การจัดการภาวะปากแห้งในผู้สูงอายุที่เป็นเบาหวาน
คำสำคัญ:
ผู้สูงอายุ, เบาหวาน, ภาวะปากแห้ง, การจัดการภาวะปากแห้งบทคัดย่อ
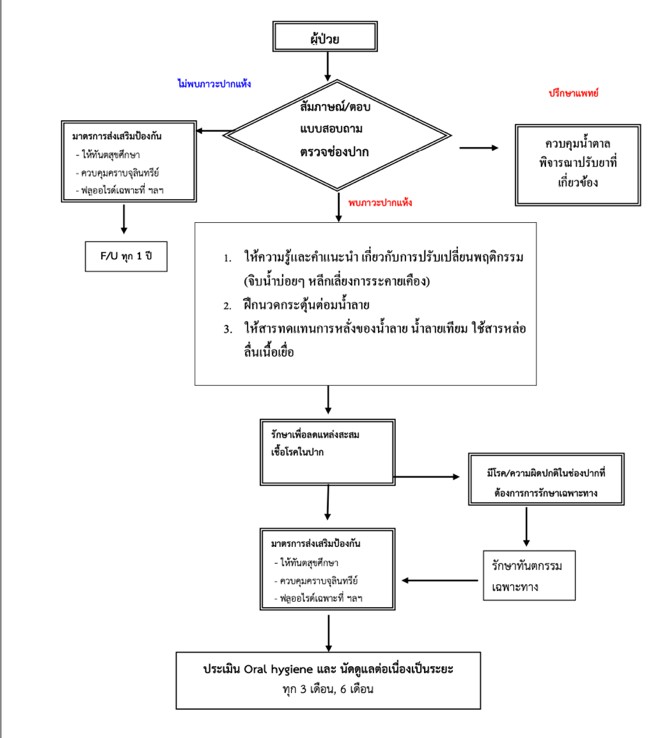
การศึกษานี้เป็นการศึกษาเชิงวิจัยและพัฒนา (Research and Development) มีวัตถุประสงค์
เพื่อศึกษาผลของการจัดการภาวะปากแห้งร่วมกับการนวดกระตุ้นต่อมน้ำลายในผู้สูงอายุที่เป็นโรคเบาหวาน จำนวน 154 คน โดยเก็บข้อมูลก่อนและหลังการจัดการด้วยแบบสอบถามวัดระดับความรุนแรงของภาวะปากแห้ง (Xerostomia Inventory)
ผลการศึกษาพบ ความชุกของภาวะปากแห้งในผู้สูงอายุที่เป็นโรคเบาหวานจำนวน 51 คน คิดเป็นร้อยละ 33.12 มีค่าคะแนนเฉลี่ยระดับความรุนแรงจากแบบประเมินภาวะปากแห้ง (Xerostomia Inventory) 21.98 (SD=3.40) คะแนน หลังจาก 2 เดือน พบว่า กลุ่มตัวอย่างมีคะแนนภาวะปากแห้ง
ต่ำกว่าก่อนการทดลองอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติ (p<0.001) คะแนนการจัดการภาวะปากแห้งลดลงเท่ากับ 5.70 คะแนน (95%CI; 4.20, 7.20)
ทั้งนี้ ควรมีการศึกษาเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้อง ผลลัพธ์และความพึงพอใจของผู้ป่วย
แต่ละวิธีเพื่อนำผลมาเป็นแนวทางในการวางแผนการดูแลและแนะนำผู้ป่วยต่อไป
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Lamster IB, Lalla E, Borgnakke WS, Taylor GW. The relationship between oral health and diabetes mellitus. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008 Oct;139 Suppl:19S-24S.
Lin J, Thompson TJ, Cheng YJ, Zhuo X, Zhang P, Gregg E, et al. Projection of the future diabetes burden in the United States through 2060. Population Health Metrics 2018; 16: 9. doi:10.1186/s12963-018-0166-4.
Wild S, Roglic G, Sicree R, King H, Green A. Global prevalence of diabetes estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1047-53.
วรรณภาภรณ์ จงกลาง, นาฏนภา หีบแก้ว ปัดชาสุวรรณ์.ปัจจัย ที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับกลุ่มเสี่ยงโรคเบาหวา นชนิดที่ 2 ของกลุ่มวัยทำงานอำเภอโนนไทย จังหวัดนครราชสีมา.วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ ปีที่ 14 ฉบับที่ 3 เดือนกันยายน - ธันวาคม 2564. หน้า 71-82.
