Characteristics of Neurogenic Bladder in Patients with Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33192/smj.v78i11.276071Keywords:
Neurogenic bladder, GBS, urinary disfunctionAbstract
Objective: This review aims to determine the prevalence and characteristics of neurogenic bladder issues in patients diagnosed with Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
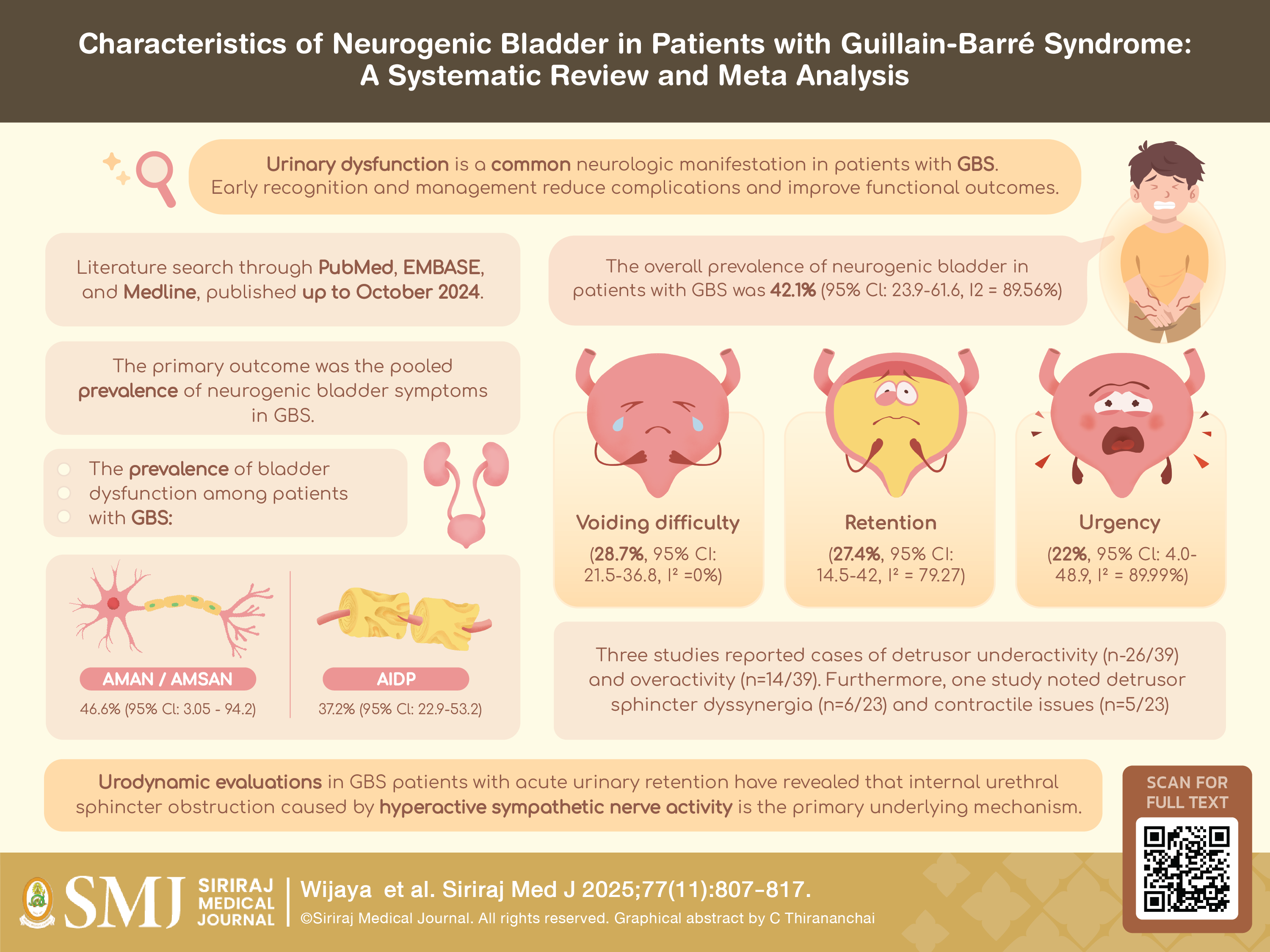
Materials and Methods: The authors conducted a literature search through PubMed, EMBASE, and Medline, published up to October 2024. Moreover, supplementary sources were obtained through the examination related references. Studies presenting the urinary dysfunction features of GBS patients in their data were included. The primary outcome was the pooled prevalence of neurogenic bladder symptoms in GBS. The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine guidelines. Selected studies were included in the meta-analysis of proportion and heterogeneity test.
