018;42(1):297-303.
Martinez-Zapata MJ, Martí-Carvajal AJ, Solà I, Exposito JA, Bolibar I, Rodriguez L, et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma for treating chronic wounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2016(5):CD006899.
Cho JM, Lee YH, Baek RM, Lee SW. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on ultraviolet b-induced skin wrinkles in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(2):e31-9.
Yuksel EP, Sahin G, Aydin F, Senturk N, Turanli AY. Evaluation of effects of platelet-rich plasma on human facial skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014;16(5):206-8.
Alves R, Grimalt R. A Review of Platelet-Rich Plasma: History, Biology, Mechanism of Action, and Classification. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018;4(1):18-24.
Eppley BL, Pietrzak WS, Blanton M. Platelet-rich plasma: a review of biology and applications in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118(6):147e-59e.
Leo MS, Kumar AS, Kirit R, Konathan R, Sivamani RK. Systematic review of the use of platelet-rich plasma in aesthetic dermatology. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14(4):315-23.
Marx RE. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): what is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent. 2001;10:225-8.
Shin MK, Lee JH, Lee SJ, Kim NI. Platelet-rich plasma combined with fractional laser therapy for skin rejuvenation. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38(4):623-30.
Bielecki T, Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Everts PA, Wiczkowski A. The role of leukocytes from L-PRP/L-PRF in wound healing and immune defense: new perspectives. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(7):1153-62.
Borrione P, Gianfrancesco AD, Pereira MT, Pigozzi F. Platelet-rich plasma in muscle healing. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;89(10):854-61.
Marx RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(4):489-96.
Pavlovic V, Ciric M, Jovanovic V, Stojanovic P. Platelet Rich Plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components. Open Med (Wars). 2016;11(1):242-7.
Sclafani AP, Romo T, 3rd, Ukrainsky G, McCormick SA, Litner J, Kevy SV, et al. Modulation of wound response and soft tissue ingrowth in synthetic and allogeneic implants with platelet concentrate. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2005;7(3):163-9.
Wang HL, Avila G. Platelet rich plasma: myth or reality? Eur J Dent. 2007;1(4):192-4.
Yu W, Wang J, Yin J. Platelet-rich plasma: a promising product for treatment of peripheral nerve regeneration after nerve injury. Int J Neurosci. 2011;121(4):176-80.
Ahn S, Kim S, Lee H, Moon S, Chang I. Correlation between a Cutometer and quantitative evaluation using Moire topography in age-related skin elasticity. Skin Res Technol. 2007;13(3):280-4.
Denadai R, Chou PY, Su YY, Lin HH, Ho CT, Lo LJ. The Impacts of Orthognathic Surgery on the Facial Appearance and Age Perception of Patients Presenting Skeletal Class III Deformity: An Outcome Study Using the FACE-Q Report and Surgical Professional-Based Panel Assessment. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;145(4):1035-46.
Kappos EA, Temp M, Schaefer DJ, Haug M, Kalbermatten DF, Toth BA. Validating Facial Aesthetic Surgery Results with the FACE-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(4):839-45.
Sinno S, Schwitzer J, Anzai L, Thorne CH. Face-Lift Satisfaction Using the FACE-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(2):239-42.
Kakudo N, Minakata T, Mitsui T, Kushida S, Notodihardjo FZ, Kusumoto K. Proliferation-promoting effect of platelet-rich plasma on human adipose-derived stem cells and human dermal fibroblasts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;122(5):1352-60.
Marques LF, Stessuk T, Camargo IC, Junior NS, Santos L, Ribeiro-Paes JT. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): methodological aspects and clinical applications. Platelets. 2015;26(2):101-13.
Maisel-Campbell AL, Ismail A, Reynolds KA, Poon E, Serrano L, Grushchak S, et al. A systematic review of the safety and effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for skin aging. Arch Dermatol Res. 2020;312(5):301-15.
Wamaphutta K, Thasen C, Sereeaphinan C, Chaweekulrat P, Boonchai W. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tertiarycare university dermatology outpatient clinic and dermatology procedures. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(12):836-43.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














