The Use of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring to Personalize Once-daily Intravenous Busulfan in Thai Pediatric Patients Underwent Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v77i8.274573Keywords:
Therapeutic drug monitoring, Busulfan, Hematopoietic Stem Cell TransplantationAbstract
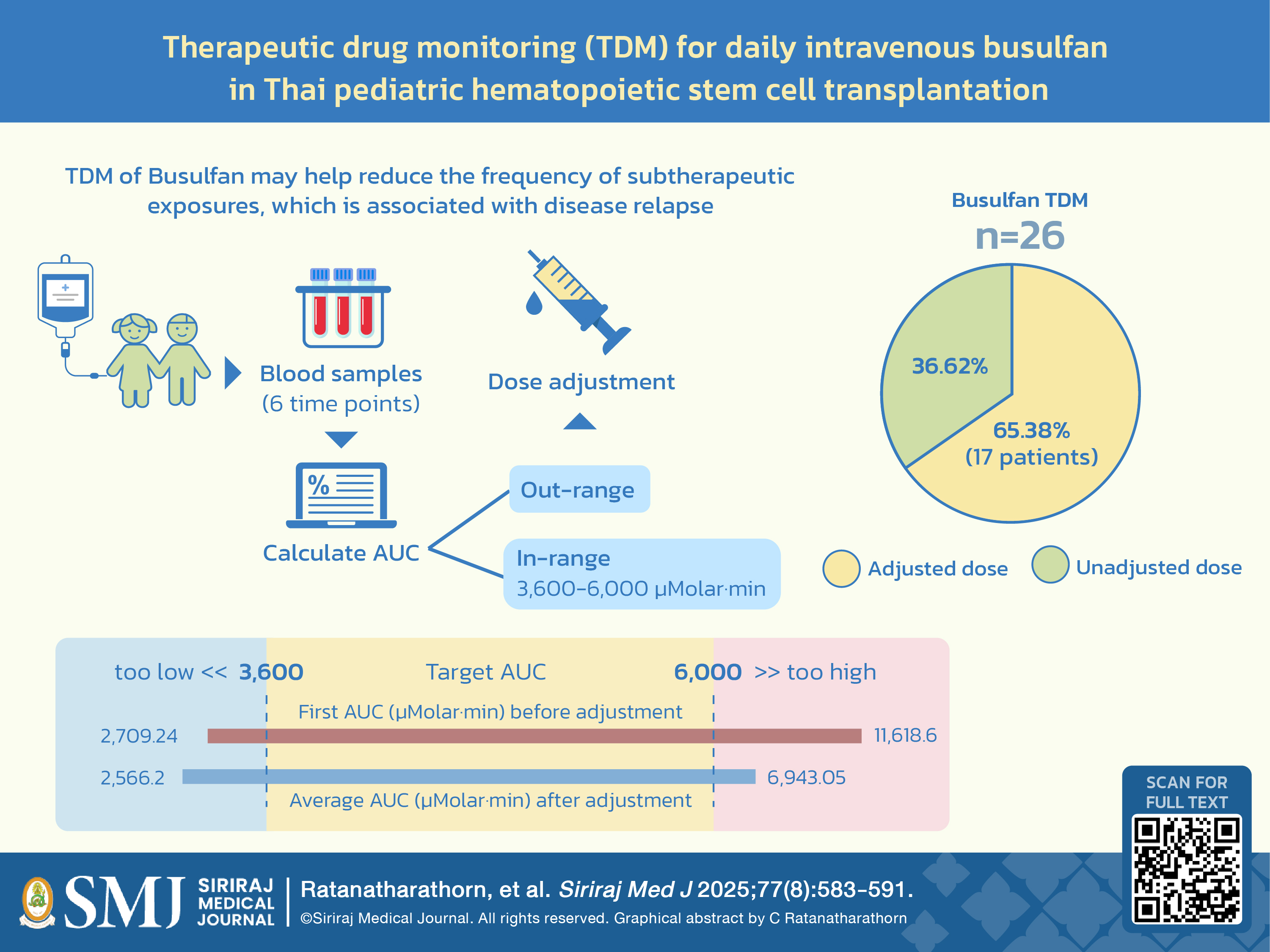
Objective: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) for personalizing busulfan dosing in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is recommended. The proportion of patients requiring dose adjustments and the frequency of achieving the target area under the time curve (AUC) was observed.
Materials and Methods: This study included children who underwent once-daily intravenous busulfan-conditioning HSCT during October 2020 to April 2024. The initial busulfan dosage followed the European Medicines Agency nomogram, set between 3.2 and 4.8 mg/kg/day. Blood samples were collected to analyze pharmacokinetics and calculate AUC. Dose adjustments were made if AUC fell outside the target of 3,600 to 6,000 μMolar·min.
Results: The study comprised 26 children. Dose adjustments for busulfan were performed in 17 patients (65.4%). Individual average AUCs ranged from 2,566.2 to 6,943.05 μMolar·min. Patients under 10 years had a higher likelihood of an out-of-range target AUC following dose adjustment compared to those aged ≥ 10 years (43.8% and 0%, respectively; P=0.023). A lower-than-target average AUC was significantly related to an earlier disease relapse compared to non-lower range AUCs (P<0.005). Conversely, higher AUCs did not correlate with busulfan-related side effects or treatment-related mortality.
