Incidence of Tympanic Membrane Perforation Affected by Intratympanic Steroid Injection: A Retrospective Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v77i4.272595Keywords:
Tympanic membrane perforation, intratympanic steroid injection, sudden sensorineural hearing lossAbstract
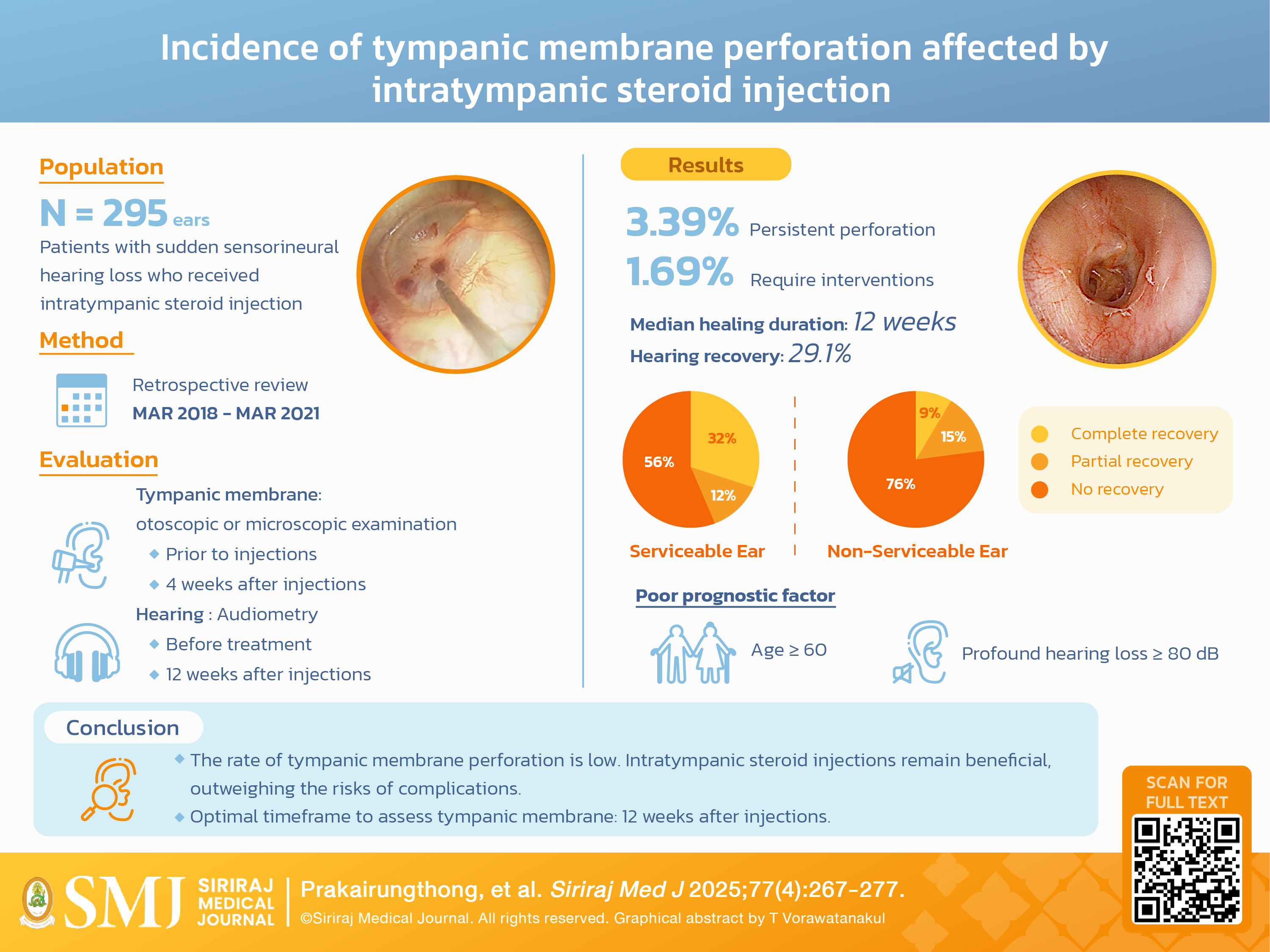
Objective: This study aims to determine the incidence of persistent tympanic membrane perforation following intratympanic steroid injection and to identify potential factors associated with delayed healing. Additionally, it aims to estimate the time required for perforation closure in prolonged cases to avoid unnecessary interventions.
Materials and Methods: Data from patients who underwent intratympanic steroid injections were reviewed. The primary outcome was the incidence of tympanic membrane perforation lasting beyond four weeks post-injection. Secondary outcomes included identifying factors affecting healing duration and closure time in prolonged cases.
Results: Of 295 ears treated between March 2018 and March 2021, 3.39% (10/295) experienced persistent perforation at four weeks. Of these, 1.69% (5/295) required intervention, while the rest healed spontaneously. The median closure time was 12 weeks. All patients with persistent perforation were female. No statistically significant differences were found between groups. Hearing recovery was achieved in 29.1% (74/254) of patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Younger age and non-profound hearing loss were favorable prognostic factors.
