Surgical Anatomy of the Lateral Thoracic Artery and Its Perforators: A Computed Tomographic Angiography and Cadaveric Dissection Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v76i12.270603Keywords:
Lateral Thoracic Artery, LTA Perforators, Cadaveric Dissection, CTAAbstract
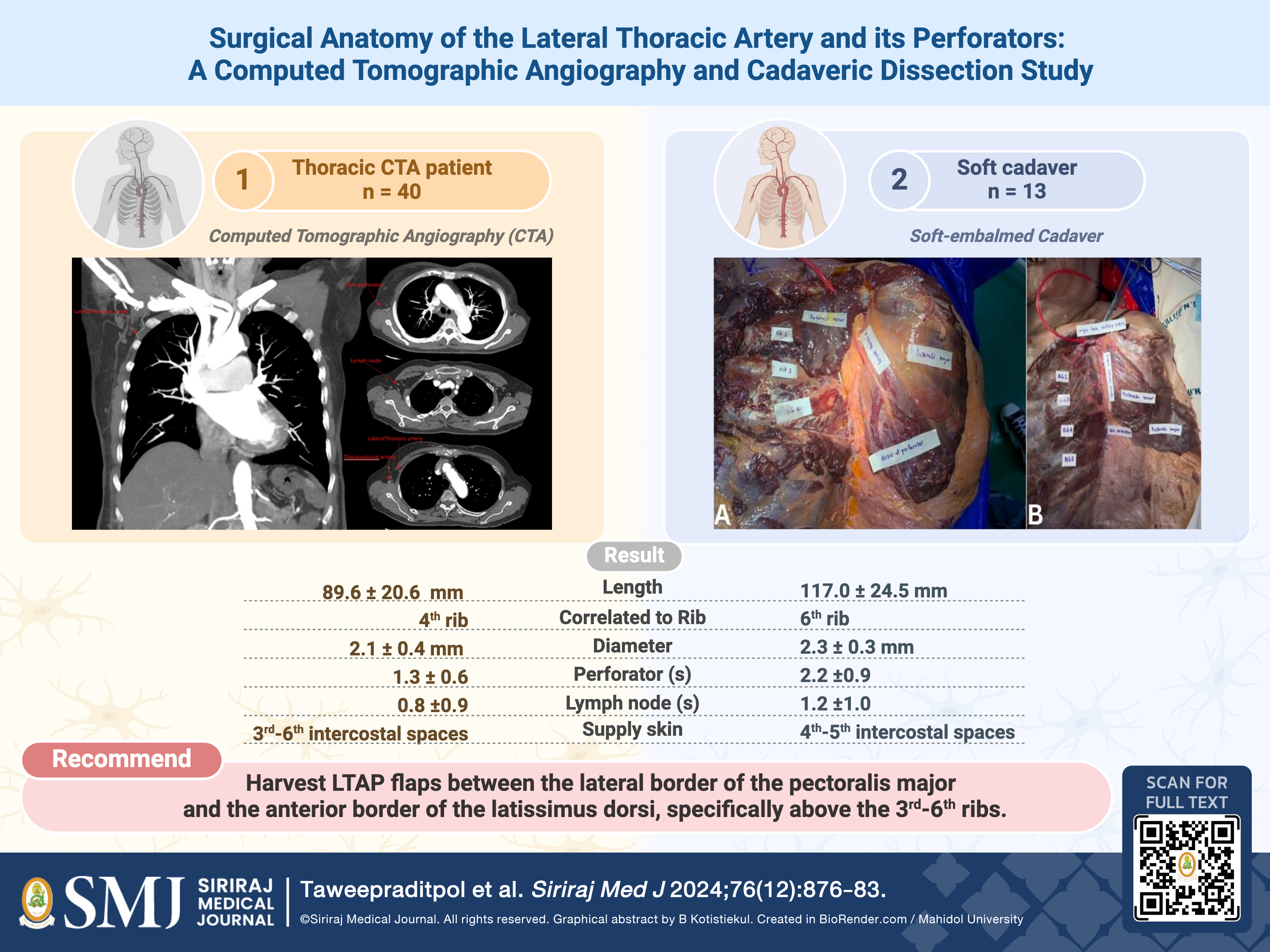
Objective: This study explores the anatomical variations and characteristics of the lateral thoracic artery (LTA) and its perforators through thoracic computed tomographic angiographies (CTA) and cadaveric dissection, aiming to enhance surgical planning and patient outcomes.
Materials and Methods: Data were recorded for both thoracic CTA patients (n = 40) and soft cadavers (n = 13) for subsequent retrospective analyses of biological sex, age, body mass index (BMI), LTA characteristics (length, diameter, origin, number of perforators, number of lymph nodes), and locations (rib level and distance from the pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, and acromioclavicular joint).
Results: Average LTA parameters for thoracic CTAs were 89.6 millimeters in length from origin and 2.1 millimeters in diameter, while cadavers were 117.0 millimeters in length and 2.3 millimeters in diameter. At least 1-2 cutaneous
perforators and 1 proximal lymph node were found across both thoracic CTAs and cadavers. No significant differences were observed between the left and right sides for both groups. On average, 73.8% and 66.4% of LTAs from thoracic CTAs and cadavers, respectively, originated from the axillary artery.
