Assessing Dysphagia in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: Validation and Cultural Adaptation of the Thai M.D. Anderson Dysphagia Inventory (TH-MDADI)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v77i4.272679Keywords:
Head and neck cancer, MDADI, SF-36, health-related quality of lifeAbstract
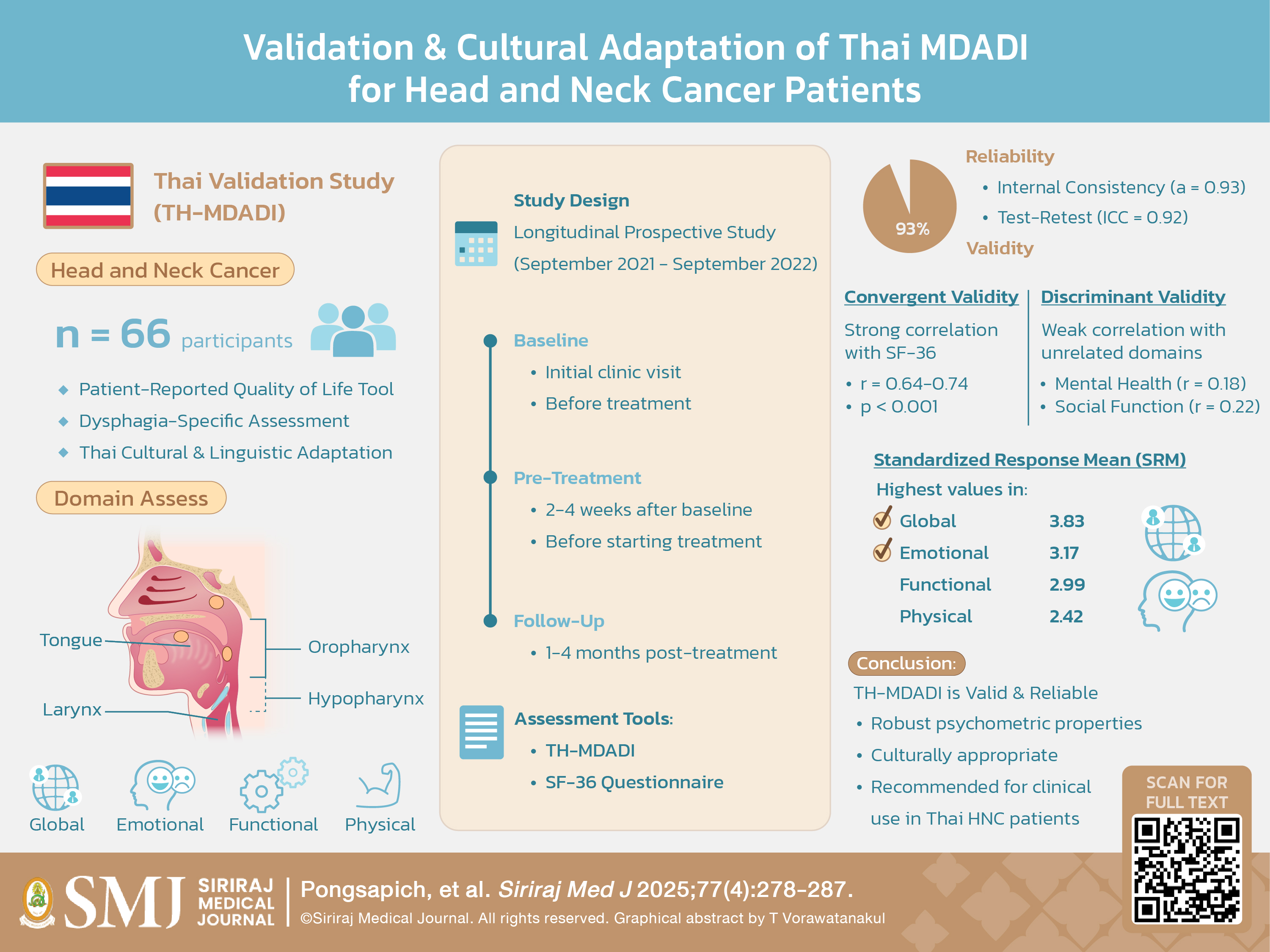
Objective: The validation study of the Thai version of the M.D. Anderson Dysphagia Inventory (TH-MDADI) addresses a critical gap in head and neck cancer (HNC) care in Thailand. At leading institutions like Siriraj Hospital, patient-reported outcomes have been historically neglected, with care primarily focusing on routine medical services. This study aimed to validate the TH-MDADI to enhance dysphagia assessment and promote patient centered care.
