FACTORS INFLUENCING DENIAL OF INSULIN USAGE AMONG TYPE II DIABETES PATIENTS WITH INDICATION FOR INSULIN USAGE IN COMMUNITY HOSPITAL
Keywords:
Type 2 diabetes, the refusal of insulin regimen, Community Hospital.Abstract
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes in Thailand. Doctors often encounter problems with patients refusing further treatment with insulin injections. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the proportion and factors involved in type 2 diabetic patients' refusal of insulin therapy with indications for insulin. This study was a cross-sectional study. The 155 samples were selected from type 2 diabetes patients aged 18–65 years following their treatment at a community hospital and were interviewed in person by questionnaires. Instruments were used as a questionnaire for demographic data, diabetes treatment, knowledge, and attitude concerning insulin therapy. Data analysis was conducted by Frequency, Percentage, Prevalence rate with 95%CI, Mean, Pearson Chi-square, and Multiple Logistic Regression.
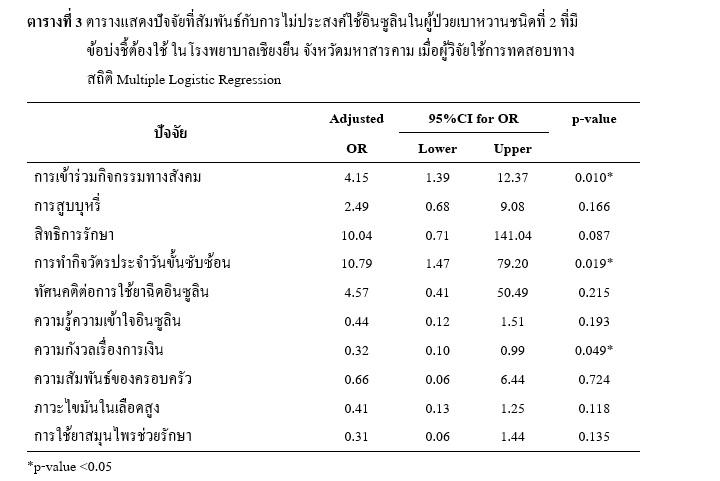
The type 2 diabetics sample consisted of 155 subjects. Most of them were females (58.10%). The proportion of type 2 diabetic patients' refusal of insulin therapy with indications for insulin was 81.94 (95% CI 75.81-88.06) and factors associated with the refusal of insulin regimen among type 2 diabetic patients with a statistically significant were concerning social participation (Adjust OR= 4.156 p-value<0.05 95%CI:1.396-12.371), High L-IADL score (Adjust OR= 10.799 p-value<0.05 95%CI: 1.473-79.203) and financial concerns 0.66, 95%CI:0.068-6.446)
The study revealed that 80% of type 2 diabetic patients with indications for insulin usage refuse insulin therapy. Educating patients with diabetes, including accurate drug information, play an important role in making patients have the right attitude towards treatment and lead to a reduction in the incidence of complications to make better quality of life.
Downloads
References
กรมควบคุมโรค. เตือนประชาชนใส่ใจดูแลสุขภาพตนเองและคนในครอบครัวระวังป่วยโรคเบาหวาน. 2560.
ชัชลิต รัตรสาร. สถานการณ์ปัจจุบัน และความร่วมมือเพื่อ ปฏิรูปการดูแลรักษาโรคเบาหวานใน ประเทศไทย การยกระดับมาตรฐานการดู แลรักษา และ ขยายการเข้าถึงการรักษาโรคเบาหวาน นำไปสู่สังคมสุขภาพที่ยั่งยืน. กรุงเทพมหานคร; 2561.
สมาคมโรคเบาหวานแห่งประเทศไทยในพระราชูปถัมภ์สมเด็จพระเทพรัตนราชสุดาฯ สยามบรมราชกุมารี, สมาคมโรคต่อมไร้ท่อแห่งประเทศไทย, กรมการแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. แนวทางเวชปฏิบัติสำหรับโรคเบาหวาน 2560. กรุงเทพมหานคร: อรุณการพิมพ์; 2560.
Goh SY, Ang E, Bajpai S, Deerochanawong C, Hong E-G, Hussein Z, et al. A patient-centric approach to optimize insulin therapy in Asia. J Diabetes Complications [Internet]. 2016 Aug;30(6):973–80. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1056872716301726
ราม รังสินธุ์. สรุปการประเมินผลลัพธ์การดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วยเบาหวานและความดันโลหิตสูง 2553-2558. 2559.
Division of Diabetes Translation. Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the Epidemiologic estimation methods, National Diabetes Statistics Report , 2014. Atlanta; 2014.
กีรตี ไตรคีรีสถิต, ทิพาพร ธาระวานิช. อัตราการยินยอมฉีดอินซูลินภายหลังการเข้าโปรแกรมอบรมแบบครอบคลุม เปรียบเทียบกับการให้คำปรึกษาตามปกติในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานชนิดที่ 2 ที่ปฏิเสธการฉีดอินซูลิน. ธรรมศาสตร์เวชสาร. 2561;18(3):291–9.
Yilmaz A, Ak M, Cim A, Palanci Y, Kilinc F. Factors influencing insulin usage among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A study in Turkish primary care. Eur J Gen Pract. 2016;22(4):255–61.
Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Kruger DF, Travis LB. Correlates of insulin injection omission. Diabetes Care. 2010 Feb;33(2):240–5.
ปิยะพร ทองเนื้อนวล. ความสัมพันธ์และอำนาจในการทำนายของการสนับสนุนทางสังคมที่มีต่อพฤติกรรมการดูแลตนเองของผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลได้. วารสารสาธารณสุขและวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ. 2562;2(2):14–25.
Arissara Sukwatjanee, Kanaungnit Pongthavornkamol, Gail Low, Nantawon Suwonnaroop W, Pinyopasakul SC. Benefits of a Self-Help Group for Rural Thai Elders with Type-2 Diabetes. Pacific Rim Int J Nurs Res. 2011;15(3):220–33.
Prommaloon S, Wattanakitkrileart D. Factors Influencing Insulin Adherence in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. 2017;35(1):61–71.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Research and Development Health System Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆบทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใด จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักษณ์อักษรจากวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทยก่อนเท่านั้น





