Structured Multidisciplinary Approach to Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Impact on Mortality and Complications in a 13-Year Cohort
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v77i9.276153Keywords:
Ruptured AAA, Protocol, Multidisciplinary team, Outcomes, Perioperative mortalityAbstract
Objective: To evaluate the impact of a comprehensive multidisciplinary protocol on 30-day survival in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (rAAA) patients and to identify factors influencing outcomes.
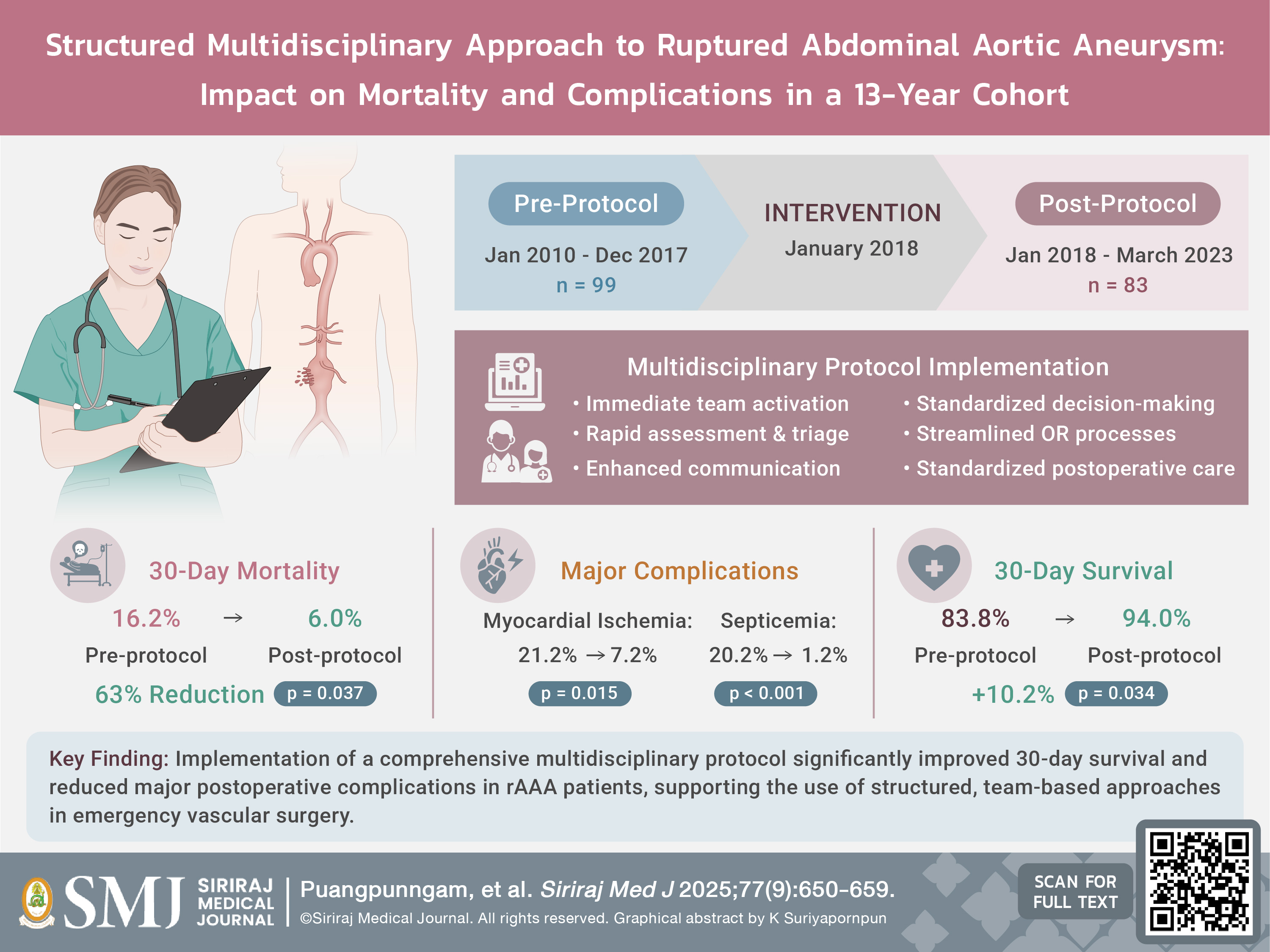
Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective study comparing outcomes before and after implementation a multidisciplinary protocol for rAAA management at Siriraj Hospital. The study included 182 patients (pre-protocol: n=99, Jan 2010-Dec 2017; post-protocol: n=83, Jan 2018-Mar 2023). Primary outcome was 30-day overall survival, with secondary outcomes including factors influencing survival, need for aortic balloon occlusion, operative parameters, length of stay, and complications.