Results: From 257 identified studies, 6 observational studies were included in the final analysis, with 375 participants included. The overall prevalence of neurogenic bladder in patients with GBS was 42.1% (95% CI: 23.9-61.6, I² = 89.56%). Voiding difficulty (28.7%, 95% CI: 21.5-36.8, I² =0%), retention (27.4%, 95% CI: 14.5–42, I² = 79.27), and urgency (22%, 95% CI: 4.0–48.9, I² = 89.99%) was commonly reported bladder symptoms, respectively. Acute Axonal Pattern (AMAN/AMSAN) was more common (46.6%, 95% CI: 3.05-94.2, I² =95.31%) than Acute Demyelinating Pattern (AIDP) (37.2%, 95% CI: 22.9-53.2, I² = 0%). Detrusor underactivity (n=26/39) was mostly reported findings based on urodynamic tests.
Conclusion: Urinary dysfunction is a common neurologic manifestation in patients with GBS. Early recognition and management reduce complications and improve functional outcomes.
References
Zaeem Z, Siddiqi ZA, Zochodne DW. Autonomic involvement in Guillain-Barré syndrome: an update. Clin Auton Res. 2019;29(3):289-99.
Burakgazi AZ, Alsowaity B, Burakgazi ZA, Unal D, Kelly JJ. Bladder dysfunction in peripheral neuropathies. Muscle Nerve. 2012;45(1):2-8.
Khoo CS, Ali AH, Remli R, Tan HJ. A case of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) presenting with acute urinary retention and T6 sensory level. Clin Med (Lond). 2018;18(4):308-10.
Sakakibara R, Uchiyama T, Kuwabara S, Mori M, Ito T, Yamamoto T, Awa Y, Yamaguchi C, Yuki N, Vernino S, Kishi M, Shirai K. Prevalence and mechanism of bladder dysfunction in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28(5):432-7.
Amatya B, Khan F, Whishaw M, Pallant JF. Guillain-Barré syndrome: prevalence and long-term factors impacting bladder function in an Australian community cohort. J Clin Neurol. 2013;9(3):144-50.
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA- P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4(1):1.
OCEBM Levels of Evidence Working Group. The Oxford Levels of Evidence 2. Oxford: Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine; 2011.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557-60.
Wheeler JS Jr, Siroky MB, Pavlakis A, Krane RJ. The urodynamic aspects of the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Urol. 1984;131(5):917-9.
Sakakibara R, Hattori T, Kuwabara S, Yamanishi T, Yasuda K. Micturitional disturbance in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63(5):649-53.
Naphade PU, Verma R, Garg RK, Singh M, Malhotra HS, Shankwar SN. Prevalence of bladder dysfunction, urodynamic findings, and their correlation with outcome in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Neurourol Urodyn. 2012;31(7):1135-40.
Chakraborty T, Kramer CL, Wijdicks EFM, Rabinstein AA. Dysautonomia in Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Prevalence, Clinical Spectrum, and Outcomes. Neurocrit Care. 2020;32(1):113-20.
Singh NK, Jaiswal AK, Misra S, Srivastava PK. Assessment of autonomic dysfunction in Guillain– Barre syndrome and its prognostic implications. Acta Neurol Scand. 1987;75(2):101–5.
Sakakibara R, Uchiyama T, Tamura N, Kuwabara S, Asahina M, Hattori T. Urinary retention and sympathetic sphincter obstruction in axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007;35(1):111–5.
Ramart P, Ackerman AL. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection in Women from a Urologist’s Perspective. Siriraj Med J. 2023;75(1):55-61.
Tagaloa E, Venter F, Liang L, Bhaika J, Aguirre D, Patel J, et al. A Rare Case of Guillain-Barré Syndrome with Severe Pandysautonomia. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021;9:23247096211019558.
Wen P, Wang L, Liu H, Gong L, Ji H, Wu H, et al. Risk factors for the severity of Guillain-Barré syndrome and predictors of short-term prognosis of severe Guillain-Barré syndrome. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):11578.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siriraj Medical Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following conditions:
Copyright Transfer
In submitting a manuscript, the authors acknowledge that the work will become the copyrighted property of Siriraj Medical Journal upon publication.
License
Articles are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). This license allows for the sharing of the work for non-commercial purposes with proper attribution to the authors and the journal. However, it does not permit modifications or the creation of derivative works.
Sharing and Access
Authors are encouraged to share their article on their personal or institutional websites and through other non-commercial platforms. Doing so can increase readership and citations.