Conclusion: Our findings support TDM as a strategy to enhance the efficacy of once-daily intravenous busulfan in HSCT among Thai pediatric patients. TDM may help reduce the frequency of subtherapeutic exposures, which is associated with disease relapse. Patients under 10 years face more difficulties in achieving the target AUC, indicating the need for careful monitoring and dose adjustments in this age group.
References
Palmer J, McCune JS, Perales MA, Marks D, Bubalo J, Mohty M, et al. Personalizing Busulfan-Based Conditioning: Considerations from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Practice Guidelines Committee. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(11):1915-25.
Kashyap A, Wingard J, Cagnoni P, Roy J, Tarantolo S, Hu W, et al. Intravenous versus oral busulfan as part of a busulfan/cyclophosphamide preparative regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: decreased incidence of hepatic venoocclusive disease (HVOD), HVOD-related mortality, and overall 100-day mortality. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8(9):493-500.
Andersson BS, Thall PF, Madden T, Couriel D, Wang X, Tran HT, et al. Busulfan systemic exposure relative to regimen-related toxicity and acute graft-versus-host disease: defining a therapeutic window for i.v. BuCy2 in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8(9):477-85.
Nguyen L, Fuller D, Lennon S, Leger F, Puozzo C. I.V. busulfan in pediatrics: a novel dosing to improve safety/efficacy for hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33(10):979-87.
Vassal G, Michel G, Espérou H, Gentet JC, Valteau-Couanet D, Doz F, et al. Prospective validation of a novel IV busulfan fixed dosing for paediatric patients to improve therapeutic AUC targeting without drug monitoring. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008;61(1):113-23.
Okamoto Y, Nagatoshi Y, Kosaka Y, Kikuchi A, Kato S, Kigasawa H, et al. Prospective pharmacokinetic study of intravenous busulfan in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in 25 children. Pediatr Transplant. 2014;18(3):294-301.
Jansing T, Sanpakit K, Tharnpanich T, Jiranantakan T, Niphandwongkorn V, Chindavijak B, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of intravenous busulfan in Thai children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A pilot study. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2021;38(4):346-57.
Ryu SG, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Lee JH, Lee YS, Seol M, et al. Randomized comparison of four-times-daily versus once-daily intravenous busulfan in conditioning therapy for hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(9):1095-105.
Madden T, de Lima M, Thapar N, Nguyen J, Roberson S, Couriel D, et al. Pharmacokinetics of once-daily IV busulfan as part of pretransplantation preparative regimens: a comparison with an every 6-hour dosing schedule. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(1):56-64.
Andersson BS, Thall PF, Valdez BC, Milton DR, Al-Atrash G, Chen J, et al. Fludarabine with pharmacokinetically guided IV busulfan is superior to fixed-dose delivery in pretransplant conditioning of AML/MDS patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(4):580-7.
Paiboon T, Worapant K. . J Med Tech Phy Ther. 2019;31.
Bubalo J, Carpenter PA, Majhail N, Perales MA, Marks DI, Shaughnessy P, et al. Conditioning chemotherapy dose adjustment in obese patients: a review and position statement by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation practice guideline committee. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(5):600-16.
Zao JH, Schechter T, Liu WJ, Gerges S, Gassas A, Egeler RM, et al. Performance of Busulfan Dosing Guidelines for Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(8):1471-8.
Domingos V, Nezvalova-Henriksen K, Dadkhah A, Moreno-Martinez ME, Ben Hassine K, Pires V, et al. A practical guide to therapeutic drug monitoring in busulfan: recommendations from the Pharmacist Committee of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024.
De Gregori S, Tinelli C, Manzoni F, Bartoli A. Comparison of Two Analytical Methods for Busulfan Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2021;46(1):155-9.
Seydoux C, Battegay R, Halter J, Heim D, Rentsch KM, Passweg JR, et al. Impact of busulfan pharmacokinetics on outcome in adult patients receiving an allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022;57(6):903-10.
Dupuis LL, Sibbald C, Schechter T, Ansari M, Gassas A, Theoret Y, et al. IV busulfan dose individualization in children undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant: limited sampling strategies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(5):576-82.
Salman B, Al-Za'abi M, Al-Huneini M, Dennison D, Al-Rawas A, Al-Kindi S, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring-guided dosing of busulfan differs from weight-based dosing in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2017;10(2):70-8.
Ngamdamrongkiat P, Arromdee E, Vongwiwatana A, Owattanapanich W, Sukpanichnant S. Histopathological and Clinical Features of Methotrexate-Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Siriraj Medical Journal. 2022;74(9):575-89.
Law S, Butpech T, Phumeetham S, Preeprem N, Limprayoon K. Characteristics, Outcomes and Bed Utilization of 15-to-18-Year-Old Adolescents in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in Thailand. Siriraj Medical Journal. 2023;75(8):555-9.
Ansari M, Curtis PH, Uppugunduri CRS, Rezgui MA, Nava T, Mlakar V, et al. GSTA1 diplotypes affect busulfan clearance and toxicity in children undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a multicenter study. Oncotarget. 2017;8(53):90852-67.
Nguyen AH, Biswas M, Puangpetch A, Prommas S, Pakakasama S, Anurathapan U, et al. Effect of GSTA1 Variants on Busulfan-Based Conditioning Regimen Prior to Allogenic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in Pediatric Asians. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(2).
Bartelink IH, Lalmohamed A, van Reij EM, Dvorak CC, Savic RM, Zwaveling J, et al. Association of busulfan exposure with survival and toxicity after haemopoietic cell transplantation in children and young adults: a multicentre, retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3(11):e526-e36.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