Materials and Methods: In this longitudinal prospective study, 66 HNC patients completed the TH-MDADI and SF-36 at baseline, pre-treatment, and post-treatment at Siriraj Hospital. Psychometric properties were evaluated, including internal consistency (Cronbach’s α), test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient, ICC), convergent and discriminant validity (correlations with SF-36 domains), and responsiveness (standardized response mean, SRM).
Results: The TH-MDADI demonstrated excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.93) and test-retest reliability (ICC = 0.92, 95% CI: 0.88–0.96). Strong correlations with related SF-36 domains (r = 0.64-0.74, p < 0.001) established convergent validity, while weak correlations with unrelated domains confirmed discriminant validity. High responsiveness to change post-treatment was observed, particularly in the Global (SRM = 3.83) and Emotional (SRM = 3.17) subscales.
Conclusion: The TH-MDADI demonstrates robust psychometric properties, establishing its value as a reliable tool for assessing dysphagia-related quality of life in Thai HNC patients. This validation represents a significant advancement in Thai cancer care, addressing the historical neglect of patient-reported outcomes. By providing clinicians with a validated assessment instrument, this study promotes a more systematic, patient-centered approach to HNC treatment in Thailand.
References
Chen AY, Frankowski R, Bishop-Leone J, Hebert T, Leyk S, Lewin J, et al. The development and validation of a dysphagia-specific quality-of-life questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer: the M. D. Anderson dysphagia inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127(7):870-6.
Tangjaturonrasme N, Vatanasapt P, Bychkov A. Epidemiology of head and neck cancer in Thailand. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018;14(1):16-22.
Herdman M, Fox-Rushby J, Badia X. ‘Equivalence’ and the translation and adaptation of health-related quality of life questionnaires. Qual Life Res. 1997;6(3):237-47.
Leurmarnkul W, Meetam P. Properties Testing of the Retranslated SF36 (Thai Version). The Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2005;29.
Ware JE, Jr., Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473-83.
Speyer R, Heijnen BJ, Baijens LW, Vrijenhoef FH, Otters EF, Roodenburg N, et al. Quality of life in oncological patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the MD Anderson Dysphagia Inventory and the Deglutition Handicap Index. Dysphagia. 2011;26(4):407-14.
Speyer R, Heijnen BJ, Baijens LW, Vrijenhoef FH, Otters EF, Roodenburg N, et al. Quality of life in oncological patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the MD Anderson Dysphagia Inventory and the Deglutition Handicap Index. Dysphagia. 2011;26(4):407-14.
Carlsson S, Rydén A, Rudberg I, Bove M, Bergquist H, Finizia C. Validation of the Swedish M. D. Anderson Dysphagia Inventory (MDADI) in patients with head and neck cancer and neurologic swallowing disturbances. Dysphagia. 2012;27(3):361-9.
Kwon CH, Kim YH, Park JH, Oh BM, Han TR. Validity and reliability of the Korean version of the MD Anderson Dysphagia inventory for head and neck cancer patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013;37(4):479-87.
Guedes RL, Angelis EC, Chen AY, Kowalski LP, Vartanian JG. Validation and application of the M.D. Anderson Dysphagia Inventory in patients treated for head and neck cancer in Brazil. Dysphagia. 2013;28(1):24-32.
Kientchockwiwat K, Thitisakulchai P, Tanvijit P. The Safety of Food and Drink Consistencies Based on a Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing Study Results in Stroke Patients with Dysphagia. Siriraj Med J. 2022;74(6):395-400.
Keskool P, Warnpeurch L, Ongard S, Pitaksurachai P, Nujchanart N, Kerdnoppakhun J. The relationships among objective measures of tongue strength and risk of aspiration. Siriraj Med J. 2018;70(4):302-9.
Guillemin F, Bombardier C, Beaton D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993;46(12):1417-32.
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(24):3186-91.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














