Immunohistochemical Markers Associated with Meningioma Recurrence: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v77i3.271973Keywords:
Immunohistochemical marker, meningioma, recurrenceAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to determine the role of immunohistochemical markers in the recurrence of surgically treated meningiomas.
Materials and Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of the PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases to locate studies published within the past decade. The inclusion criteria for this study were patients aged ≥ 18 years who had undergone surgical treatment for meningioma. Studies that were not written in English, case report studies, case series studies, literature review studies, and studies involving patients who received treatments other than surgery or multimodal therapy were excluded. All studies that met the inclusion criteria were subjected to critical appraisal.
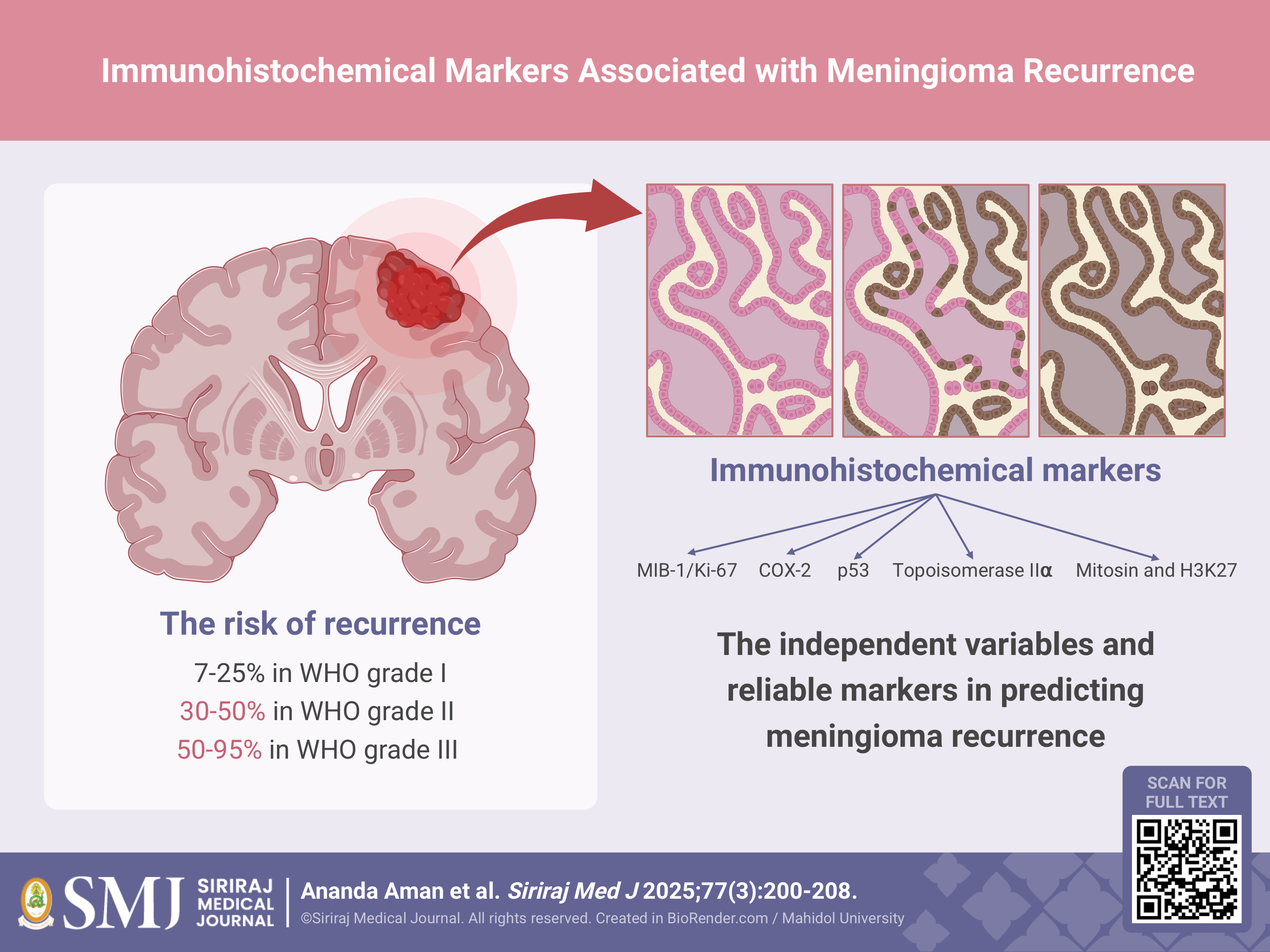
Results: Four studies comprising 3176 cases of meningioma cases were included in the analysis. Multivariate analysis showed that two immunohistochemical markers (COX-2 and MIB-1/Ki-67) were independent variables of meningioma recurrence. This study also found no statistical differences between grade I and II meningiomas with respect to the overexpression of COX-2 and MIB-1/Ki-67. The second study compared the nonrecurrence/relapse (non-R/R) and recurrence/relapse (R/R) groups and found a significant correlation between MIB-1 percentage, intensity, histoscore, and p53 percentage, regardless of tumor grade. The third study found that mitosin and topoisomerase IIa were significant predictors of recurrence but not MIB-1. The fourth study demonstrated that H3K27me3 loss is significantly associated with more aggressive meningiomas.