Conclusion: This knowledge is crucial for surgical planning, both to minimize damage to the LTA and ensure the inclusion of its perforators and proximal lymph nodes in the lateral thoracic region. The researchers recommend lateral thoracic artery perforator flap harvest between the lateral border of the pectoralis major and the anterior border of the latissimus dorsi, specifically above the 3rd-6th ribs, which is correlated to the length of LTA at 89.6-117 millimeters from origins.
References
Yamamoto T, Yamamoto N, Kageyama T, Sakai H, Fuse Y, Tsuihiji K, et al. Definition of perforator flap: what does a" perforator" perforate? Glob Health Med. 2019;1(2):114-6.
Geddes CR, Morris SF, Neligan PC. Perforator flaps: evolution, classification, and applications. Ann Plast Surg. 2003;50(1):90-9.
Koshima I, Soeda S. Inferior epigastric artery skin flaps without rectus abdominis muscle. Br J Plast Surg. 1989;42(6):645-8.
Kroll SS, Rosenfield L, Kroll SJ. Perforator-based flaps for low posterior midline defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988;81(4):561-6.
Kim JT, Ng S-W, Naidu S, Do Kim J, Kim YH. Lateral thoracic perforator flap: additional perforator flap option from the lateral thoracic region. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(12):1596-602.
Kim DY, Kim HY, Han YS, Park JH. Chest wall reconstruction with a lateral thoracic artery perforator propeller flap for a radiation ulcer on the anterior chest. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013;66(1):134-6.
Mangialardi ML, Baldelli I, Salgarello M, Raposio E. Breast reconstruction using the lateral thoracic, thoracodorsal, and intercostal arteries perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(1):e3334.
Bhattacharya S, Bhagia S, Bhatnagar S, Aabdi S, Chandra R. The anatomical basis of the lateral thoracic flap. European Journal of Plastic Surgery. 1990;13:238-40.
Taylor GI, Daniel RK. The anatomy of several free flap donor sites. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975;56(3):243-53.
Rowsell AR, Davies DM, Eizenberg N, Taylor GI. The anatomy of the subscapular-thoracodorsal arterial system: study of 100 cadaver dissections. Br J Plast Surg. 1984;37(4):574-6.
McCulley SJ, Schaverien MV, Tan VK, Macmillan RD. Lateral thoracic artery perforator (LTAP) flap in partial breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68(5):686-91.
Harii K, Torii S, Sekicuchi J. The free lateral thoracic flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1978;62(2):212-22.
Kagaya Y, Arikawa M, Sekiyama T, Mitsuwa H, Takanashi R, Taga M, et al. The concept of “whole perforator system” in the lateral thoracic region for latissimus dorsi muscle-preserving large flaps: An anatomical study and case series. PLoS One. 2021;16(9):e0256962.
Munhoz AM, Montag E, Arruda E, Brasil JA, Aldrighi JM, Gemperli R, et al. Immediate conservative breast surgery reconstruction with perforator flaps: new challenges in the era of partial mastectomy reconstruction? Breast. 2011;20(3):233-40.
Yamamoto T, Yoshimatsu H, Yamamoto N. Complete lymph flow reconstruction: a free vascularized lymph node true perforator flap transfer with efferent lymphaticolymphatic anastomosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(9):1227-33.
Tinhofer IE, Meng S, Steinbacher J, Roka-Palkovits J, Gyori E, Reissig LF, et al. The surgical anatomy of the vascularized lateral thoracic artery lymph node flap—A cadaver study. J Surg Oncol. 2017;116(8):1062-8.
Loukas M, Du Plessis M, Owens DG, Kinsella Jr CR, Litchfield CR, Nacar A, et al. The lateral thoracic artery revisited. Surg Radiol Anat. 2014;36:543-9.
Ratanayotha A, Oo EM. Chronicle of Anatomical Education in Thailand: Experiences at Siriraj Medical School. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(7):463-71.
Christison-Lagay ER, Darcy DG, Stanelle EJ, Dasilva S, Avila E, La Quaglia MP. "Trap-door" and "clamshell" surgical approaches for the management of pediatric tumors of the cervicothoracic junction and mediastinum. J Pediatr Surg. Jan 2014;49(1):172-6; discussion 176-7.
Kim JT, Kim SW. Perforator flap versus conventional flap. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(5):514-22.
Mangialardi ML, Baldelli I, Salgarello M, Raposio E. Breast reconstruction using the lateral thoracic, thoracodorsal, and intercostal arteries perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021;9(1):e3334.
McCulley SJ, Schaverien MV, Tan VKM, Macmillan RD. Lateral thoracic artery perforator (LTAP) flap in partial breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015;68(5):686-91.
Schaverien MV, Badash I, Patel KM, Selber JC, Cheng M-H. Vascularized lymph node transfer for lymphedema. Thieme Medical Publishers; 2018.p.028-035.
Turbpaiboon C, Puprasert C, Lohasammakul S, Dacharux W, Numwong T, Pandeya A, et al. Deep peroneal nerve: From an anatomical basis to clinical implementation. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(7):448-62.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














