การจัดบริการดูแลผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้ไม่ดี ผ่านระบบการแพทย์ทางไกล ของโรงพยาบาลส่งเสริมสุขภาพตำบล (Telemedicine NCDs on Cloud)
คำสำคัญ:
ผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวาน, ระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด, ระบบการแพทย์ทางไกลบทคัดย่อ
งานวิจัยนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อพัฒนารูปแบบการจัดบริการดูแลผู้ป่วยโรคเบาหวานที่ควบคุมระดับน้ำตาลในเลือดได้ไม่ดี ผ่านระบบการแพทย์ทางไกล กลุ่มตัวอย่างคัดเลือกด้วยวิธีเจาะจงเป็นตัวแทนผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน เจ้าหน้าที่ผู้ให้บริการ กลุ่มละ 10 คน ผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน 166 คน ขั้นตอนการพัฒนา ศึกษาความต้องการ การจัดบริการของผู้ป่วย และผู้ให้บริการ พัฒนาและประเมินผลการพัฒนารูปแบบ เครื่องมือวิจัย ได้แก่ แนวคำถามการสนทนากลุ่ม แบบสอบถามความพึงพอใจ แบบสอบถามความเป็นไปได้ และแบบประเมินผลการจัดบริการ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติเชิงพรรณนา และวิเคราะห์เชิงเนื้อหา
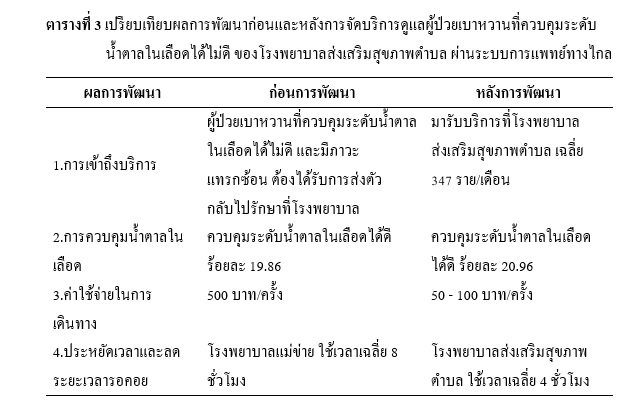
ผลการวิจัย พบว่า รูปแบบที่พัฒนาประกอบด้วย การเชื่อมต่อระบบสื่อสาร และฐานข้อมูล Hosxp-PCU การจัดหาเตรียมอุปกรณ์เชื่อมต่อ และขั้นตอนการบริการตั้งแต่เตรียมข้อมูล เชื่อมโยงระบบสื่อสาร และฐานข้อมูล ตรวจร่างกาย บันทึกการรักษา จัดยา ให้คำแนะนำ และออกวันนัดติดตามผลการพัฒนา ผู้ป่วยรับบริการเฉลี่ย 347 ราย/เดือน ร้อยละ 77.39 ควบคุมน้ำตาลในเลือดได้ดี ร้อยละ 20.96 ค่าใช้จ่ายลดลงจากรายละ 500 บาท/ครั้ง เหลือ 50-100 บาท/ครั้ง ลดเวลารอคอยลงเฉลี่ย 8 ชั่วโมง เป็นเฉลี่ย 4 ชั่วโมง และความพึงพอใจต่อการบริการระดับมาก ( = 2.93, S.D.= 0.87)ผู้ให้บริการมีความเป็นไปได้การจัดบริการระดับมาก (
= 4.30, S.D.= 0.59) เห็นว่า ไม่ได้เป็นการเพิ่มภาระงาน ช่วยให้การทำงานสะดวกขึ้น ง่ายและลดขั้นตอน เป็นบริการทางเลือกของผู้ป่วย
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดบึงกาฬ. รายงานการดำเนินงานสาธารณสุข ประจำปีงบประมาณ พ.ศ. 2564. เอกสารอัดสำเนา; 2564.
กรมการแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. คู่มือการจัดบริการคลินิกเบาหวานวิถีใหม่แบบยึดประชาชนเป็นศูนย์กลาง (สำหรับผู้ปฏิบัติงาน). กรุงเทพมหานคร : สำนักพิมพ์กิจการโรงพิมพ์ องค์การสงเคราะห์ทหารผ่านศึก ในพระบรมราชูปถัมภ์; 2563.
วรรษา เปาอินทร์. Thailand Health 4.0 challenges and opportunities. Journal of the Thai Medical Informatics Association; 1, 2560: 31-36.
ดาราวรรณ รองเมือง และคณะ. การพัฒนารูปแบบระบบแพทย์ทางไกลเพื่อการดูแลรักษาผู้ป่วยล้างไตทางช่องท้อง บทเรียนจากการระบาดของโควิด-19. วารสารสถาบันวิจัยระบบสาธารณสุข 2564; 1: 108-27.
วีระชณ ทวีศักดิ์. การพัฒนารูปแบบการรับและส่งต่อผู้ป่วยโรคเรื้อรังโดยใช้ เครือข่าย สุขภาพร่วมกับระบบการแพทย์ทางไกล อำเภอพิบูลมังสาหาร จังหวัดอุบลราชธานี. วารสารวิชาการสาธารณสุขชุมชน 2566; 9(01): 148-158.
วนิดา พงษ์ศักดิ์ชาติ. (2563). การคำนวณหาขนาดตัวอย่างเพื่องานวิจัย. [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 20 พฤศจิกายน 2564]; เข้าถึงได้จาก: https://thaimed.buu.ac.th/public/backend/
upload/thaimed.buu.ac.th/document/file/document161717461088510200.pdf
ชูศรี วงศ์รัตนะ. เทคนิคการใช้สถิติเพื่อการวิจัย. กรุงเทพฯ: อมรการพิมพ์; 2560.
พิราลักษณ์ ลาภหลาย และมารศรี ปิ่นสุวรรณ์. การใช้ Telehealth ดูแลผู้ป่วยบาดแผลเรื้อรังในสถานการณ์การระบาดของ COVID-19. [อินเตอร์เน็ต]. 2563 [เข้าถึงเมื่อ 20 พฤศจิกายน 2564];เข้าถึงได้จาก: http://www.ayhosp.go.th/ayh/index.php/ic-news/156-ha/quality-day-2563/5594-wound-care-challenges-and-solutions-by-telehealth-during-the-covid-19-pandemic-qd63
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2023 สำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดกาฬสินธุ์

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
เนื้อหาและข้อมูลในบทความที่ลงตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นข้อคิดเห็นและความรับผิดชอบของผู้เขียนบทความโดยตรงซึ่งกองบรรณาธิการวารสาร ไม่จำเป็นต้องเห็นด้วย หรือร่วมรับผิดชอบใด ๆบทความ ข้อมูล เนื้อหา รูปภาพ ฯลฯ ที่ได้รับการตีพิมพ์ในวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย ถือเป็นลิขสิทธิ์ของวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทย หากบุคคลหรือหน่วยงานใดต้องการนำทั้งหมดหรือส่วนหนึ่งส่วนใดไปเผยแพร่ต่อหรือเพื่อกระทำการใด จะต้องได้รับอนุญาตเป็นลายลักณอักษรจากวารสารศูนย์ดัชนีการอ้างอิงวารสารไทยก่อนเท่านั้น