Conclusion: The incidence of perforation in this study is lower than previously reported but consistent with other literature. Intratympanic steroid injections remain beneficial, outweighing the risks of complications.
References
Alexander TH, Harris JP. Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2013;34(9):1586-9.
Wu CS, Lin HC, Chao PZ. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: evidence from Taiwan. Audiol Neurootol. 2006;11(3):151-6.
Swain SK, Das S, Lenka S. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss among COVID-19 Patients-Our Experiences at an Indian Teaching Hospital. Siriraj Medical Journal. 2021;73(2):77-83.
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980;106(12):772-6.
Itoh A, Sakata E. Treatment of vestibular disorders. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1991;481:617-23.
Silverstein H, Choo D, Rosenberg SI, Kuhn J, Seidman M, Stein I. Intratympanic steroid treatment of inner ear disease and tinnitus (preliminary report). Ear Nose Throat J. 1996;75(8):468-71, 74, 76 passim.
Chandrasekhar SS. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: clinical and laboratory evaluation. Otol Neurotol. 2001;22(1):18-23.
Ho HG, Lin HC, Shu MT, Yang CC, Tsai HT. Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone injection in sudden-deafness patients as salvage treatment. Laryngoscope. 2004;114(7):1184-9.
Xenellis J, Papadimitriou N, Nikolopoulos T, Maragoudakis P, Segas J, Tzagaroulakis A, et al. Intratympanic steroid treatment in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a control study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134(6):940-5.
Kiliç R, Safak MA, Oğuz H, Kargin S, Demirci M, Samim E, et al. Intratympanic methylprednisolone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2007;28(3):312-6.
Filipo R, Covelli E, Balsamo G, Attanasio G. Intratympanic prednisolone therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A new protocol. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010;130(11):1209-13.
Lavigne P, Lavigne F, Saliba I. Intratympanic corticosteroids injections: a systematic review of literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;273(9):2271-8.
Liu YC, Chi FH, Yang TH, Liu TC. Assessment of complications due to intratympanic injections. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016;2(1):13-6.
Topf MC, Hsu DW, Adams DR, Zhan T, Pelosi S, Willcox TO, et al. Rate of tympanic membrane perforation after intratympanic steroid injection. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017;38(1):21-5.
Kim YH, Lee DY, Lee DH, Oh S. Tympanic Membrane Perforation After Intratympanic Steroid Injection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022;166(2):249-59.
Simani L, Shilo S, Oron Y, Eta RA, Handzel O, Muhanna N, et al. Residual Perforation Risk Assessment of Intratympanic Steroids via Tympanostomy Tube Versus Transtympanic Injections. Laryngoscope. 2021;131(9):E2583-e91.
Limviriyakul S. TK, Prakairungthong S, Atipas S, Chongvisal S. Methylprednisolone intratympanic injection in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a retrospective review of 167 cases. J Med Assoc Thai. 2018(101(6)):707-12.
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR, Bontempo LJ, Faucett EA, Finestone SA, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;161(1_suppl):S1-s45.
Kuri M, Nakagawa M, Tanaka H, Hasuo S, Kishi Y. Determination of the duration of preoperative smoking cessation to improve wound healing after head and neck surgery. Anesthesiology. 2005;102(5):892-6.
Chan LK, Withey S, Butler PE. Smoking and wound healing problems in reduction mammaplasty: is the introduction of urine nicotine testing justified? Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56(2):111-5.
Mills E, Eyawo O, Lockhart I, Kelly S, Wu P, Ebbert JO. Smoking cessation reduces postoperative complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Med. 2011;124(2):144-54.e8.
Chen SL, Yang SW. Factors affecting the treatment outcomes of myringoplasty in patients with small tympanic membrane perforations. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;276(11):3005-12.
Tachibana T, Kariya S, Orita Y, Makino T, Haruna T, Matsuyama Y, et al. Spontaneous closure of traumatic tympanic membrane perforation following long-term observation. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019;139(6):487-91.
Lou Z, Yang J, Tang Y, Xiao J. Risk factors affecting human traumatic tympanic membrane perforation regeneration therapy using fibroblast growth factor-2. Growth Factors. 2015;33(5-6):410-8.
Banerjee A, Parnes LS. The biology of intratympanic drug administration and pharmacodynamics of round window drug absorption. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2004;37(5):1035-51.
Parnes LS, Sun AH, Freeman DJ. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: an animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope. 1999;109(7 Pt 2):1-17.
Vrabec JT. Tympanic membrane perforations in the diabetic rat: a model of impaired wound healing. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;118(3 Pt 1):304-8.
Byl FM, Jr. Sudden hearing loss: eight years' experience and suggested prognostic table. Laryngoscope. 1984;94(5 Pt 1):647-61.
Fetterman BL, Saunders JE, Luxford WM. Prognosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol. 1996;17(4):529-36.
Kuhn M, Heman-Ackah SE, Shaikh JA, Roehm PC. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011;15(3):91-105.
Wu H, Wan W, Jiang H, Xiong Y. Prognosis of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: The Nomogram Perspective. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2023;132(1):5-12.
Mattox DE, Simmons FB. Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977;86(4 Pt 1):463-80.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