Conclusion: Our study showed that MIB-1/Ki-67, COX-2, p53, topoisomerase IIa, mitosin, and H3K27 are independent variables and reliable markers for predicting meningioma recurrence.
References
Quddusi A, Virani QUA, Shamim MS. Factors affecting postoperative recurrence or growth of meningiomas, other than histological grade and extent of resection. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69(10):1570-1.
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(6):803-20.
Perry A, Scheithauer BW, Stafford SL, Lohse CM, Wollan PC. “Malignancy” in meningiomas: A clinicopathologic study of 116 patients, with grading implications. Cancer. 1999;85(9):2046–56.
Alexiou GA, Gogou P, Markoula S, Kyritsis AP. Management of meningiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112(3):177–82.
Pieper DR, Al-Mefty O, Hanada Y, Buechner D. Hyperostosis associated with meningioma of the cranial base: Secondary changes or tumor invasion. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(4):742–7.
Voß KM, Spille DC, Sauerland C, Suero Molina E, Brokinkel C, Paulus W, et al. The Simpson grading in meningioma surgery: does the tumor location influence the prognostic value? J Neurooncol. 2017;133(3):641–51.
Nanda A, Bir SC, Maiti TK, Konar SK, Missios S, Guthikonda B. Relevance of Simpson grading system and recurrencefree survival after surgery for World Health Organization Grade I meningioma. J Neurosurg. 2017;126(1):201–11.
Sanz J, Ruiz J, Hernández S, Ferrer M, Zimman H, Sáez C, et al. Chromosome 1p36 loss and COX-2 overexpression predict recurrence-free survival in completely removed meningioma grade I and II. Rev Esp Patol. 2013;46(1):14–25.
Csonka T, Murnyák B, Szepesi R, Bencze J, Bognár L, Klekner Á, et al. Assessment of candidate immunohistochemical prognostic markers of meningioma recurrence. Folia Neuropathol. 2016;54(2):114–26.
Winther TL, Torp SH. DNA topoisomerase IIα and mitosin expression predict meningioma recurrence better than histopathological grade and MIB-1 after initial surgery. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):1–13.
Cello G, Patel R V., McMahon JT, Santagata S, Bi WL. Impact of H3K27 trimethylation loss in meningiomas: a meta-analysis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023;11(1):1–11.
Karaarslan N, Gurbuz MS, Calıskan T, Ayan E, Aker FV, Berkman MZ. The Effect of Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 on the Prognosis and Biological Behaviour of Meningiomas. Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26(5):678–83.
Suppiah S, Nassiri F, Bi WL, Dunn IF, Hanemann CO, Horbinski CM, et al. Molecular and translational advances in meningiomas. Neuro Oncol. 2019;21:I4–17.
Bie L, Zhao G, Ju Y, Zhang B. Integrative genomic analysis identifies CCNB1 and CDC2 as candidate genes associated with meningioma recurrence. Cancer Genet. 2011;204(10):536–40.
Sukpanichnant S. Malignancy of the Lymph Node: How General Practitioners and Pathologists can achieve a Definitive Diagnosis. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(9):604–17.
Hortobágyi T, Bencze J, Murnyák B, Kouhsari MC, Bognár L, Marko-Varga G. Pathophysiology of meningioma growth in pregnancy. Open Med. 2017;12(1):195–200.
Konstantinidou AE, Korkolopoulou P, Kavantzas N, Mahera H, Thymara I, Kotsiakis X, et al. Mitosin, a novel marker of cell proliferation and early recurrence in intracranial meningiomas. Histol Histopathol. 2003;18(1):67–74.
Ros-Sanjuan A, Iglesias-Moroño S, Carrasco-Brenes A, Bautista-Ojeda D, Arraez-Sanchez MA. Atypical Meningiomas: Histologic and Clinical Factors Associated With Recurrence. World Neurosurg. 2019;125:e248–56.
Sumkovski R, Micunovic M, Kocevski I, Ilievski B, Petrov I. Surgical treatment of meningiomas-outcome associated with type of resection, recurrence, karnofsky performance score, mitotic count. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019;7(1):56–64.
Liu N, Song SY, Jiang JB, Wang TJ, Yan CX. The prognostic role of Ki-67/MIB-1 in meningioma: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Med (United States). 2020;99(9):1–10.
Korshunov A, Shishkina L, Golanov A. DNA topoisomerase II-α and cyclin A immunoexpression in meningiomas and its prognostic significance: An analysis of 263 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(9):1079–86.
Kunishio K, Morisaki K, Matsumoto Y, Nagao S. DNA topoisomerase IIalpha protein and mRNA expression in intracranial meningiomas. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2000;17(3):105–10.
Lanzafame S, Torrisi A, Barbagallo G, Emmanuele C, Alberio N, Albanese V. Correlation between histological grade, MIB-1, p53, and recurrence in 69 completely resected primary intracranial meningiomas with a 6 year mean follow-up. Pathol Res Pract. 2000;196(7):483–8.
Cho H, Ha SY, Park SH, Park K, Chae YS. Role of p53 gene mutation in tumor aggressiveness of intracranial meningiomas. J Korean Med Sci. 1999;14(2):199-205.
Choi EM, Kwak SJ, Kim YM, Ha KS, Kim J Il, Lee SW, et al. COX-2 inhibits anoikis by activation of the PI-3K/Akt pathwayin human bladder cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 2005;37(3):199–203.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