นุจิฬาภรณ์ ศิริไมย, วิลาวัณย์ ชมนิรัตน์.การพัฒนาระบบบริการสุขภาพผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่2ที่ไม่สามารถควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดโรงพยาบาลน้ำหนาว อำเภอน้ำหนาว จังหวัดเพชรบูรณ์. วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ ปีที่ 14 ฉบับที่ 3 เดือนกันยายน - ธันวาคม หน้า 57-70.
Poskerová H, Linhartová PB, Hollá LI. Oral diseases in diabetic patients. Vnitr Lek. 2019 Spring;65(4):314-320. English. PMID: 31091953.
Mauri-Obradors E, Estrugo-Devesa A, Jané-Salas E, Viñas M, López-López J. Oral manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017 Sep 1;22(5):
e586-e594. doi: 10.4317/medoral.21655. PMID: 28809366; PMCID: PMC5694181.
ณฐิตา อยู่ขำ. ความชุกของภาวะปากแห้งในผู้สูงอายุ อำเภอเมือง จังหวัดร้อยเอ็ด.วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ ปีที่ 15 ฉบับที่ 1 เดือนมกราคม - เมษายน 2565. หน้า 129-141 https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/RDHSJ/article/view/254322/175113.
Molania T, Alimohammadi M, Akha O, Mousavi J, Razvini R, Salehi M. The effect of xerostomia and hyposalivation on the quality of life of patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Electron Physician. 2017 Nov 25;9(11):5814-5819. doi: 10.19082/5814. PMID: 29403624; PMCID: PMC5783133.
López-Pintor RM, Casañas E, González-Serrano J, Serrano J, Ramírez L, de Arriba L, Hernández G. Xerostomia, Hyposalivation, and Salivary Flow in Diabetes Patients. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:4372852. doi: 10.1155/2016/4372852. Epub 2016 Jul 10. PMID: 27478847; PMCID: PMC4958434.
Sandberg, G. E., Sundberg, H. E., & Wikblad, K. F. (2001). A controlled study of oral self-care and self-perceived oral health in type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica, 59(1), 28-33.
Samnieng, P., Ueno, M., Shinada, K., Zaitsu, T., Wright, F. A., & Kawaguchi, Y. (2012). Association of hyposalivation with oral function, nutrition and oral health in community-dwelling elderly Thai. Community Dent Health, 29(1), 117-23.
Turner MD, Ship JA. Dry mouth and its effects on the oral health of elderly people. J Am Dent Assoc 2007; 138: S15-20.
Tanasiewicz M, Hildebrandt T, Obersztyn I. Xerostomia of various etiologies: A review of the literature. Adv Clin Exp Med 2016;25: 199-206.
Gupta A, Epstein JB, Sroussi H. Hyposalivation in elderly patients. J Can Dent Assoc 2006; 72(9): 841-6.
Frydrych AM. Dry mouth: Xerostomia and salivary gland hypofunction. Aust Fam Physician 2016; 45:488-92.
Gil-Montoya JA, Silestre FJ, Barrios R, Silvestre-Rangil J.Treatment of xerostomia and hyposalivation in the elderly: a systemstic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2016; 21: e355-66.
Miranda-Rius J, Brunet-Llobet L, Lahor-Soler E, Farre M. Salivary secretory disorders, inducing drugs and clinical management. Int J Med Sci 2015; 12:811-24.
Plemons JM, Al-Hashimi I, Marek CL. Managing xerostomia and salivary gland hypofunction: executive summary of a report from the American Dental Association Council on scientificaffairs. J Am Dent Assoc 2014; 145:867-73.
Chomkhakhai, U., Thanakun, S., Khovidhunkit, S. O. P., Khovidhunkit, W., & Thaweboon, (2009). Oral health in Thai patients with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 3(4), 192-197.
Wayne, W. D. (1995). Biostatistics: A foundation of analysis in the health sciences (6th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Raj BT, Sreelekha B, Manjula A. Effectiveness of oral exercise on oral function among the elderly:J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Apr 30;9(4): 1896-1903.
Ibayashi H, Fujino Y, Pham TM, Matsuda S. Intervention study of exercise program for oral function in healthy elderly people. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2008; 215:237–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Weerapong D, Hume PA, Kolt GS. The mechanism of message and effect of performance, muscle recovery and injury prevention. Sports Med. 2005; 35:235–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nam M, Uhm D. A comparative study of the effects of intra and extra circumoral exercise for older people on oral health at nursing homes: A non-equivalent trial. J Adv Nurs. 72:2114–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2022 วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนาระบบสุขภาพ

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆบทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใด จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักณอักษรจากวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทยก่อนเท่านั้น