Results: The 30-day mortality rate significantly decreased from 16.2% pre-protocol to 6.0% post-protocol (p=0.037). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed improved 30-day survival in the post-protocol group (94.0% vs 83.8%, p=0.034). However, while protocol implementation was associated with a non-significant reduction in mortality hazard (adjusted HR 0.509, 95% CI 0.175-1.478, p=0.213), multivariable analysis identified cardiac arrest (aHR 8.180, p<0.001) and unfit patient status (aHR 6.420, p=0.003) as independent predictors of mortality. The post-protocol group had significantly reduced myocardial ischemia (7.2% vs 21.2%, p=0.015) and septicemia (1.2% vs 20.2%, p<0.001), with no significant differences in operative parameters or length of stay.
Conclusion: Implementation of a multidisciplinary protocol for rAAA management was associated with improved 30-day survival and reduced postoperative complications, supporting the use of structured protocols in rAAA management.
References
Prapassaro T, Chinsakchai K, Techarattanaprasert S, Wongwanit C, Ruansetakit C, Hongku K, et al. Determining Perioperative Mortality in Patients with Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Insights from a Retrospective Cohort Study. Siriraj Med J. 2024;76(8):480-7.
Sweeting MJ, Balm R, Desgranges P, Ulug P, Powell JT. Individual-patient meta-analysis of three randomized trials comparing endovascular versus open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102(10):1229-39.
van Beek SC, Conijn AP, Koelemay MJ, Balm R. Editor's Choice - Endovascular aneurysm repair versus open repair for patients with a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review and meta-analysis of short-term survival. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014;47(6):593-602.
Moore R, Nutley M, Cina CS, Motamedi M, Faris P, Abuznadah W. Improved survival after introduction of an emergency endovascular therapy protocol for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(3):443-50.
Azhar B, Patel SR, Holt PJ, Hinchliffe RJ, Thompson MM, Karthikesalingam A. Misdiagnosis of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endovasc Ther. 2014;21(4):568-75.
Bown MJ, Sutton AJ, Bell PR, Sayers RD. A meta-analysis of 50 years of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Br J Surg. 2002;89(6):714-30.
Mell MW, Callcut RA, Bech F, Delgado MK, Staudenmayer K, Spain DA, et al. Predictors of emergency department death for patients presenting with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 2012;56(3):651-5.
Kontopodis N, Galanakis N, Antoniou SA, Tsetis D, Ioannou CV, Veith FJ, et al. Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Analysis of Outcomes of Endovascular and Open Repair for Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020;59(3):399-410.
Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, Allaire E, Bown M, Cohnert T, et al. Editor's Choice - European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57(1):8-93.
Brown LC, Epstein D, Manca A, Beard JD, Powell JT, Greenhalgh RM. The UK Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) trials: design, methodology and progress. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004;27(4):372-81.
Reimerink JJ, van der Laan MJ, Koelemay MJ, Balm R, Legemate DA. Systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2013;100(11):1405-13.
Karthikesalingam A, Holt PJ, Vidal-Diez A, Ozdemir BA, Poloniecki JD, Hinchliffe RJ, et al. Mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: clinical lessons from a comparison of outcomes in England and the USA. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):963-9.
Takei Y, Tezuka M, Saito S, Ogasawara T, Seki M, Kato T, et al. A protocol-based treatment for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm contributed to improving aorta-related mortality: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023;23(1):436.
Comparative clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of endovascular strategy v open repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: three year results of the IMPROVE randomised trial. BMJ. 2017;359:j4859.
D'Oria M, Lembo R, Hörer TM, Rasmussen T, Mani K, Parlani G, et al. An International Expert-Based CONsensus on Indications and Techniques for aoRtic balloOn occLusion in the Management of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (CONTROL-RAAA). J Endovasc Ther. 2023:15266028231217233.
Scali ST, Stone DH. Modern management of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10:1323465.
Duceppe E, Parlow J, MacDonald P, Lyons K, McMullen M, Srinathan S, et al. Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines on Perioperative Cardiac Risk Assessment and Management for Patients Who Undergo Noncardiac Surgery. Can J Cardiol. 2017;33(1):17-32.
Salhab M, Farmer J, Osman I. Impact of delay on survival in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Vascular. 2006;14(1):38-42.
Harris DG, Garrido D, Oates CP, Kalsi R, Huffner ME, Toursavadkohi S, et al. Repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm after cardiac arrest. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(5):1497-502.
Guni A, Varma P, Zhang J, Fehervari M, Ashrafian H. Artificial Intelligence in Surgery: The Future is Now. Eur Surg Res. 2024;65(1):22-39.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














